J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Nov;69(5):337-341. 10.3348/jksr.2013.69.5.337.
A Tumefactive Multiple Sclerosis Lesion in the Brain: An Uncommon Site with Atypical Magnetic Resonance Image Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea. khs46359@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2002849
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.69.5.337
Abstract
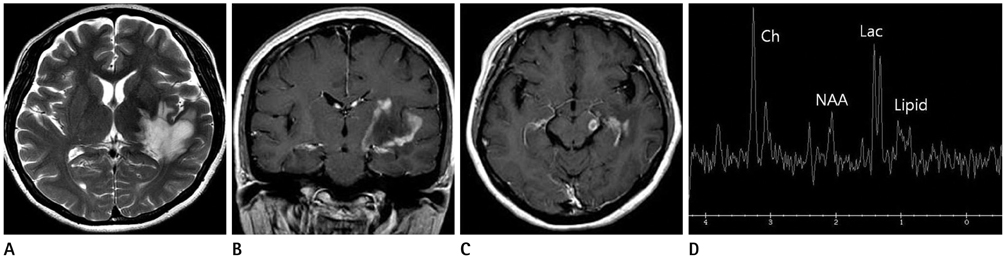
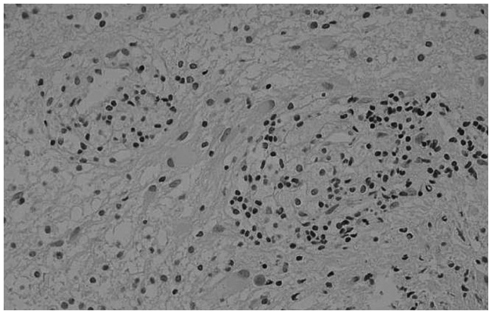
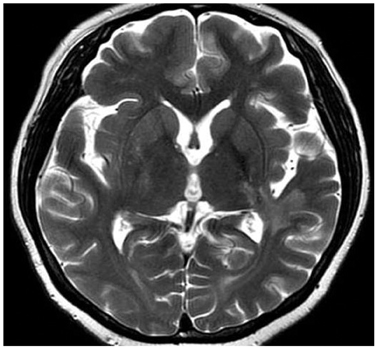
- Tumefactive multiple sclerosis (MS) is a rare type of demyelinating disease. Typical magnetic resonance (MR) image findings show incomplete ring enhancement with a mild mass effect. This lesion is otherwise indistinguishable from other mass-like lesions in the brain. Knowledge of the MR imaging findings for tumefactive MS is thus helpful for correct diagnosis and appropriate therapy. In this report we describe the MR image findings for pathology-confirmed tumefactive MS in an uncommon location, alongside a discussion of its aggressive features.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rusin JA, Vezina LG, Chadduck WM, Chandra RS. Tumoral multiple sclerosis of the cerebellum in a child. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995; 16:1164–1166.2. Comi G. Multiple sclerosis: pseudotumoral forms. Neurol Sci. 2004; 25:Suppl 4. S374–S379.3. Kim DS, Na DG, Kim KH, Kim JH, Kim E, Yun BL, et al. Distinguishing tumefactive demyelinating lesions from glioma or central nervous system lymphoma: added value of unenhanced CT compared with conventional contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2009; 251:467–475.4. Elsone L, Platkajis A, Karelis G, Dzelzite S, Murzina M. Tumefactive multiple sclerosis mimicking neoplasm. Acta Chirurgica Latviensis. 2010; 10:91–97.5. Lucchinetti CF, Gavrilova RH, Metz I, Parisi JE, Scheithauer BW, Weigand S, et al. Clinical and radiographic spectrum of pathologically confirmed tumefactive multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2008; 131(Pt 7):1759–1775.6. Mandrioli J, Ficarra G, Callari G, Sola P, Merelli E. Monofocal acute large demyelinating lesion mimicking brain glioma. Neurol Sci. 2004; 25:Suppl 4. S386–S388.7. Annesley-Williams D, Farrell MA, Staunton H, Brett FM. Acute demyelination, neuropathological diagnosis, and clinical evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000; 59:477–489.8. Law M, Yang S, Wang H, Babb JS, Johnson G, Cha S, et al. Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1989–1998.9. Given CA 2nd, Stevens BS, Lee C. The MRI appearance of tumefactive demyelinating lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:195–199.10. Schwartz KM, Erickson BJ, Lucchinetti C. Pattern of T2 hypointensity associated with ring-enhancing brain lesions can help to differentiate pathology. Neuroradiology. 2006; 48:143–149.11. Kantarci OH, Weinshenker BG. Natural history of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Clin. 2005; 23:17–38. v
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Tumefactive Lesion: Demyelinating Disease Versus Brain Tumor
- A Case of Multiple Sclerosis Presenting with Tumefactive Lesions
- Concurrence of Multiple Sclerosis and Brain Tumor: A case report
- Analysis of Visual Field Defect in Patient with Brain Lesion
- Clinicoradiological Factors for Predicting and Monitoring the Progression of Multiple Sclerosis