Restor Dent Endod.
2012 Mar;37(1):16-23. 10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.16.
Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. chanyoungl@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1995679
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.16
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Present study was undertaken to investigate the crystal growth onto synthetic hydroxyapatite (HA) seeds in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions with different fluoride concentrations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
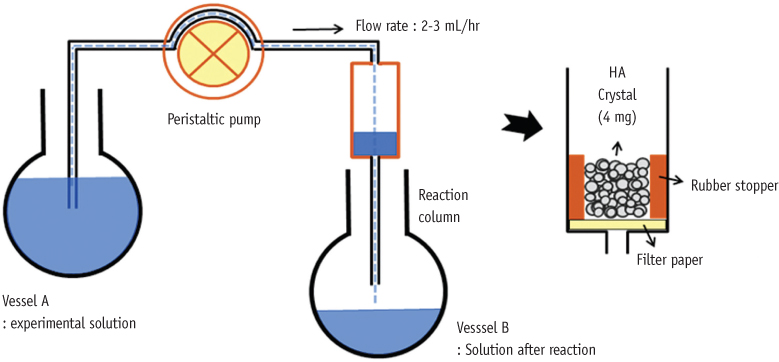
8 groups of pH 4.3 and 7.0 calcium phosphate supersaturated solutions were prepared with different fluoride concentrations (0, 1, 2 and 4 ppm). Calcium phosphate precipitates yield crystal growth onto the HA seed surface while solutions flow. For evaluation of crystallizing process, the changes of Ca2+, PO4(3-), F- concentrations of the inlet and outlet solutions were determined. The recovered solid samples were weighed to assess the amount of minerals precipitated, and finally determined their composition to deduce characteristics of crystals.
RESULTS
During the seeded crystal growth, there were significantly more consumption of Ca2+, PO4(3-), F- in pH 4.3 solutions than pH 7.0 (p < 0.05). As fluoride concentration increased in pH 4.3 solution, Ca2+, PO4(3-), F- consumption in experimental solutions, weight increment of HA seed, and fluoride ratio in crystallized samples were increased. There were significant differences among the groups (p < 0.05). But in pH 7.0 solution, these phenomena were not significant. In pH 7.0 solutions, analyses of crystallized samples showed higher Ca/P ratio in higher fluoride concentration. There were significant differences among the groups (p < 0.05). But in pH 4.3 solution, there were not significant differences in Ca/P ratio.
CONCLUSIONS
Crystal growth in pH 4.3 solutions was superior to that in pH 7.0 solutions. In pH 4.3 solutions, crystal growth increased with showed in higher fluoride concentration up to 4 ppm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Margolis HC, Moreno EC. Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of enamel demineralization. Caries Res. 1985. 19:22–35.
Article2. Aoba T. Solubility properties of human tooth mineral and pathogenesis of dental caries. Oral Dis. 2004. 10:249–257.
Article3. Robinson C, Brookes SJ, Bonass WA, Shore RC, Kirkham J. Enamel maturation. Ciba Found Symp. 1997. 205:156–170.
Article4. Nancollas GH, Mohan MS. The growth of hydroxyapatite crystals. Arch Oral Biol. 1970. 15:731–745.
Article5. Aoba T, Moreno EC. Preparation of hydroxyapatite crystals and their behavior as seeds for crystal growth. J Dent Res. 1984. 63:874–880.
Article6. Barone JP, Nancollas GH, Tomson M. The seeded growth of calcium phosphates. The kinetics of growth of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate on hydroxyapatite. Calcif Tissue Res. 1976. 21:171–182.
Article7. Eanes ED. The influence of fluoride on the seeded growth of apatite from stable supersaturated solutions at pH 7.4. J Dent Res. 1980. 59:144–150.
Article8. Mura-Galelli MJ, Narusawa H, Shimada T, Iijima M, Aoba T. Effects of fluoride on precipitation and hydrolysis of octacalcium phosphate in an experimental model simulating enamel mineralization during amelogenesis. Cells Mater. 1992. 2:221–230.9. Kwun JW, Kim KY, Lee SJ, Jung IY, Lee CY. The effect of the supersaturated solutions containing high concentrations of fluoride on seeded crystal growth. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1999. 24:330–336.10. Lee CY, Aoba T. Seeded crystal growth onto enamal mineral and synthetic hydroxyapatite in dilute supersaturated solutions containing low concentration of fluoride. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1995. 20:818–826.11. Oh SY, Jung IY, Kum KY, Lee CY. Effects of fluoride concentration and seed material on seeded crystal growth. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1997. 22:560–574.12. Iijima M, Moradian-Oldak J. Control of apatite crystal growth in a fluoride containing amelogenin-rich matrix. Biomaterials. 2005. 26:1595–1603.
Article13. Fan Y, Nelson JR, Alvarez JR, Hagan J, Berrier A, Xu X. Amelogenin-assisted ex vivo remineralization of human enamel: effects of supersaturation degree and fluoride concentration. Acta Biomater. 2011. 7:2293–2302.
Article14. Matsumoto T, Okazaki M, Inoue M, Sasaki J, Hamada Y, Takahashi J. Role of acidic amino acid for regulating hydroxyapatite crystal growth. Dent Mater J. 2006. 25:360–364.
Article15. Iijima M, Tohda H, Suzuki H, Yanagisawa T, Moriwaki Y. Effects of F- on apatite-octacalcium phosphate intergrowth and crystal morphology in a model system of tooth enamel formation. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992. 50:357–361.
Article16. Aoba T. The effect of fluoride on apatite structure and growth. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997. 8:136–153.
Article17. Elliot JC. Studies in inorganic chemistry: structure and chemistry of the apatites and other calcium orthophosphates. 1994. Amsterdam: Elsevier;111.18. Robinson C, Connell S, Kirkham J, Brookes SJ, Shore RC, Smith AM. The effect of fluoride on the developing tooth. Caries Res. 2004. 38:268–276.
Article19. Yanagisawa T, Takuma S, Tohda H, Fejerskov O, Fearnhead RW. High resolution electron microscopy of enamel crystals in cases of human dental fluorosis. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 1989. 38:441–448.20. Amjad Z, Nancollas GH. Effect of fluoride on the growth of hydroxyapatite and human dental enamel. Caries Res. 1979. 13:250–258.
Article21. Cate JM, Arends J. Remineralization of artificial enamel lesions in vitro. Caries Res. 1977. 11:277–286.22. Han WS, Kum KY, Lee CY. The influence of fluoride on remineralization of artificial dental caries. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1996. 21:161–173.23. Lammers PC, Borggreven JM, Driessens FC. Influence of fluoride on in vitro remineralization of artificial subsurface lesions determined with a sandwich technique. Caries Res. 1990. 24:81–85.
Article24. Feagin F, Patel PR, Koulourides T, Pigman W. Study of the effect of calcium, phosphate, fluoride and hydrogen ion concentrations on the remineralization of partially demineralized human and bovine enamel surfaces. Arch Oral Biol. 1971. 16:535–548.
Article25. Featherstone JD, Rodgers BE, Smith MW. Physicochemical requirements for rapid remineralization of early carious lesions. Caries Res. 1981. 15:221–235.
Article26. Kim MK, Kum KY, Lee CY. The influence of pH on remineralization of artificial dental caries. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1997. 22:193–208.27. Kwon JW, Suh DG, Song YJ, Lee Y, Lee CY. The effect of lactic acid concentration and pH of lactic acid buffer solutions on enamel remineralization. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2008. 33:507–517.
Article28. Yamazaki H, Margolis HC. Enhanced enamel remineralization under acidic conditions in vitro. J Dent Res. 2008. 87:569–574.
Article29. Song YJ. Development of diffusion pathway in the initial enamel caries lesion. 2009. Graduate School of Yonsei University;Doctoral Dissertation.30. Song SC. Effect of fluoride on remineralization of artificial enamel caries in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 remineralized solution. 2011. Graduate School of Yonsei University;Doctoral Dissertation.31. Kwak YJ, Kim ES, Park SH, Gong HK, Lee Y, Lee CY. The remineralizing features of pH 5.5 solutions of different degree of saturations on artifically demineralized enamel. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2008. 33:481–492.
Article32. Yi JS, Roh BD, Shin SJ, Lee Y, Kong HK, Lee CY. The dynamic change of artificially demineralized enamel by degree of saturation of remineralization soultion at pH 4.3. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2009. 34:20–29.
Article33. Park JS, Park SH, Park JW, Lee CY. The remineralization aspect of enamel according to change of the degree of saturation of the organic acid buffering solution in pH 5.5. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010. 35:96–105.
Article34. Eanes ED, Meyer JL. The influence of fluoride on apatite formation from unstable supersaturated solutions at pH 7.4. J Dent Res. 1978. 57:617–624.
Article35. LeGeros RZ. Calcium phosphates in oral biology and medicine. Monogr Oral Sci. 1991. 15:1–201.36. Nelson DG, Featherstone JD, Duncan JF, Cutress TW. Effect of carbonate and fluoride on the dissolution behaviour of synthetic apatites. Caries Res. 1983. 17:200–211.
Article37. Wu W, Nancollas GH. Determination of interfacial tension from crystallization and dissolution data: a comparison with other methods. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1999. 79:229–279.
Article38. Barone JP, Nancollas GH. The growth of calcium phosphates on hydroxyapatite crystals. The effect of fluoride and phosphonate. J Dent Res. 1978. 57:735–742.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of the pH of remineralized buffer solutions on dentin remineralization
- The effects of the fluoride concentration of acidulated buffer solutions on dentine remineralization
- Effect of concentration of polyacrylic acid and sulfate ion on the cystal growth-a topographic study
- The influence of pH and lactic acid concentration on the formation of artificial root caries in acid buffer solution
- The change of the configuration of hydroxyapatite crystals in enamel by changes of pH and degree of saturation of lactic acid buffer solution