J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Jun;68(6):499-502. 10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.499.
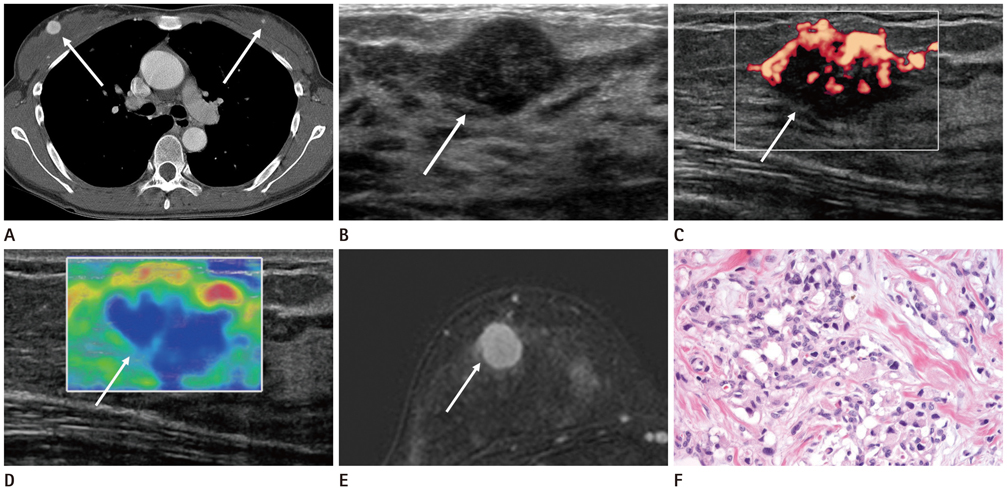
Breast Metastasis from Malignant Paraganglioma: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bkhan@skku.edu
- 2Department of Radiology, Gil Hospital, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2002902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.499
Abstract
- We report a case of metastatic breast cancer from paraganglioma and describe the radiologic findings in a 32-year-old woman who had a history of excision for carotid body paraganglioma. Breast metastasis from malignant paraganglioma showed a well-defined mass with hypoechogenicity, posterior acoustic enhancement and increased vascularity on ultrasonography, and strong enhancements on contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion restriction on diffusion weighted image.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sandison AT. Metastatic tumours in the breast. Br J Surg. 1959; 47:54–58.2. Hajdu SI, Urban JA. Cancers metastatic to the breast. Cancer. 1972; 29:1691–1696.3. Paulus DD, Libshitz HI. Metastasis to the breast. Radiol Clin North Am. 1982; 20:561–568.4. Toombs BD, Kalisher L. Metastatic disease to the breast: clinical, pathologic, and radiographic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977; 129:673–676.5. Vergier B, Trojani M, de Mascarel I, Coindre JM, Le Treut A. Metastases to the breast: differential diagnosis from primary breast carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1991; 48:112–116.6. Vaughan A, Dietz JR, Moley JF, Debenedetti MK, Aft RL, Gillanders WE, et al. Metastatic disease to the breast: the Washington University experience. World J Surg Oncol. 2007; 5:74.7. Williams SA, Ehlers RA 2nd, Hunt KK, Yi M, Kuerer HM, Singletary SE, et al. Metastases to the breast from nonbreast solid neoplasms: presentation and determinants of survival. Cancer. 2007; 110:731–737.8. Lee JH, Kim SH, Kang BJ, Cha ES, Kim HS, Choi JJ. Metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies-sonographic features. J Clin Ultrasound. 2011; 39:248–255.9. Kliewer KE, Wen DR, Cancilla PA, Cochran AJ. Paragangliomas: assessment of prognosis by histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural techniques. Hum Pathol. 1989; 20:29–39.10. Lee JH, Barich F, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Zhen WK, Gantz BJ, et al. National Cancer Data Base report on malignant paragangliomas of the head and neck. Cancer. 2002; 94:730–737.11. Rao AB, Koeller KK, Adair CF. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. From the archives of the AFIP. Paragangliomas of the head and neck: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1999; 19:1605–1632.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case report of malignant paraganglioma with hepatic metastases
- A Case Report of Recurrent Malignant Paraganglioma with Lung and Spine Metastasis that Occurred Sixteen Years after Primary Tumor Excision
- A Case of Metastatic Malignant Paraganglioma Causing Spinal Root Compression
- Malignant Paraganglioma in the Common Hepatic Duct
- Pancreatic metastasis from malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast