J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2011 Jan;49(1):49-56. 10.4047/jkap.2011.49.1.49.
Influence of sandblasting and primer on shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Division of Dentistry, Graduate School, Kyung-Hee University, Seoul, Korea. yhwoo@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2000283
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2011.49.1.49
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of mechanical, chemical surface treatments on the zirconia-to-resin cement shear bond strength (SBS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
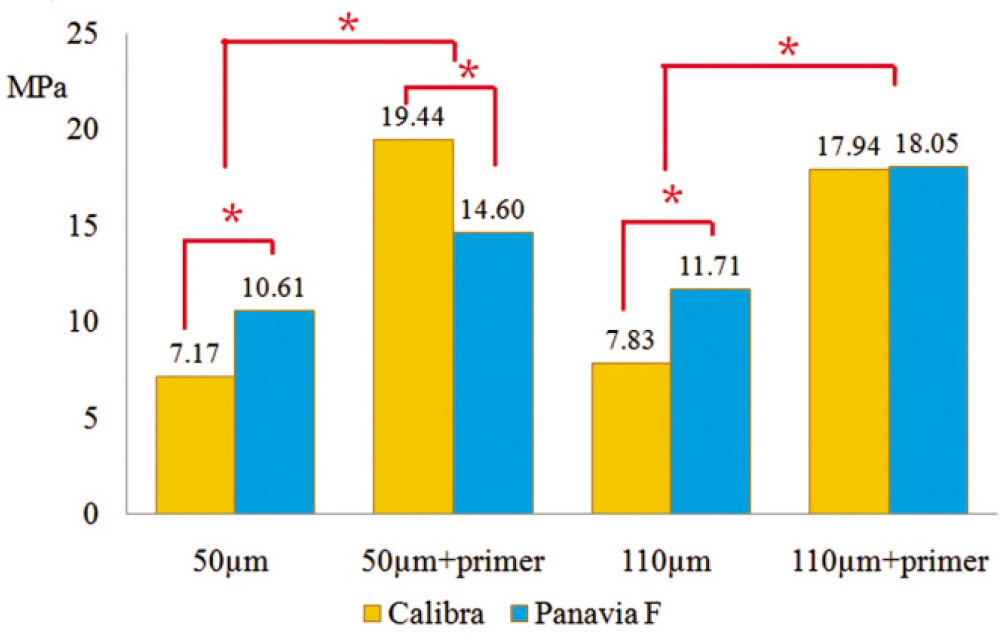
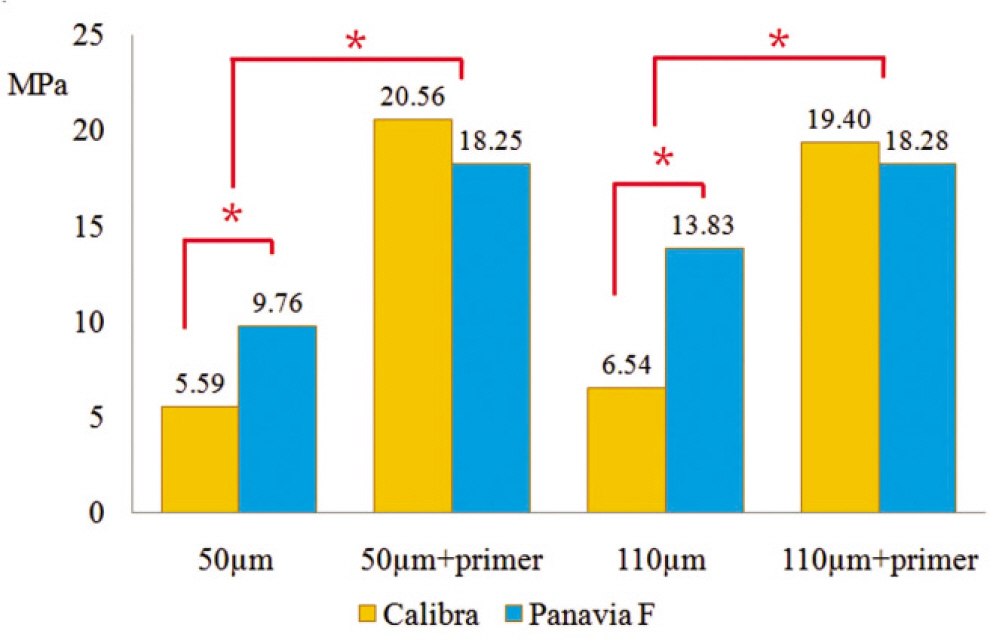
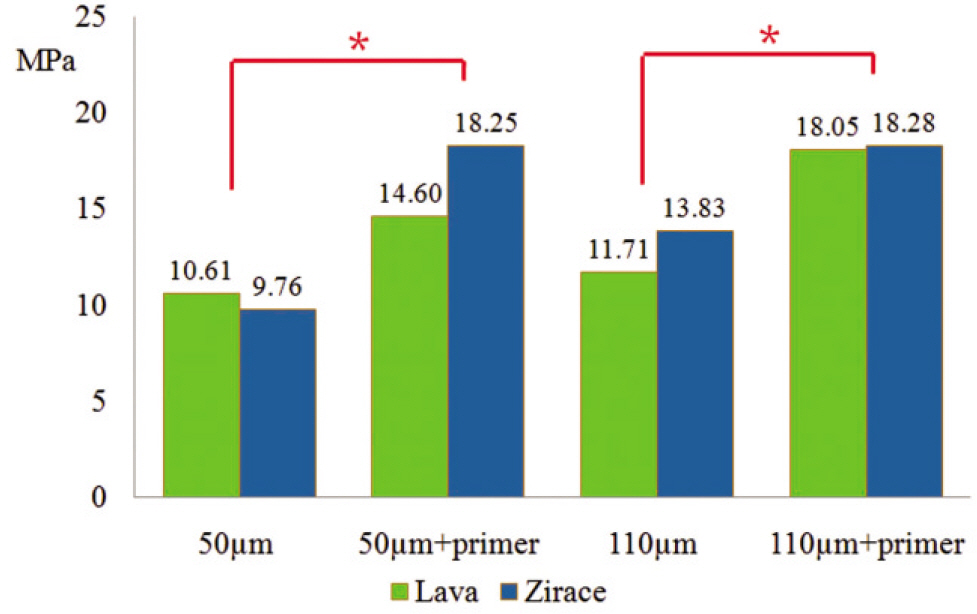
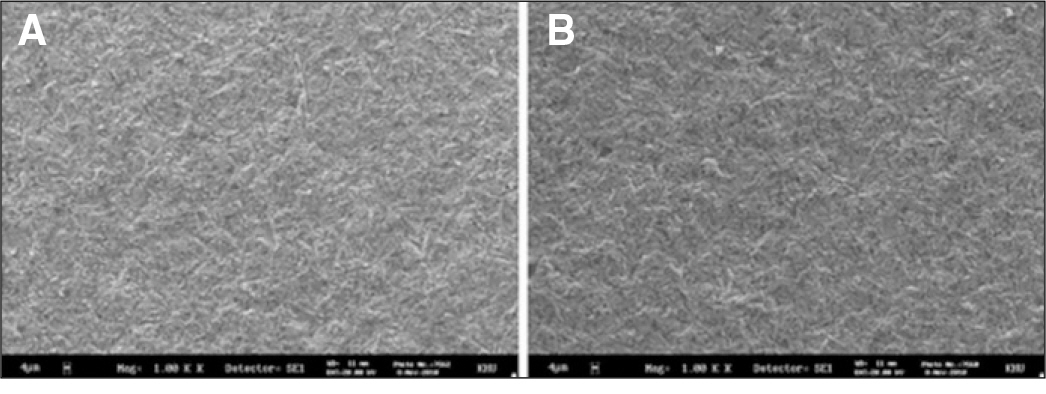
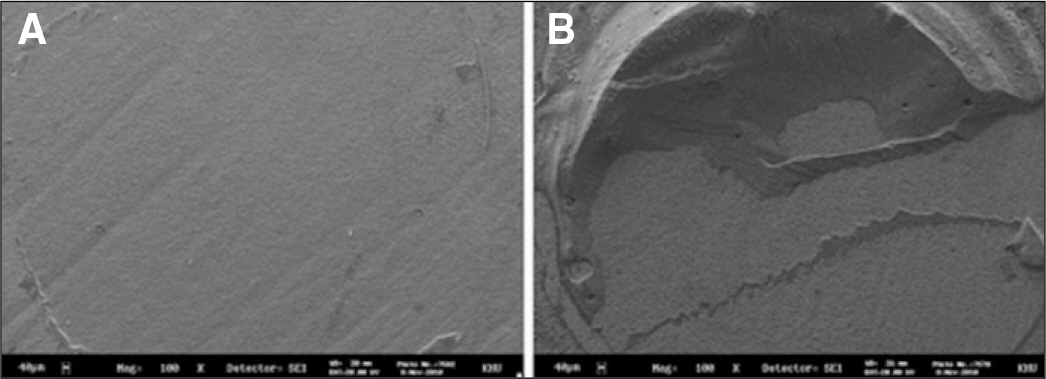
Eighty zirconia discs (Lava, 3M ESPE) and eighty zirconia/alumina composite (Zirace, Acucera) were embedded in an epoxy resin base. Zirconia discs were randomly divided in to four treatment groups(10 for each manufacturer): 50 microm Al2O3 sandblasting (S50),110 microm Al2O3 sandblasting (S110), 50 microm Al2O3 and primer (Z-Prime Plus, Bisco Inc) (S50z) and 110 microm Al2O3 and primer (Z-Prime Plus) (S110z). Two resin-based luting cements (Calibra, Panavia F) were used to build 2 mm-diameter cylinders onto the zirconia. After 24 h of storage in water, SBS testing was evaluate using a universal testing machine.Bond strength data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA test and post hoc comparison was done using Tukey test (alpha=.05).
