Korean J Orthod.
2010 Feb;40(1):6-15. 10.4041/kjod.2010.40.1.6.
Comparison of midsagittal reference plane in PA cephalogram and 3D CT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Korea. jjhdent@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1975617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2010.40.1.6
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study is to find the most helpful midsagittal reference plane for diagnosis in PA cephalometry compared with 3D CT.
METHODS
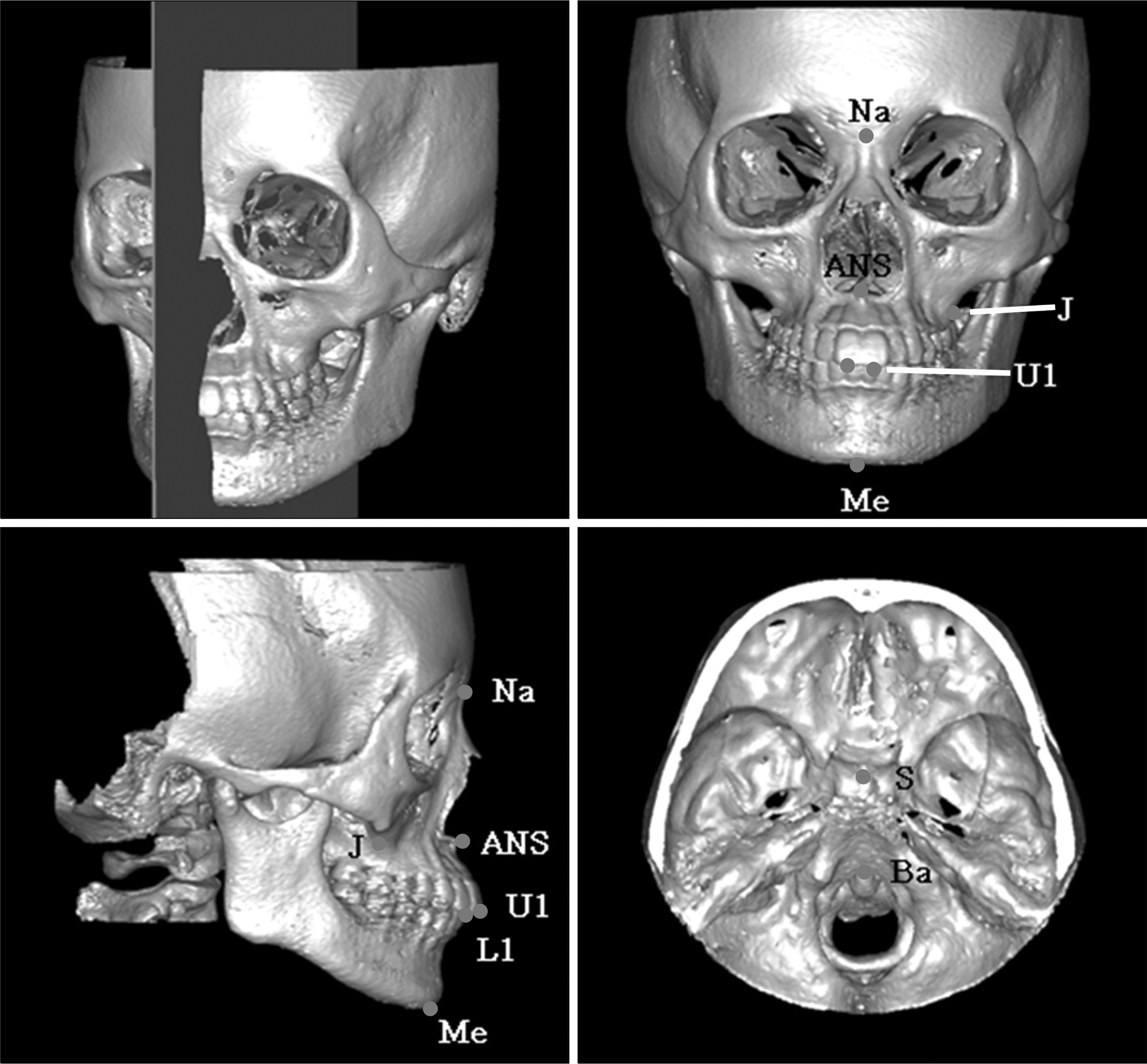
The subjects consisted of 25 adults who showed no facial asymmetry by gross inspection. 3D CT and posteroanterior cephalogram of the subjects were taken. To find the most helpful midsagittal reference plane in PA cephalometry, we considered five kinds of midsagittal planes from which the distances to five landmarks were measured and compared the result with that of 3D CT. The midsagittal plane for 3D CT was determined by the landmarks Nasion, Sella and Basion.
RESULTS
PA measurements using the midsagittal reference plane on a perpendicular plane lying through the midpoint of the right and left latero-orbitales was closest to those of 3D CT.
CONCLUSIONS
It was considered that latero-orbitale perpendicular could be used as the helpful midsagittal reference plane to assess facial asymmetry in PA cephalometry.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The relation between idiopathic scoliosis and the frontal and lateral facial form
Tae-Hwan Kim, Joo-Hwan Kim, Yae-Jin Kim, Il-Sik Cho, Yong-Kyu Lim, Dong-Yul Lee
Korean J Orthod. 2014;44(5):254-262. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2014.44.5.254.Three-dimensional symmetry and parallelism of the skeletal and soft-tissue poria in patients with facial asymmetry
Min-Gun Kim, Jin-Woo Lee, Kyung-Suk Cha, Dong-Hwa Chung, Sang-Min Lee
Korean J Orthod. 2014;44(2):62-68. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2014.44.2.62.
Reference
-
1.Broadbent BH. A new x-ray technique and its application to orthodontia. Angle Orthod. 1931. 1:45–66.2.Grummons DC., Kappeyne van de Coppello MA. A frontal asymmetry analysis. J Clin Orthod. 1987. 21:448–65.3.El-Mangoury NH., Shaheen SI., Mostafa YA. Landmark identification in computerized posteroanterior cephalometrics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987. 91:57–61.
Article4.Katsumata A., Fujishita M., Maeda M., Ariji Y., Ariji E., Langlais RP. 3D-CT evaluation of facial asymmetry. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005. 99:212–20.
Article5.Peck S., Peck L., Kataja M. Skeletal asymmetry in esthetically pleasing faces. Angle Orthod. 1991. 61:43–8.6.Shah SM., Joshi MR. An assessment of asymmetry in the normal craniofacial complex. Angle Orthod. 1978. 48:141–8.7.Chebib FS., Chamma AM. Indices of craniofacial asymmetry. Angle Orthod. 1981. 51:214–26.8.Trpkova B., Prasad NG., Lam EW., Raboud D., Glover KE., Major PW. Assessment of facial asymmetries from posteroanterior cephalograms: validity of reference lines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003. 123:512–20.
Article9.Ricketts RM. Perspectives in the clinical application of cephalometrics. The first fifty years. Angle Orthod. 1981. 51:115–50.10.Sassouni V. Position of the maxillary first permanent molar in the cephalofacial complex: a study in three dimensions. Am J Orthod. 1957. 43:477–510.11.Paek SH., Ahn BK., Kim SH., Shon HB., Han HJ., Kang SM. A frontal cephalometric study on the reference lines to assess the craniomaxillofacial asymmetry. Korean J Orthod. 1993. 23:1–15.12.Hwang HS., Hwang CH., Lee KH., Kang BC. Maxillofacial 3-dimensional image analysis for the diagnosis of facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 130:779–85.
Article13.Togashi K., Kitaura H., Yonetsu K., Yoshida N., Nakamura T. Three-dimensional cephalometry using helical computer tomography: measurement error caused by head inclination. Angle Orthod. 2002. 72:513–20.14.Park SH., Yu HS., Kim KD., Lee KJ., Baik HS. A proposal for a new analysis of craniofacial morphology by 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 129:600. .e23-34.
