J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2014 Dec;22(4):230-231. 10.4250/jcu.2014.22.4.230.
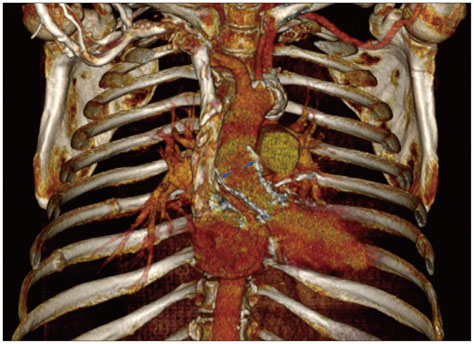
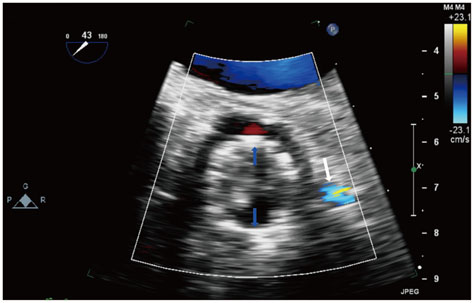
Valve in Valve: Three-Dimensional Transoesophageal Echocardiogram and Multi-Slice CT Images of Bio-Prosthetic Aortic Valve Replaced by Medtronic CoreValve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Chesterman Wing, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield, UK. pankajvic@gmail.com
- KMID: 1980430
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2014.22.4.230
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eggebrecht H, Schäfer U, Treede H, Boekstegers P, Babin-Ebell J, Ferrari M, Möllmann H, Baumgartner H, Carrel T, Kahlert P, Lange P, Walther T, Erbel R, Mehta RH, Thielmann M. Valve-in-valve transcatheter aortic valve implantation for degenerated bioprosthetic heart valves. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011; 4:1218–1227.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Echocardiographic Preoperative Prediction of Prosthetic Aortic Valve Size in Patient with Aortic Valve Replacment
- A Case of Double Orifice Mitral Valve in a Patient with Bicuspid Aortic Valve: Coincidental or a Missed Finding?
- Surgical Management of Aortic Valve Injury after Nonpenetrating Trauma
- Quadricuspid Aortic Valve : Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Prosthetic Valve Dysfunction in the Aortic Position: Caused by Pannus Formation