Korean J Urol.
2006 Apr;47(4):402-406. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.4.402.
Comparison of the Effectiveness of the Renogram, the Serial Renal Scan and the Diuretic Half Time according to the Renal Function for Interpreting a Diuretic DTPA Scan following Pyeloplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1997151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.4.402
Abstract
- PURPOSE
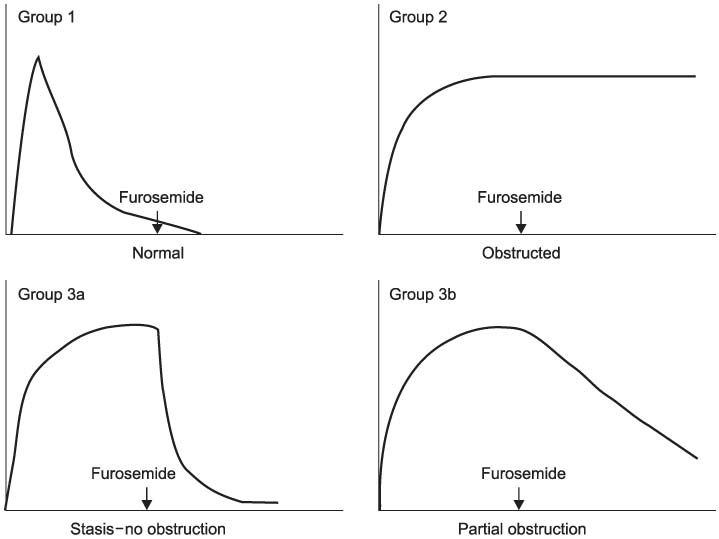
The diuretic renal scan has been considered to be a good tool for evaluating the postoperative renal function in the patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO). We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of the renogram, the serial renal scan and the diuretic half time according to the differential renal function (DRF) on the diuretic renal scan.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the diuretic renal scans of 27 pediatric patients (25 males and 2 females) who underwent pyeloplasty due to unilateral UPJO. Diuretic renal scanning was done using the 99mTc- DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid) standardized protocol. We compared the diagnostic accuracy of the renogram, the serial renal scan and the diuretic half time according to the DRF (group I: above 40%, group II: below 40%).
RESULTS
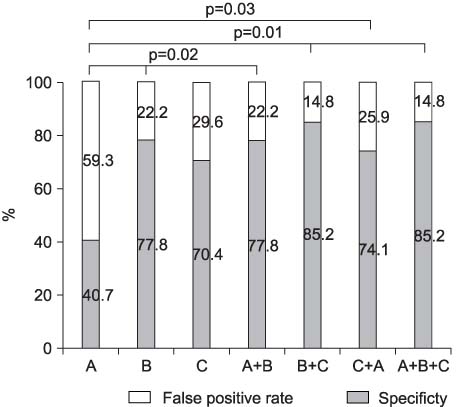
The mean age of the patients was 48.0 59.2 months (range: 2-210 months). The diuretic half time, renogram, serial renal scan and each combination demonstrated statistical significance for the interpretation of ureteral obstruction (generalized estimation equation, p=0.003). The interpretation of the diuretic renal scan was not affected by the DRF (McNemar test, p=0.598). The false positive rate and specificity of the renogram, serial renal scan and diuretic half time were 22.2%, 29.6%, 59.3% and 77.8%, 70.4%, 40.7%, respectively. In addition, the false positive rate and specificity of a combination of the diuretic half time and renogram, the diuretic half time and serial renal scan, the renogram and serial renal scan, the diuretic half time and renogram, and serial renal scan were 22.2%, 25.9%, 14.8%, 14.8%, and 77.8%, 74.1%, 85.2%, 85.2%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The diuretic half time, renogram and serial renal scan were individually correlated with the postoperative status of the UPJO. However, a combination of various factors of the renal scan should be considered for evaluating the postoperative status of UPJO.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Scintigraphic Assessment of Renal Function Using 99mTc-DTPA in Miniature Pigs with Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction
Se Eun Kim, Kyung Mi Shim, Won Guk Lee, Seok Hwa Choi, Soo Hyun Park, Ho Jae Han, Seong Soo Kang
Lab Anim Res. 2010;26(1):103-108. doi: 10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.103.
Reference
-
1. Rado JP, Banos C, Tako J. Frusemide renography. Lancet. 1967. 2:1419–1420.2. Hyun IY, Lee DS, Lee KH, Chung JK, Lee MC, Koh CS, et al. Improvement of diagnostic accuracy by standardization in diuretic renal scan. Korean J Nucl Med. 1995. 29:497–503.3. Koff SA, Thrall JH, Keyes JW Jr. Assessment of hydroureteronephrosis in children using diuretic radionuclide urography. J Urol. 1980. 123:531–534.4. Whitaker RH. Methods of assessing obstruction in dilated ureters. Br J Urol. 1973. 45:15–22.5. Britton KE, Nawaz MK, Whitfield HN, Nimmon CC, Carroll MJ, Granowska M, et al. Obstructive nephropathy: comparison between parenchymal transit time index and furosemide diuresis. Br J Urol. 1987. 59:127–132.6. Conway JJ. "Well-tempered" diuresis renography: its historical development, physiological and technical pitfalls, and standardized technique protocol. Semin Nucl Med. 1992. 22:74–84.7. Conway JJ, Maizels M. The "well tempered" diuretic renogram: a standard method to examine the asymptomatic neonate with hydronephrosis or hydroureteronephrosis. A report from combined meetings of The Society for Fetal Urology and members of The Pediatric Nuclear Medicine Council--The Society of Nuclear Medicine. J Nucl Med. 1992. 33:2047–2051.8. O'Reilly PH, Testa HJ, Lawson RS, Farrar DJ, Edwards EC. Diuresis renography in equivocal urinary tract obstruction. Br J Urol. 1978. 50:76–80.9. Lupton EW, Testa HJ, O'Reilly PH, Gosling JA, Dixon JS, Lawson RS, et al. Diuresis renography and morphology in upper urinary tract obstruction. Br J Urol. 1979. 51:10–14.10. Woodard JR. Hydronephrosis in the neonate. Urology. 1993. 42:620–621.11. Duckett JW Jr. When to operate on neonatal hydronephrosis. Urology. 1993. 42:617–619.12. Allen TD. The swing of the pendulum. J Urol. 1992. 148:534–535.13. Dhillon HK. Prenatally diagnosed hydronephrosis: the Great Ormond Street experience. Br J Urol. 1998. 81:Suppl 2. 39–44.14. Kang SS, Bum HS, Ryu SB. The Effect of dismembered pyeloplasty on renal function in patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Korean J Urol. 1993. 34:274–278.15. Ellenbogen PH, Scheible FW, Talner LB, Leopold GR. Sensitivity of gray scale ultrasound in detecting urinary tract obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978. 130:731–733.16. O'Reilly PH, Lawson RS, Shields RA, Testa HJ, Edwards EC, Carroll RN. Dynamic scintigraphy in clinical urology. Br J Urol. 1977. 49:575–582.17. Yokoyama M, Ishine M, Nishio S, Watanabe K, Ochi K, Takeuchi M, et al. Individual renal function study using computed tomography. Eur Urol. 1983. 9:211–215.18. Choong KK, Gruenewald SM, Hodson EM, Antico VF, Farlow DC, Cohen RC. Volume expanded diuretic renography in the postnatal assessment of suspected uretero-pelvic junction obstruction. J Nucl Med. 1992. 33:2094–2098.19. Gordon I, Dhillon HK, Gatanash H, Peters AM. Antenatal diagnosis of pelvic hydronephrosis: assessment of renal function and drainage as a guide to management. J Nucl Med. 1991. 32:1649–1654.20. Yang KR, Lim GY, Sohn HS, Hahn ST, Lee JM. The value of Tc-99m DTPA diuretic renography for assessment of dilated upper urinary tract in children. Korean J Nucl Med. 1999. 33:57–64.21. Koh CS, Lee MC, Chung JK, Lee DS, Choi CW, Choi Y, et al. Assessment of hydroureteronephrosis in children using diuretic radionuclide ureterography. Korean J Nucl Med. 1994. 28:75–84.22. Palmer LS, Maizels M, Cartwright PC, Fernbach SK, Conway JJ. Surgery versus observation for managing obstructive grade 3 to 4 unilateral hydronephrosis: a report from the Society for Fetal Urology. J Urol. 1998. 159:222–228.23. Blyth B, Snyder HM, Duckett JW. Antenatal diagnosis and subsequent management of hydronephrosis. J Urol. 1993. 149:693–698.24. Oh CJ, Seo YJ, Chung SK. Clinical course of prenatally diagnosed ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:145–149.25. Koff SA, Thrall JH, Keyes JW Jr. Diuretic radionuclide urography: a non-invasive method for evaluating nephroureteral dilatation. J Urol. 1979. 122:451–454.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Value of Tc-99m DTPA Diuretic Renography for Assessment of Dilated Upper Urinary Tract in Children
- The effect of dismembered pyeloplasty on renal function in patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Optimal Timing of Surgery of Hydronephrosis Due to Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Neonates and Infants
- Tc-99m MAG3 Renal Scan in Children: A Comparative Study with I-131 Hippuran Renal Scan
- Comparison of DMSA scan and DTPA scan for evaluation of relative renal function in pediatric hydronephrosis