Article15.Kim WS., Lee KH., Hwang HS. Comparison of asymmetric degree between maxillofacial hard and soft tissue in facial asymmetric subjects using three-dimensional computed tomography. Korean J Orthod. 2005. 35:163–73.16.Huang J., Bumann A., Mah J. Three-dimensional radiographic analysis in orthodontics. J Clin Orthod. 2005. 39:421–8.17.Lim MY., Lim SH. Comparison of model analysis measurements among plaster model, laser scan digital model, and cone beam CT image. Korean J Orthod. 2009. 39:6–17.
Article18.Seo SA., Baik HS., Hwang CJ., Yu HS. Analysis of masseter muscle in facial asymmetry before and after orthognathic surgery using 3-dimensional computed tomography. Korean J Orthod. 2009. 39:18–27.
Article19.Kim YI., Kim SS., Son WS., Park SB. Pharyngeal airway analysis of different craniofacial morphology using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Korean J Orthod. 2009. 39:136–45.
Article20.Park SB., Park JH., Jung YH., Jo BH., Kim YI. Correlation between menton deviation and dental compensation in facial asymmetry using cone-beam CT. Korean J Orthod. 2009. 39:300–9.
Article21.Mah J., Hatcher D. Three-dimensional craniofacial imaging. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 126:308–9.
Article22.Association of Professors for Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology. Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology. 3rd ed.Seoul: Narae Publi-shing Co.;2001. p. 170–3.23.Choi YS., Kim GT., Hwang EH. Basic principle of cone beam computed tomography. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2006. 36:123–9.24.Jeon YN., Lee KH., Hwang HS. Validity of midsagittal reference planes constructed in 3D CT images. Korean J Orthod. 2007. 37:182–91.25.Cheney EA. Dentofacial asymmetries and their clinical significance. Am J Orthod. 1961. 47:814–29.
Article26.Harvold E. Cleft lip and palate: morphologic studies of the facial skeleton. Am J Orthod. 1954. 40:493–506.27.Vig PS., Hewitt AB. Asymmetry of the human facial skeleton. Angle Orthod. 1975. 45:125–9.28.Baumrind S., Frantz RC. The reliability of head film measurements. 1. Landmark identification. Am J Orthod. 1971. 60:111–27.29.Major PW., Johnson DE., Hesse KL., Glover KE. Effect of head orientation on posterior anterior cephalometric landmark identification. Angle Orthod. 1996. 66:51–60.30.Letzer GM., Kronman JH. A posteroanterior cephalometric evaluation of craniofacial asymmetry∗. Angle Orthod. 1967. 37:205–11.31.Major PW., Johnson DE., Hesse KL., Glover KE. Landmark identification error in posterior anterior cephalometrics. Angle Orthod. 1994. 64:447–54.32.Ghafari J., Cater PE., Shofer FS. Effect of film-object distance on posteroanterior cephalometric measurements: suggestions for standardized cephalometric methods. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995. 108:30–7.
Article33.de Oliveira AE., Cevidanes LH., Phillips C., Motta A., Burke B., Tyndall D. Observer reliability of three-dimensional cephalometric landmark identification on cone-beam computerized tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009. 107:256–65.
Article34.Grayson BH., McCarthy JG., Bookstein F. Analysis of craniofacial asymmetry by multiplane cephalometry. Am J Orthod. 1983. 84:217–24.
Article35.Suri S., Utreja A., Khandelwal N., Mago SK. Craniofacial computerized tomography analysis of the midface of patients with repaired complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008. 134:418–29.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Formulation of a reference coordinate system of three-dimensional head and neck images: Part II. Reproducibility of the horizontal reference plane and midsagittal plane
- Validity of midsagittal reference planes constructed in 3D CT images
- Deviation of landmarks in accordance with methods of establishing reference planes in three-dimensional facial CT evaluation
- Comparison of landmark position between conventional cephalometric radiography and CT scans projected to midsagittal plane
- Validity of Horizontal Reference Planes on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Generated Postero-Anterior Cephalogram