J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2008 Sep;33(5):457-462. 10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.457.
Comparison of the residual stress of the nanofilled composites
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Korea. pjw@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1986784
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.457
Abstract
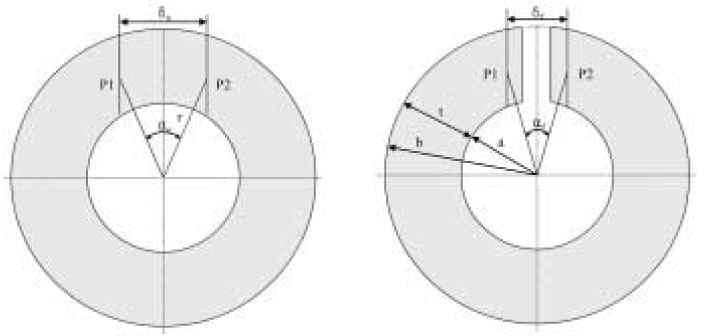
- "Residual stress" can be developed during polymerization of the dental composite and it can be remained after this process was completed. The total amount of the force which applied to the composite restoration can be calculated by the sum of external and internal force. For the complete understanding of the restoration failure behavior, these two factors should be considered. In this experiment, I compared the residual stress of the recently developed nanofilled dental composite by ring slitting methods. The composites used in this study can be categorized in two groups, one is microhybrid type-Z250, as control group, and nanofilled type-Grandio, Filtek Supreme, Ceram-X, as experimental ones. Composite ring was made and marked two reference points on the surface. Then measure the change of the distance between these two points before and after ring slitting. From the distance change, average circumferential residual stress (sigmatheta) was calculated. In 10 minutes and 1 hour measurement groups, Filtek Supreme showed higher residual stress than Z250 and Ceram-X. In 24 hour group, Filtek showed higher stress than the other groups. Following the result of this experiment, nanofilled composite showed similar or higher residual stress than Z250, and when comparing the Z250 and Filtek Supreme, which have quite similar matrix components, Filtek Supreme groups showed higher residual stress.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2009;34(4):333-339. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.333.
Reference
-
1. Versluis A, Tantbirojn D, Douglas WH. Distribution of transient properties during polymerization of a light-initiated restorative composite. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:543–553.
Article2. Versluis A, Tantbirojn D, Pintado MR, DeLong R, Douglas WH. Residual shrinkage stress distributions in molars after composite restoration. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:554–564.
Article3. Toschi F, Melandri C, Pinasco P, Roncari E, Guicciardi S, de Portu G. Influence of residual stresses on the wear behavior of alumina/alumina-zirconia laminated composites. J Am Ceram Soc. 2003. 86:1547–1553.
Article4. Whittle AJ, Burford RP, Hoffman MJ. Influence of Residual Stress on the Relationship Between Pipe Pressure and C-Ring Tests. Polym Eng Sci. 2000. 40:2311–2316.
Article5. Choi KK, Ryu GJ, Choi SM, Lee MJ, Park SJ, Ferracane JL. Effects of cavity configuration on composite restoration. Oper Dent. 2004. 29:462–469.6. Davidson CL, de Gee AJ, Feilzer AJ. The competition between the composite-dentin bond strength and the polymerization contraction stress. J Dent Res. 1984. 63:1396–1399.
Article7. Eick JD, Welch FH. Polymerization shrinkage of posterior composite resins and its possible influence on postoperative sensitivity. Quintessence Int. 1986. 17:103–111.8. Ferracane JL, Mitchem JC. Relationship between composite contraction stress and leakage in Class V cavities. Am J Dent. 2003. 16:239–243.9. Alkhiary YM, Morgano SM, Giordano RA. Effect of acid hydrolysis and mechanical polishing on surface residual stresses of low-fusing dental ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 90:133–142.
Article10. Taskonak B, Mecholsky JJ Jr, Anusavice KJ. Residual stresses in bilayer dental ceramics. Biomaterials. 2005. 26:3235–3241.
Article11. Kemp-Scholte CK, Davidson CL. Complete marginal seal of class V resin composite restorations effected by increased flexibility. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:1240–1243.
Article12. Uno S, Asmussen E. Marginal adaptation of a restorative resin polymerized at reduced rate. Scand J Dent Res. 1991. 99:440–444.
Article13. Condon JR, Ferracane JL. Reduction of composite contraction stress through non-bonded microfiller particles. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:256–260.
Article14. Yoshikawa T, Burrow MF, Tagami J. The effects of bonding system and light curing method on reducing stress of different C-factor cavities. J Adhes Dent. 2001. 3:177–183.15. Braga RR, Hilton TJ, Ferracane JL. Contraction stress of flowable composite materials and their efficacy as stress-relieving layers. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003. 134:721–728.
Article16. Ferracane JL. Developing a more complete understanding of stresses produced in dental composites during polymerization. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:36–42.
Article17. Witzel MF, Calheiros FC, Goncalves F, Kawano Y, Braga RR. Influence of photoactivation method on conversion, mechanical properties, degradation in ethanol and contraction stress of resin-based materials. J Dent. 2005. 33:773–779.
Article18. Lu J. Lu J, editor. Introduction. Handbook of measurement of residual stress. 1996. Lilburn, GA: The Fairmont press Inc;1–4.19. Seif MA, Kishawy HA, Hassan MA. Residual stresses in plastic pipes by laser speckle technique. J Test Eval. 1997. 25:465–470.
Article20. Seif MA, Short SR. Determination of residual stresses in thin-walled composite cylinders. Exp Tech. 2002. 26:43–46.
Article21. Park JW, Ferracane JL. Measuring the residual stress in dental composites using a ring slitting method. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:882–889.
Article22. Park JW, Ferracane JL. Residual stress in composites with the thin-ring-slitting approach. J Dent Res. 2006. 85:945–949.
Article23. Kim KH, Ong JL, Okuno O. The effect of filler loading and morphology on the mechanical properties of contemporary composites. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 87:642–649.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of light-transmittance in dental tissues and dental composite restorations using incremental layering build-up with varying enamel resin layer thickness
- Comparison of microleakage after load cycling for nanofilled composite resin fillings with or without flowable resin lining
- The effect of red and white wine on color changes of nanofilled and nanohybrid resin composites
- Evaluation of polymerization shrinkage stress in silorane-based composites
- Polymerization shrinkage kinetics of silorane-based composites