J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2011 Jun;19(2):51-61. 10.4250/jcu.2011.19.2.51.
Role of Echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. younhj@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1980351
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2011.19.2.51
Abstract
- Atrial fibrillation (AF) is most common arrhythmia and its prevalence appears to be increasing as the population ages. Echocardiography can play a key role in risk stratification and management of patients with AF. Transthoracic echocardiography allows rapid and comprehensive assessment of cardiac anatomical structure and function. Pulmonary vein flow monitoring using echocardiography has the potential to an increasing role in the evaluation of cardiac function and AF ablation procedures. Transesophageal echocardiography also provides accurate information about the presence of a thrombus in the atria and thromboembolic risk. The novel technique of intracardiac echocardiography has emerged as a popular and useful tool in the everyday practice of interventional electrophysiology. Other imaging modalities, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have complementary roles in risk stratification and assessment of patients with AF. Echocardiography continues to be the foundation of clinical evaluation and management of AF.
MeSH Terms
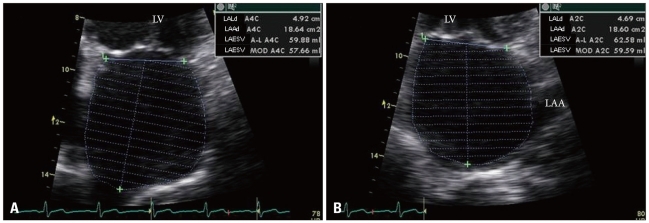
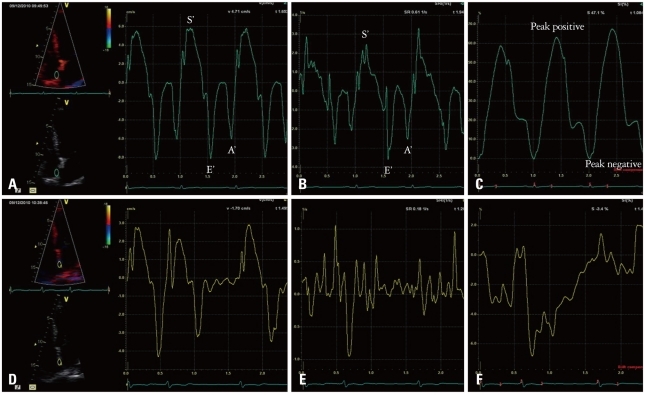
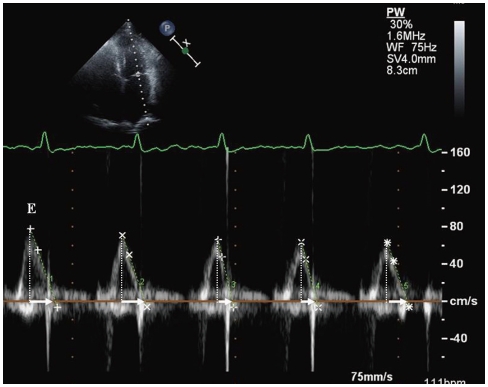
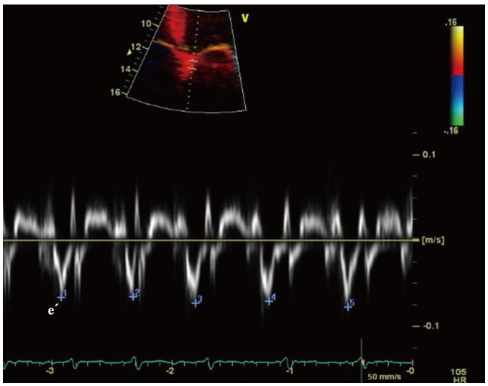
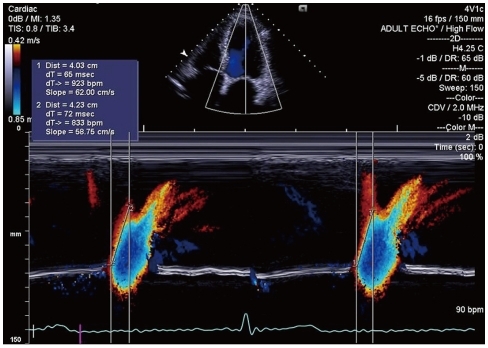
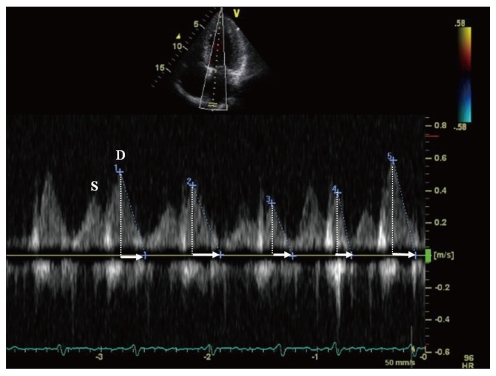
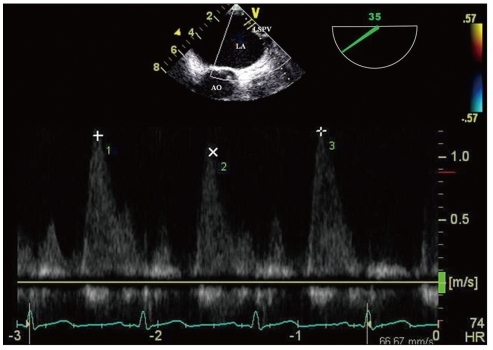
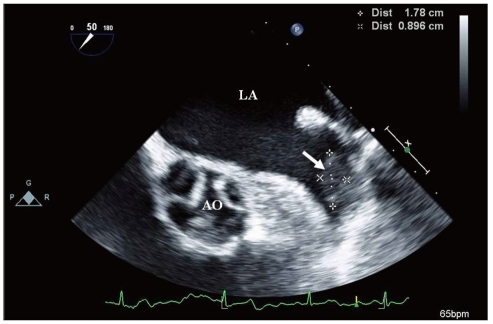
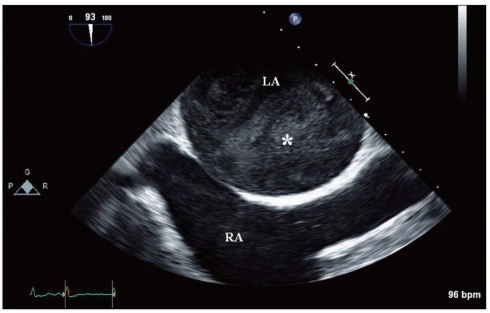
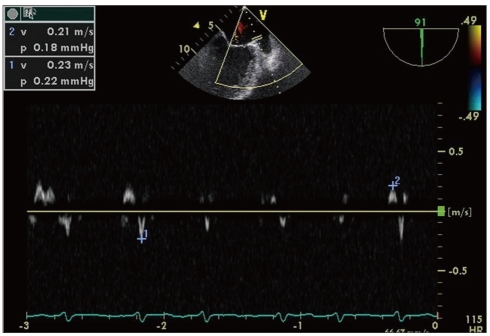
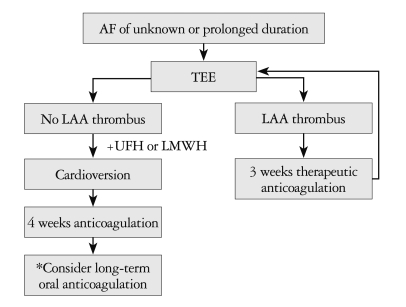
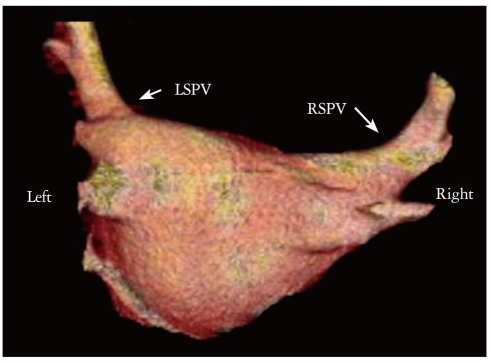
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Membranous Ventricular Septum Aneurysm as a Cause of Recurrent Transient Ischemic Attack
Damir Fabijanic, Cristijan Bulat, Tonci Batinic, Vedran Carevic, Kresimir Caljkusic
J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2012;20(2):114-115. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.2.114.