RESULTS
Groups using primer showed the high shear bond strength. The groups that did not use primer presented lower shear bond strengths.
CONCLUSION
The use of primer (Z-Prime Plus, Bisco) had significantly higher shear bond strengths.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Blatz MB., Sadan A., Kern M. Resin-ceramic bonding: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 89:268–74.
Article2.Blatz MB., Chiche G., Holst S., Sadan A. Influence of surface treatment and simulated aging on bond strengths of luting agents to zirconia. Quintessence Int. 2007. 38:745–53.3.Luthardt RG., Holzhu ¨ter M., Sandkuhl O., Herold V., Schnapp JD., Kuhlisch E., Walter M. Reliability and properties of ground Y-TZP-zirconia ceramics. J Dent Res. 2002. 81:487–91.4.Luthardt R., Weber A., Rudolph H., Scho ¨ne C., Quaas S., Walter M. Design and production of dental prosthetic restorations: basic research on dental CAD/CAM technology. Int J Comput Dent. 2002. 5:165–76.5.Kakehashi Y., Lu ¨thy H., Naef R., Wohlwend A., Scha ¨rer P. A new all-ceramic post and core system: clinical, technical, and in vitro results. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1998. 18:586–93.6.Meyenberg KH., Lu ¨thy H., Scha ¨rer P. Zirconia posts: a new all-ceramic concept for nonvital abutment teeth. J Esthet Dent. 1995. 7:73–80.
Article7.Yildirim M., Fischer H., Marx R., Edelhoff D. In vivo fracture resistance of implant-supported all-ceramic restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 90:325–31.
Article8.Glauser R., Sailer I., Wohlwend A., Studer S., Schibli M., Scha ¨rer P. Experimental zirconia abutments for implant-supported single-tooth restorations in esthetically demanding regions: 4-year results of a prospective clinical study. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:285–90.9.De′rand P., De′rand T. Bond strength of luting cements to zirconium oxide ceramics. Int J Prosthodont. 2000. 13:131–5.10.O ¨zcan M., Vallittu PK. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the bond strength of luting cement to ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003. 19:725–31.11.Zhang Y., Lawn BR., Malament KA., Van Thompson P., Rekow ED. Damage accumulation and fatigue life of particle-abraded ceramics. Int J Prosthodont. 2006. 19:442–8.12.Zhang Y., Lawn BR., Rekow ED., Thompson VP. Effect of sandblasting on the long-term performance of dental ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004. 71:381–6.
Article13.Wolfart M., Lehmann F., Wolfart S., Kern M. Durability of the resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic after using different surface conditioning methods. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:45–50.
Article14.Kern M., Wegner SM. Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:64–71.
Article15.Blatz MB., Sadan A., Martin J., Lang B. In vitro evaluation of shear bond strengths of resin to densely-sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic after long-term storage and thermal cycling. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 91:356–62.
