Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2012 Jul;55(7):534-537. 10.5468/KJOG.2012.55.7.534.
A Case of Giant Ovarian Cyst Managed Successfully Through Laparoscopic Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. parkdkog@naver.com
- KMID: 1992567
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/KJOG.2012.55.7.534
Abstract
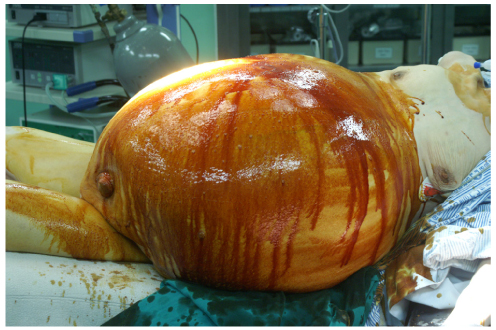
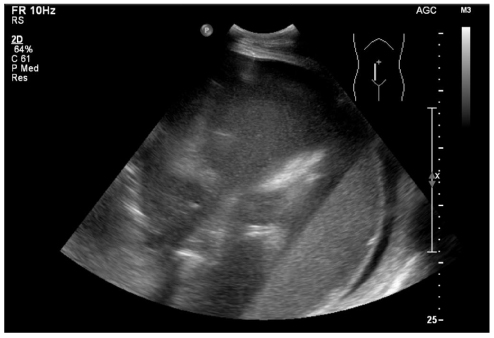
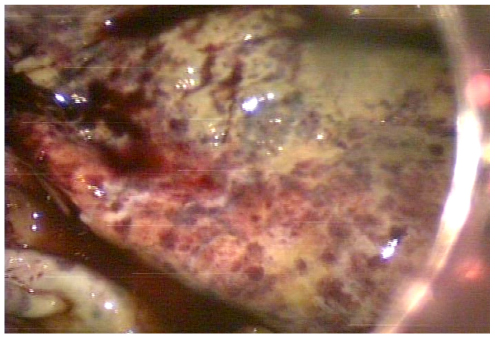
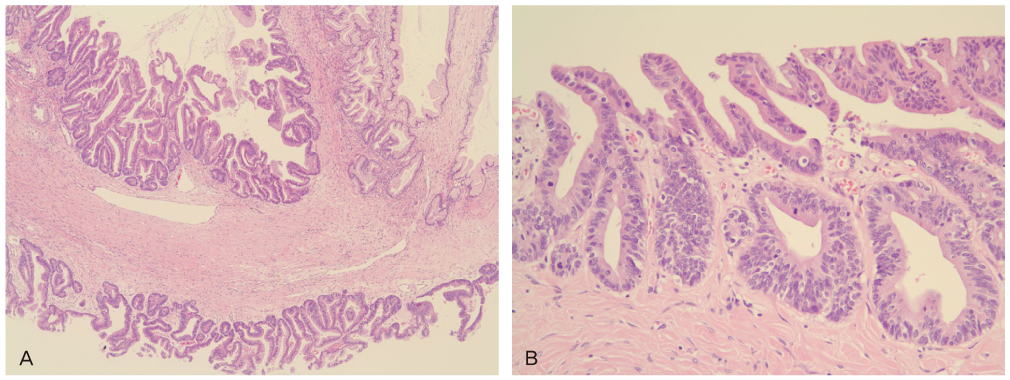
- Mucinous ovarian tumors account for 15% all ovarian neoplasms, of which giant variants rarely occur. Recently huge ovarian cysts (more than 12 kg) are now rarely seen because of the development in health care systems and education. The patient is 26-year-old nulligravida female who presented with abdominal distension. A laparoscopic left salpingo-oophorectomy was performed. Laparoscopic approach to giant ovarian cyst may be difficult regarding the risk of cyst rupture and limited working space. To reduce the limitations of the laparoscopy, we performed laparoscopy after aspirating the cystic contents. During laparoscopy, abdominal cavity was explored by the scope. Cyst contained about 53 L of fluid. The histopathologic examination revealed a borderline mucinous tumor of the left ovary. Laparoscopic excision of giant ovarian cyst seems to be safe and applicable treatment modality.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yuen PM, Yu KM, Yip SK, Lau WC, Rogers MS, Chang A. A randomized prospective study of laparoscopy and laparotomy in the management of benign ovarian masses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997. 177:109–114.2. Knudsen UB, Tabor A, Mosgaard B, Andersen ES, Kjer JJ, Hahn-Pedersen S, et al. Management of ovarian cysts. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2004. 83:1012–1021.3. Menahem S, Shvartzman P. Giant ovarian cyst mimicking ascites. J Fam Pract. 1994. 39:479–481.4. Spohn AE. Multicystic ovarian tumor weighing 328 lb. Tex State J Med. 1905-1906. 1:273–274.5. Malkan AD, Singh-Braich P, Panait L, Dudrick SJ. Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary presenting as unilateral lower extremity edema. Conn Med. 2009. 73:517–519.6. Tagge DU, Baron PL. Giant adrenal cyst: management and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997. 63:744–746.7. Polat C, Ozacmak ID, Yücel T, Ozmen V. Laparoscopic resection of giant mesenteric cyst. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2000. 10:337–339.8. Webb MJ, Decker DG, Mussey E, Williams TJ. Factor influencing survival in Stage I ovarian cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973. 116:222–228.9. Salem HA. Laparoscopic excision of large ovarian cysts. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2002. 28:290–294.10. Jones DR, Vasilakis A, Pillai L, Timberlake GA. Giant, benign, mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary: case study and literature review. Am Surg. 1992. 58:400–403.11. Hunter DJ. Management of a massive ovarian cyst. Obstet Gynecol. 1980. 56:254–255.12. Nakamura M, Saitoh M, Miyamoto S, Kubo Y, Tomita H, Andoh A. Case of a giant mucinous ovarian carcinoma with bone metastasis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2005. 31:576–578.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Giant Follicular Ovarian Cyst with Torsion in Juvenile Primary Hypothyroidism
- A Case of laparoscopic surgery for huge dermoid cyst
- Laparoscopic repair of a rectal fistula due to a benign ovarian dermoid cyst
- A Case of Ruptured Ovarian Cyst in a Newborn
- Laparoscopic management of giant hepatic hydatid cyst in a 12-year-old boy: a case report