Reference
-
1. Peters NS, Schilling RJ, Kanagaratnam P, Markides V. Atrial fibrillation: strategies to control, combat, and cure. Lancet. 2002; 359:593–603. PMID: 11867130.2. Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001; 285:2370–2375. PMID: 11343485.3. Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, D'Agostino RB, Massaro JM, Beiser A, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004; 110:1042–1046. PMID: 15313941.4. Vaziri SM, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Echocardiographic predictors of nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1994; 89:724–730. PMID: 8313561.5. Fuster V, Rydén LE, Asinger RW, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Frye RL, Halperin JL, Kay GN, Klein WW, Lévy S, McNamara RL, Prystowsky EN, Wann LS, Wyse DG, Gibbons RJ, Antman EM, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gregoratos G, Hiratzka LF, Jacobs AK, Russell RO, Smith SC Jr, Klein WW, Alonso-Garcia A, Blomström-Lundqvist C, de Backer G, Flather M, Hradec J, Oto A, Parkhomenko A, Silber S, Torbicki A. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation). North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation) Developed in Collaboration With the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation. 2001; 104:2118–2150. PMID: 11673357.6. Lester SJ, Ryan EW, Schiller NB, Foster E. Best method in clinical practice and in research studies to determine left atrial size. Am J Cardiol. 1999; 84:829–832. PMID: 10513783.7. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiographys Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:1440–1463. PMID: 16376782.8. Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Appleton CP, Douglas PS, Oh JK, Tajik AJ, Tsang TS. Left atrial size: physiologic determinants and clinical applications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 47:2357–2363. PMID: 16781359.9. Jenkins C, Bricknell K, Marwick TH. Use of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography to measure left atrial volume: comparison with other echocardiographic techniques. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:991–997. PMID: 16153532.10. Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA, Levy D. Left atrial size and the risk of stroke and death. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1995; 92:835–841. PMID: 7641364.11. Tani T, Tanabe K, Ono M, Yamaguchi K, Okada M, Sumida T, Konda T, Fujii Y, Kawai J, Yagi T, Sato M, Ibuki M, Katayama M, Tamita K, Yamabe K, Yamamuro A, Nagai K, Shiratori K, Morioka S. Left atrial volume and the risk of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004; 17:644–648. PMID: 15163936.12. Beinart R, Boyko V, Schwammenthal E, Kuperstein R, Sagie A, Hod H, Matetzky S, Behar S, Eldar M, Feinberg MS. Long-term prognostic significance of left atrial volume in acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44:327–334. PMID: 15261927.13. Psaty BM, Manolio TA, Kuller LH, Kronmal RA, Cushman M, Fried LP, White R, Furberg CD, Rautaharju PM. Incidence of and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation. 1997; 96:2455–2461. PMID: 9337224.14. Tsang TS, Abhayaratna WP, Barnes ME, Miyasaka Y, Gersh BJ, Bailey KR, Cha SS, Seward JB. Prediction of cardiovascular outcomes with left atrial size: is volume superior to area or diameter? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 47:1018–1023. PMID: 16516087.15. Brodsky MA, Allen BJ, Capparelli EV, Luckett CR, Morton R, Henry WL. Factors determining maintenance of sinus rhythm after chronic atrial fibrillation with left atrial dilatation. Am J Cardiol. 1989; 63:1065–1068. PMID: 2705376.16. Dittrich HC, Erickson JS, Schneiderman T, Blacky AR, Savides T, Nicod PH. Echocardiographic and clinical predictors for outcome of elective cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1989; 63:193–197. PMID: 2909999.17. Shin SH, Park MY, Oh WJ, Hong SJ, Pak HN, Song WH, Lim DS, Kim YH, Shim WJ. Left atrial volume is a predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008; 21:697–702. PMID: 18187293.18. Van Gelder IC, Crijns HJ, Van Gilst WH, Hamer HP, Lie KI. Decrease of right and left atrial sizes after direct-current electrical cardioversion in chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1991; 