Article16.Atsu SS., Kilicarslan MA., Kucukesmen HC., Aka PS. Effect of zirconium-oxide ceramic surface treatments on the bond strength to adhesive resin. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 95:430–6.
Article17.Tanaka R., Fujishima A., Shibata Y., Manabe A., Miyazaki T. Cooperation of phosphate monomer and silica modification on zirconia. J Dent Res. 2008. 87:666–70.
Article18.Tsuo Y., Yoshida K., Atsuta M. Effects of alumina-blasting and adhesive primers on bonding between resin luting agent and zirconia ceramics. Dent Mater J. 2006. 25:669–74.
Article19.Aida M., Hayakawa T., Mizukawa K. Adhesion of composite to porcelain with various surface conditions. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 73:464–70.
Article20.Lu ¨thy H., Loeffel O., Hammerle CH. Effect of thermocycling on bond strength of luting cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:195–200.21.Akgungor G., Sen D., Aydin M. Influence of different surface treatments on the short-term bond strength and durability between a zirconia post and a composite resin core material. J Prosthet Dent. 2008. 99:388–99.
Article22.Wegner SM., Kern M. Long-term resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic. J Adhes Dent. 2000. 2:139–47.23.Matinlinna JP., Heikkinen T., Ozcan M., Lassila LV., Vallittu PK. Evaluation of resin adhesion to zirconia ceramic using some organosilanes. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:824–31.
Article24.Kern M., Thompson VP. Sandblasting and silica coating of a glass-infiltrated alumina ceramic: volume loss, morphology, and changes in the surface composition. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 71:453–61.
Article25.Della Bona A., Borba M., Benetti P., Cecchetti D. Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength of a zirconia-reinforced ceramic to composite resin. Braz Oral Res. 2007. 21:10–5.26.Uo M., Sjo ¨gren G., Sundh A., Goto M., Watari F., Bergman M. Effect of surface condition of dental zirconia ceramic (Denzir) on bonding. Dent Mater J. 2006. 25:626–31.
Article27.Kosmac T., Oblak C., Jevnikar P., Funduk N., Marion L. Strength and reliability of surface treated Y-TZP dental ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000. 53:304–13.28.Guazzato M., Quach L., Albakry M., Swain MV. Influence of surface and heat treatments on the flexural strength of Y-TZP dental ceramic. J Dent. 2005. 33:9–18.
Article29.Wang H., Aboushelib MN., Feilzer AJ. Strength influencing variables on CAD/CAM zirconia frameworks. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:633–8.
Article30.Karakoca S., Yilmaz H. Influence of surface treatments on surface roughness, phase transformation, and biaxial flexural strength of Y-TZP ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009. 91:930–7.
Article31.Kern M., Thompson VP. Bonding to glass infiltrated alumina ceramic: adhesive methods and their durability. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 73:240–9.
Article32.Tanaka T., Nagata K., Takeyama M., Atsuta M., Nakabayashi N., Masuhara E. 4-META opaque resin-a new resin strongly adhesive to nickel-chromium alloy. J Dent Res. 1981. 60:1697–706.33.Lindgren J., Smeds J., Sjo ¨gren G. Effect of surface treatments and aging in water on bond strength to zirconia. Oper Dent. 2008. 33:675–81.
Article34.Silikas N., Wincott PL., Vaughan D., Watts DC., Eliades G. Surface characterization of precious alloys treated with thione metal primers. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:665–73.
Article35.O ¨zcan M., Nijhuis H., Valandro LF. Effect of various surface conditioning methods on the adhesion of dual-cure resin cement with MDP functional monomer to zirconia after thermal aging. Dent Mater J. 2008. 27:99–104.36.Magne P., Paranhos MP., Burnett LH Jr. New zirconia primer improves bond strength of resin-based cements. Dent Mater. 2010. 26:345–52.
Article37.Wang H., Aboushelib MN., Feilzer AJ. Strength influencing variables on CAD/CAM zirconia frameworks. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:633–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of various surface treatment methods of highly translucent zirconia on the shear bond strength with resin cement
- Resin bonding of metal brackets to glazed zirconia with a porcelain primer
- Effect of surface treatments of zirconia ceramic on the bond strength of resin cements
- The effect of surface treatment conditioning on shear bond strength between zirconia and dental resin cements
- Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite