Int J Stem Cells.
2014 Nov;7(2):108-117. 10.15283/ijsc.2014.7.2.108.
Transcriptional Profiles of Imprinted Genes in Human Embryonic Stem Cells During In vitro Differentiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biological Sciences and Center for Stem Cell Differentiation, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea. ymhan@kaist.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1974598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc.2014.7.2.108
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Genomic imprinting is an inheritance phenomenon by which a subset of genes are expressed from one allele of two homologous chromosomes in a parent of origin-specific manner. Even though fine-tuned regulation of genomic imprinting process is essential for normal development, no other means are available to study genomic imprinting in human during embryonic development. In relation with this bottleneck, differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) into specialized lineages may be considered as an alternative to mimic human development.
METHODS AND RESULTS
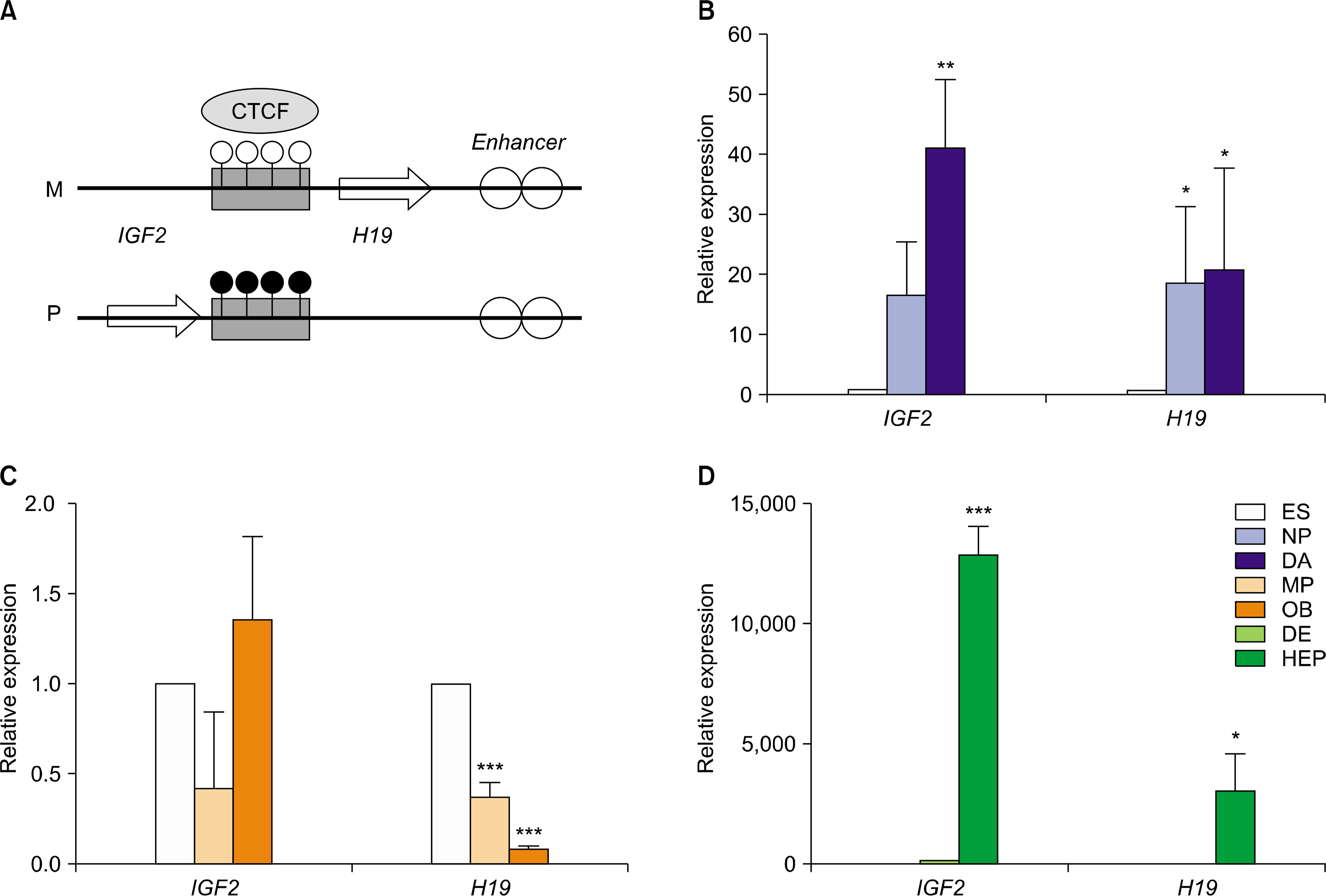
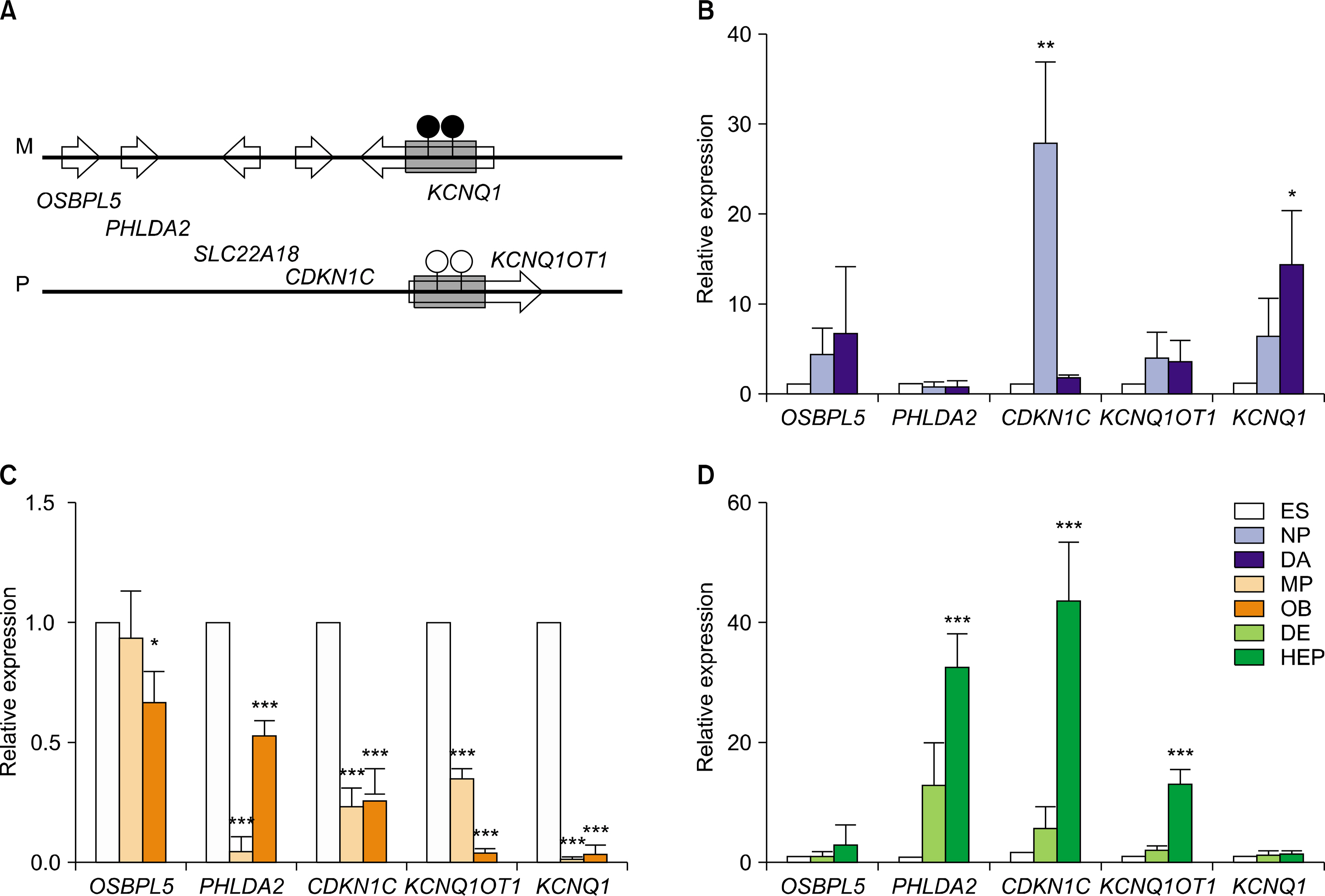
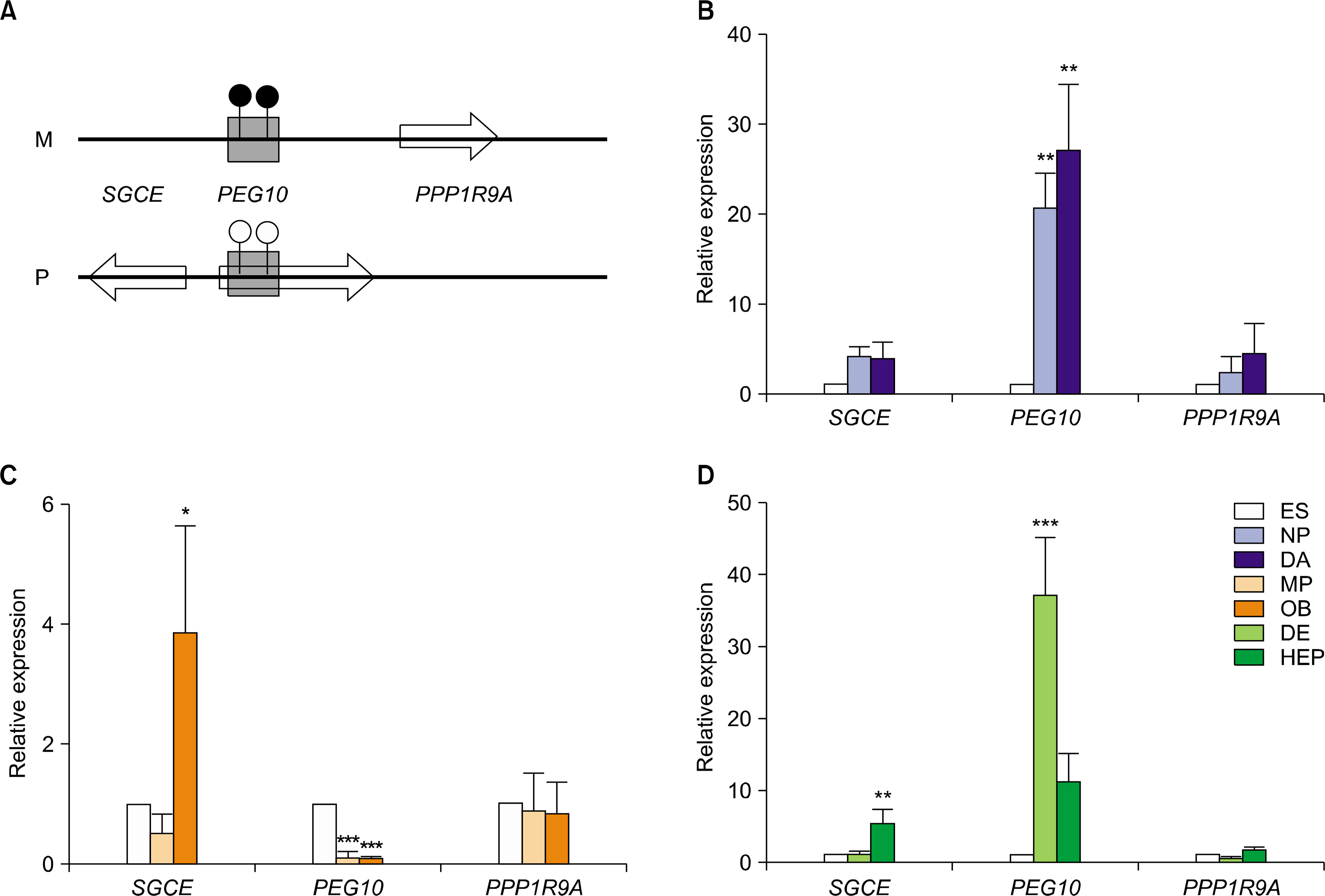
In this study, hESCs were differentiated into three lineage cell types to analyze temporal and spatial expression of imprinted genes. Of 19 imprinted genes examined, 15 imprinted genes showed similar transcriptional level among two hESC lines and two human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) lines. Expressional patterns of most imprinted genes were varied in progenitors and fully differentiated cells which were derived from hESCs. Also, no consistence was observed in the expression pattern of imprinted genes within an imprinting domain during in vitro differentiation of hESCs into three lineage cell types.
CONCLUSIONS
Transcriptional expression of imprinted genes is regulated in a cell type-specific manner in hESCs during in vitro differentiation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Edwards CA, Ferguson-Smith AC. Mechanisms regulating imprinted genes in clusters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007. 19:281–289.
Article2. Verona RI, Mann MR, Bartolomei MS. Genomic imprinting: intricacies of epigenetic regulation in clusters. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003. 19:237–259.
Article3. Reik W, Dean W, Walter J. Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science. 2001. 293:1089–1093.
Article4. Ideraabdullah FY, Vigneau S, Bartolomei MS. Genomic imprinting mechanisms in mammals. Mutat Res. 2008. 647:77–85.
Article5. Frost JM, Moore GE. The importance of imprinting in the human placenta. PLoS Genet. 2010. 6:e1001015.
Article6. Xie W, Barr CL, Kim A, Yue F, Lee AY, Eubanks J, Dempster EL, Ren B. Base-resolution analyses of sequence and parent-of-origin dependent DNA methylation in the mouse genome. Cell. 2012. 148:816–831.
Article7. Peters J. The role of genomic imprinting in biology and disease: an expanding view. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. 15:517–530.
Article8. Morison IM, Ramsay JP, Spencer HG. A census of mammalian imprinting. Trends Genet. 2005. 21:457–465.
Article9. Ko JY, Park CH, Koh HC, Cho YH, Kyhm JH, Kim YS, Lee I, Lee YS, Lee SH. Human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors as a continuous, stable, and on-demand source for human dopamine neurons. J Neurochem. 2007. 103:1417–1429.
Article10. Mahmood A, Harkness L, Schrøder HD, Abdallah BM, Kassem M. Enhanced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to mesenchymal progenitors by inhibition of TGF-beta/activin/nodal signaling using SB-431542. J Bone Miner Res. 2010. 25:1216–1233.
Article11. Cai J, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Ye F, Song Z, Qin H, Meng S, Chen Y, Zhou R, Song X, Guo Y, Ding M, Deng H. Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into functional hepatic cells. Hepatology. 2007. 45:1229–1239.
Article12. Park SW, Kim J, Park JL, Ko JY, Im I, Do HS, Kim H, Tran NT, Lee SH, Kim YS, Cho YS, Lee DR, Han YM. Variable allelic expression of imprinted genes in human pluripotent stem cells during differentiation into specialized cell types in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. 446:493–498.
Article13. Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000. 405:482–485.
Article14. Ono R, Nakamura K, Inoue K, Naruse M, Usami T, Wakisaka-Saito N, Hino T, Suzuki-Migishima R, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Kohda T, Ogura A, Yokoyama M, Kaneko-Ishino T, Ishino F. Deletion of Peg10, an imprinted gene acquired from a retrotransposon, causes early embryonic lethality. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:101–106.
Article15. Berg JS, Lin KK, Sonnet C, Boles NC, Weksberg DC, Nguyen H, Holt LJ, Rickwood D, Daly RJ, Goodell MA. Imprinted genes that regulate early mammalian growth are coexpressed in somatic stem cells. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e26410.
Article16. Sun BW, Yang AC, Feng Y, Sun YJ, Zhu Yf, Zhang Y, Jiang H, Li CL, Gao FR, Zhang ZH, Wang WC, Kong XY, Jin G, Fu SJ, Jin Y. Temporal and parental-specific expression of imprinted genes in a newly derived Chinese human embryonic stem cell line and embryoid bodies. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. 15:65–75.
Article17. Onyango P, Jiang S, Uejima H, Shamblott MJ, Gearhart JD, Cui H, Feinberg AP. Monoallelic expression and methylation of imprinted genes in human and mouse embryonic germ cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:10599–10604.
Article18. Freed WJ, Chen J, Bäckman CM, Schwartz CM, Vazin T, Cai J, Spivak CE, Lupica CR, Rao MS, Zeng X. Gene expression profile of neuronal progenitor cells derived from hESCs: activation of chromosome 11p15.5 and comparison to human dopaminergic neurons. PLoS One. 2008. 3:e1422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Alteration of Genomic Imprinting Status of Human Parthenogenetic Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells during Neural Lineage Differentiation
- Lineage-specific Expression of miR-200 Family in Human Embryonic Stem Cells during In Vitro Differentiation
- SIRT1 Inhibits p53 but not NF-kappaB Transcriptional Activity during Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells into Embryoid Bodies
- Detection of Neural Fates from Random Differentiation: Application of Support Vector MachineMin
- Stem Cell ; New Paradigm in the Era of Genomic Medicine