Korean J Urol.
2007 Apr;48(4):467-469. 10.4111/kju.2007.48.4.467.
The Effect of Oral Prednisolone on Pseudo-tumor following Bacillus Calmette Guerin Intravesical Instillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. kowj00@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1997118
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2007.48.4.467
Abstract
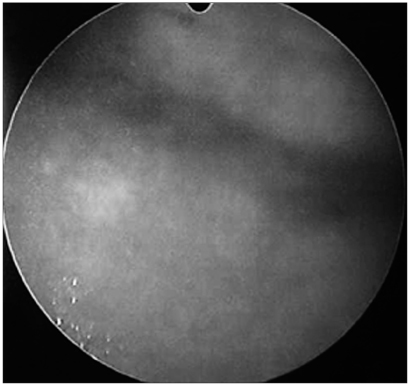
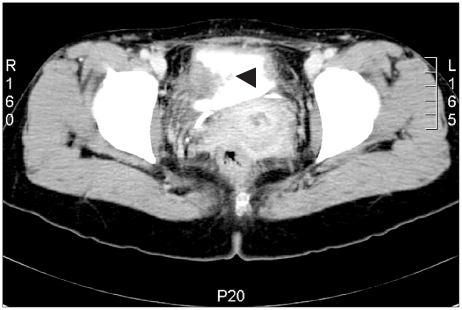
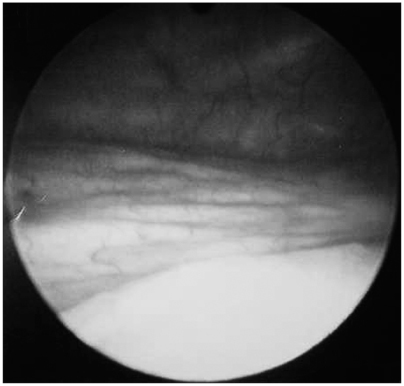
- Herein, the case of a patient where a pseudo-tumor on the bladder wall, with irritable bladder symptoms following a Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) intravesical instillation, was treated by prednisolone administration is reported. A 40-year-old female underwent a transurethral resection for a bladder carcinoma, with subsequent BCG intravesical instillation. After the final BCG intravesical instillation, the patient presented with lower urinary tract symptoms. A mass on the lateral wall of the bladder, reported as a granuloma formation, was treated with oral prednisolone, after which the symptoms and cystoscopic finding were dramatically improved. Finally, all bladder lesions and irritable bladder symptoms disappeared.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morales A, Eidinger D, Bruce AW. Intracavitary Bacillus Cal mette-Guerin in the treatment of superficial bladder tumors. J Urol. 1976. 116:180–183.2. Luftenegger W, Ackermann DK, Futterlieb A, Kraft R, Minder CE, Nadelhaft P, et al. Intravesical versus intravesical plus intradermal bacillus Calmette-Guerin: a prospective radomnized study in patients with recurrent superficial bladder tumors. J Urol. 1996. 155:483–487.3. Patard JJ, Muscatelli-Groux B, Saint F, Popov Z, Maille P, Abbou C, et al. Evaluation of local immune response after intravesical bacilli Calmette-Guerin treatment for superficial bladder cancer. Br J Urol. 1996. 78:709–714.4. O'Donnell MA, DeWolf WC. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy for superficial bladder cancer. New prospects for an old warhorse. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 1995. 4:189–202.5. Coplen DE, Marcus MD, Myers JA, Ratliff TL, Catalona WJ. Long-term follow up of patients treated with 1 or 2, 6-week courses of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin: analysis of possible predictors of response free of tumor. J Urol. 1990. 144:652–657.6. Stanley BM. Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan ED, Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, editors. Management of superficial bladder cancer. Campbell's urology. 2002. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2792.7. Rischmann P, Desgrandchamps F, Malavaud B, Chopin DK. BCG intravesical instillations: recommendations for side-effects management. Eur Urol. 2000. 37:Suppl 1. 33–36.8. Lamm DL. Complications of bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy. Urol Clin North Am. 1992. 19:565–572.9. Kimura K, Matsuura O, Isobe Y, Kamihira O, Kondo A. A case in which severely irritable bladder following intravesical instillation of Bacillus Calmette Guerin was successfully treated by steroid therapy. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2003. 94:574–577.10. Wittes R, Klotz L, Kosecka U. Severe bacillus Calmette-Guerin cystitis responds to systemic steroids when antituberculous drugs and local steroids fail. J Urol. 1999. 161:1568–1569.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Intraperitoneal and Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin on Bladder Carcinogenesis in Rats Induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine
- Tuberculous Prostatic Abscess Following Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Instillation
- The Effect of Lubricant on the Viabillty of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin
- Intravesical bacillus Calmette–Guérin-induced myopathy presenting as rhabdomyolysis: a case report
- Evaluation of T-subsets and NK cell activity in patients with superficial bladder cancer after intravesical treatment with bacillus calmette-guerin