67:93–95. PMID: 1986512.19. Reant P, Lafitte S, Jaïs P, Serri K, Weerasooriya R, Hocini M, Pillois X, Clementy J, Haïssaguerre M, Roudaut R. Reverse remodeling of the left cardiac chambers after catheter ablation after 1 year in a series of patients with isolated atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2005; 112:2896–2903. PMID: 16260634.20. Stefanadis C, Dernellis J, Stratos C, Tsiamis E, Tsioufis C, Toutouzas K, Vlachopoulos C, Pitsavos C, Toutouzas P. Assessment of left atrial pressure-area relation in humans by means of retrograde left atrial catheterization and echocardiographic automatic boundary detection: effects of dobutamine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998; 31:426–436. PMID: 9462589.21. Choong CY, Herrmann HC, Weyman AE, Fifer MA. Preload dependence of Doppler-derived indexes of left ventricular diastolic function in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987; 10:800–808. PMID: 2958532.22. Manning WJ, Silverman DI, Katz SE, Riley MF, Doherty RM, Munson JT, Douglas PS. Temporal dependence of the return of atrial mechanical function on the mode of cardioversion of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm. Am J Cardiol. 1995; 75:624–626. PMID: 7887393.23. Thomas L, Thomas SP, Hoy M, Boyd A, Schiller NB, Ross DL. Comparison of left atrial volume and function after linear ablation and after cardioversion for chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2004; 93:165–170. PMID: 14715341.24. Manning WJ, Silverman DI, Katz SE, Riley MF, Come PC, Doherty RM, Munson JT, Douglas PS. Impaired left atrial mechanical function after cardioversion: relation to the duration of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994; 23:1535–1540. PMID: 8195510.25. Sohn DW, Chai IH, Lee DJ, Kim HC, Kim HS, Oh BH, Lee MM, Park YB, Choi YS, Seo JD, Lee YW. Assessment of mitral annulus velocity by Doppler tissue imaging in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997; 30:474–480. PMID: 9247521.26. Thomas L, Levett K, Boyd A, Leung DY, Schiller NB, Ross DL. Changes in regional left atrial function with aging: evaluation by Doppler tissue imaging. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2003; 4:92–100. PMID: 12749870.27. Hesse B, Schuele SU, Thamilasaran M, Thomas J, Rodriguez L. A rapid method to quantify left atrial contractile function: Doppler tissue imaging of the mitral annulus during atrial systole. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2004; 5:86–92. PMID: 15113019.28. Wang T, Wang M, Fung JW, Yip GW, Zhang Y, Ho PP, Tse DM, Yu CM, Sanderson JE. Atrial strain rate echocardiography can predict success or failure of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation: a combined transthoracic tissue Doppler and transoesophageal imaging study. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 114:202–209. PMID: 16822565.29. Di Salvo G, Caso P, Lo Piccolo R, Fusco A, Martiniello AR, Russo MG, D'Onofrio A, Severino S, Calabró P, Pacileo G, Mininni N, Calabró R. Atrial myocardial deformation properties predict maintenance of sinus rhythm after external cardioversion of recent-onset lone atrial fibrillation: a color Doppler myocardial imaging and transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic study. Circulation. 2005; 112:387–395. PMID: 16006491.30. Hwang HJ, Choi EY, Rhee SJ, Joung B, Lee BH, Lee SH, Kim J, Lee MH, Jang Y, Chung N, Kim SS. Left atrial strain as predictor of successful outcomes in catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: a two-dimensional myocardial imaging study. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2009; 26:127–132. PMID: 19529886.31. Thomas L, McKay T, Byth K, Marwick TH. Abnormalities of left atrial function after cardioversion: an atrial strain rate study. Heart. 2007; 93:89–95. PMID: 16818487.32. Thomas L, Hoy M, Byth K, Schiller NB. The left atrial function index: a rhythm independent marker of atrial function. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2008; 9:356–362. PMID: 17689293.33. Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, Leip EP, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Murabito JM, Kannel WB, Benjamin EJ. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2003; 107:2920–2925. PMID: 12771006.34. Nagueh SF, Kopelen HA, Quiñones MA. Assessment of left ventricular filling pressures by Doppler in the presence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1996; 94:2138–2145. PMID: 8901664.35. Temporelli PL, Scapellato F, Corrà U, Eleuteri E, Imparato A, Giannuzzi P. Estimation of pulmonary wedge pressure by transmitral Doppler in patients with chronic heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1999; 83:724–727. PMID: 10080426.36. Matsukida K, Kisanuki A, Toyonaga K, Murayama T, Nakashima H, Kumanohoso T, Yoshifuku S, Saigo M, Abe S, Hamasaki S, Otsuji Y, Minagoe S, Tei C. Comparison of transthoracic Doppler echocardiography and natriuretic peptides in predicting mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2001; 14:1080–1087. PMID: 11696832.37. Nagueh SF, Sun H, Kopelen HA, Middleton KJ, Khoury DS. Hemodynamic determinants of the mitral annulus diastolic velocities by tissue Doppler. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001; 37:278–285. PMID: 11153752.38. Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, Miller FA, Oh JK, Redfield MM, Tajik AJ. Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: A comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study. Circulation. 2000; 102:1788–1794. PMID: 11023933.39. Park HS, Naik SD, Aronow WS, Visintainer PF, Das M, McClung JA, Belkin RN. Differences of lateral and septal mitral annulus velocity by tissue Doppler imaging in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. Am J Cardiol. 2006; 98:970–972. PMID: 16996885.40. Sohn DW, Song JM, Zo JH, Chai IH, Kim HS, Chun HG, Kim HC. Mitral annulus velocity in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1999; 12:927–931. PMID: 10552353.41. Khouri SJ, Maly GT, Suh DD, Walsh TE. A practical approach to the echocardiographic evaluation of diastolic function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004; 17:290–297. PMID: 14981433.42. Garcia MJ, Thomas JD, Klein AL. New Doppler echocardiographic applications for the study of diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998; 32:865–875. PMID: 9768704.43. Bollmann A, Binias KH, Grothues F, Schwerdtfeger A, Klein HU. Left atrial appendage function and pulmonary venous flow in patients with nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation and their relation to spontaneous echo contrast. Echocardiography. 2002; 19:37–43. PMID: 11884253.44. Okçün B, Yigit Z, Küçükoglu MS, Mutlu H, Sansoy V, Güzelsoy D, Uner S. Predictors for maintenance of sinus rhythm after cardioversion in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. 2002; 19:351–357. PMID: 12174197.45. Paraskevaidis IA, Theodorakis GN, Katritsis DG, Tsiapras DP, Livanis EG, Kremastinos DT. Pulmonary vein flow analysis by transoesophageal echocardiogr phy in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation; 1 year follow-up after cardioversion. Eur Heart J. 1999; 20:375–385. PMID: 10206384.46. Donal E, Grimm RA, Yamada H, Kim YJ, Marrouche N, Natale A, Thomas JD. Usefulness of Doppler assessment of pulmonary vein and left atrial appendage flow following pulmonary vein isolation of chronic atrial fibrillation in predicting recovery of left atrial function. Am J Cardiol. 2005; 95:941–947. PMID: 15820159.47. Chirillo F, Brunazzi MC, Barbiero M, Giavarina D, Pasqualini M, Franceschini-Grisolia E, Cotogni A, Cavarzerani A, Rigatelli G, Stritoni P, Longhini C. Estimating mean pulmonary wedge pressure in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation from transthoracic Doppler indexes of mitral and pulmonary venous flow velocity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997; 30:19–26. PMID: 9207616.48. Jander N, Minners J, Arentz T, Görnandt L, Fürmaier R, Kalusche D, Neumann FJ. Transesophageal echocardiography in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of pulmonary vein stenosis after radiofrequency ablation therapy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:654–659. PMID: 15947769.49. Lee DH, Oh YS, Shin WS, Kim JH, Choi YS, Jang SW, Park CS, Youn HJ, Lee MY, Chung WS, Seung KB, Rho TH, Kim JH, Choi KB. A transthoracic echocardiographic follow-up study after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: can we detect pulmonary vein stenosis by transthoracic echocardiography? Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:442–447. PMID: 20967145.50. Holmes DR Jr, Monahan KH, Packer D. Pulmonary vein stenosis complicating ablation for atrial fibrillation: clinical spectrum and interventional considerations. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009; 2:267–276. PMID: 19463436.51. Omran H, Jung W, Rabahieh R, Wirtz P, Becher H, Illien S, Schimpf R, Lüderitz B. Imaging of thrombi and assessment of left atrial appendage function: a prospective study comparing transthoracic and transoesophageal echocardiography. Heart. 1999; 81:192–198. PMID: 9922358.52. Klein AL, Murray RD, Grimm RA. Role of transesophageal echocardiography-guided cardioversion of patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001; 37:691–704. PMID: 11693739.53. Leung DY, Black IW, Cranney GB, Hopkins AP, Walsh WF. Prognostic implications of left atrial spontaneous echo contrast in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994; 24:755–762. PMID: 8077549.54. Leung DY, Davidson PM, Cranney GB, Walsh WF. Thromboembolic risks of left atrial thrombus detected by transesophageal echocardiogram. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 79:626–629. PMID: 9068521.55. Jue J, Winslow T, Fazio G, Redberg RF, Foster E, Schiller NB. Pulsed Doppler characterization of left atrial appendage flow. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1993; 6:237–244. PMID: 8333971.56. Transesophageal echocardiographic correlates of thromboembolism in high-risk patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators Committee on Echocardiography. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128:639–647. PMID: 9537937.57. Blackshear JL, Pearce LA, Hart RG, Zabalgoitia M, Labovitz A, Asinger RW, Halperin JL. Aortic plaque in atrial fibrillation: prevalence, predictors, and thromboembolic implications. Stroke. 1999; 30:834–840. PMID: 10187888.58. Agmon Y, Khandheria BK, Gentile F, Seward JB. Echocardiographic assessment of the left atrial appendage. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999; 34:1867–1877. PMID: 10588196.59. Sahin T, Ural D, Kilic T, Bildirici U, Kozdag G, Agacdiken A, Ural E. Evaluation of left atrial appendage functions according to different etiologies of atrial fibrillation with a tissue Doppler imaging technique by using transesophageal echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2009; 26:171–181. PMID: 19207995.60. Nakajima H, Seo Y, Ishizu T, Yamamoto M, Machino T, Harimura Y, Kawamura R, Sekiguchi Y, Tada H, Aonuma K. Analysis of the left atrial appendage by three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 2010; 106:885–892. PMID: 20816132.61. Weinberg DM, Mancini J. Anticoagulation for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1989; 63:745–746. PMID: 2923062.62. Arnold AZ, Mick MJ, Mazurek RP, Loop FD, Trohman RG. Role of prophylactic anticoagulation for direct current cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992; 19:851–855. PMID: 1545081.63. Singer DE, Albers GW, Dalen JE, Go AS, Halperin JL, Manning WJ. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004; 126:429S–456S. PMID: 15383480.64. Black IW, Fatkin D, Sagar KB, Khandheria BK, Leung DY, Galloway JM, Feneley MP, Walsh WF, Grimm RA, Stollberger C, et al. Exclusion of atrial thrombus by transesophageal echocardiography does not preclude embolism after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. A multicenter study. Circulation. 1994; 89:2509–2513. PMID: 8205657.65. Klein AL, Grimm RA, Murray RD, Apperson-Hansen C, Asinger RW, Black IW, Davidoff R, Erbel R, Halperin JL, Orsinelli DA, Porter TR, Stoddard MF. Assessment of Cardioversion Using Transesophageal Echocardiography Investigators. Use of transesophageal echocardiography to guide cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1411–1420. PMID: 11346805.66. Murray RD, Shah A, Jasper SE, Goodman A, Deitcher SR, Katz WE, Malouf JF, Stoddard MF, Grimm RA, Klein AL. ACUTE II pilot study. Transesophageal echocardiography guided enoxaparin antithrombotic strategy for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: the ACUTE II pilot study. Am Heart J. 2000; 139:E1–E7. PMID: 10827367.67. Klein AL, Jasper SE, Katz WE, Malouf JF, Pape LA, Stoddard MF, Apperson-Hansen C, Lieber EA. ACUTE II Steering and Publications Committe for the ACUTE II Investigators. The use of enoxaparin compared with unfractionated heparin for short-term antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation patients undergoing transoesophageal echocardiography-guided cardioversion: assessment of Cardioversion Using Transoesophageal Echocardiography (ACUTE) II randomized multicentre study. Eur Heart J. 2006; 27:2858–2865. PMID: 17098762.68. Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Métayer P, Clémenty J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:659–666. PMID: 9725923.69. Marrouche NF, Martin DO, Wazni O, Gillinov AM, Klein A, Bhargava M, Saad E, Bash D, Yamada H, Jaber W, Schweikert R, Tchou P, Abdul-Karim A, Saliba W, Natale A. Phased-array intracardiac echocardiography monitoring during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: impact on outcome and complications. Circulation. 2003; 107:2710–2716. PMID: 12756153.70. Ren JF, Marchlinski FE. Utility of intracardiac echocardiography in left heart ablation for tachyarrhythmias. Echocardiography. 2007; 24:533–540. PMID: 17456073.71. Saliba W, Thomas J. Intracardiac echocardiography during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2008; 10(Suppl 3):iii42–iii47. PMID: 18955398.72. Schwartzman D, Lacomis J, Wigginton WG. Characterization of left atrium and distal pulmonary vein morphology using multidimensional computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 41:1349–1357. PMID: 12706931.73. Mansour M, Holmvang G, Sosnovik D, Migrino R, Abbara S, Ruskin J, Keane D. Assessment of pulmonary vein anatomic variability by magnetic resonance imaging: implications for catheter ablation techniques for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2004; 15:387–393. PMID: 15089984.74. Dong J, Calkins H, Solomon SB, Lai S, Dalal D, Lardo AC, Brem E, Preiss A, Berger RD, Halperin H, Dickfeld T. Integrated electroanatomic mapping with three-dimensional computed tomographic images for real-time guided ablations. Circulation. 2006; 113:186–194. PMID: 16401772.75. Sra J, Narayan G, Krum D, Malloy A, Cooley R, Bhatia A, Dhala A, Blanck Z, Nangia V, Akhtar M. Computed tomography-fluoroscopy image integration-guided catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007; 18:409–414. PMID: 17284262.76. Schietinger BJ, Bozlar U, Hagspiel KD, Norton PT, Greenbaum HR, Wang H, Isbell DC, Patel RA, Ferguson JD, Gay SB, Kramer CM, Mangrum JM. The prevalence of extracardiac findings by multidetector computed tomography before atrial fibrillation ablation. Am Heart J. 2008; 155:254–259. PMID: 18215594.77. Boldt A, Wetzel U, Lauschke J, Weigl J, Gummert J, Hindricks G, Kottkamp H, Dhein S. Fibrosis in left atrial tissue of patients with atrial fibrillation with and without underlying mitral valve disease. Heart. 2004; 90:400–405. PMID: 15020515.78. Kim YY, Klein AL, Halliburton SS, Popovic ZB, Kuzmiak SA, Sola S, Garcia MJ, Schoenhagen P, Natale A, Desai MY. Left atrial appendage filling defects identified by multidetector computed tomography in patients undergoing radiofrequency pulmonary vein antral isolation: a comparison with transesophageal echocardiography. Am Heart J. 2007; 154:1199–1205. PMID: 18035095.79. Oakes RS, Badger TJ, Kholmovski EG, Akoum N, Burgon NS, Fish EN, Blauer JJ, Rao SN, DiBella EV, Segerson NM, Daccarett M, Windfelder J, McGann CJ, Parker D, MacLeod RS, Marrouche NF. Detection and quantification of left atrial structural remodeling with delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2009; 119:1758–1767. PMID: 19307477.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Influence of Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation on Left Atrial Appendage Function: A Transesophageal Echocardiography Study
- Relation between Atrial Fibrillation and Echocardiographic Size of Left Atrium
- Left Atrial Size in Hypertensive Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Assessment of Mitral Stenosis by Doppler Echocardiography: Influence of Atrial Fibrillation of Doppler Pressure Half-Time
- The Mechanism of and Preventive Therapy for Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation