Int J Stem Cells.
2014 Nov;7(2):63-69. 10.15283/ijsc.2014.7.2.63.
Efficacy and Safety of Stem Cell Therapies for Patients with Stroke: a Systematic Review and Single Arm Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. y1693@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Seo-myeon Branch Office of the Community Health Center, Uljin, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, International St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Medical Library, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Clinical Research Coordinating Center, Catholic Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Catholic High-Performance Cell Therapy Center & Department of Medical Lifescience, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1974593
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc.2014.7.2.63
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Stem cell-based therapy is a potential new approach in the treatment of stroke. However, the efficacy and safety of these treatments are not yet fully understood. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of available single-arm studies using stem cell-based therapy in patients with stroke.
METHODS
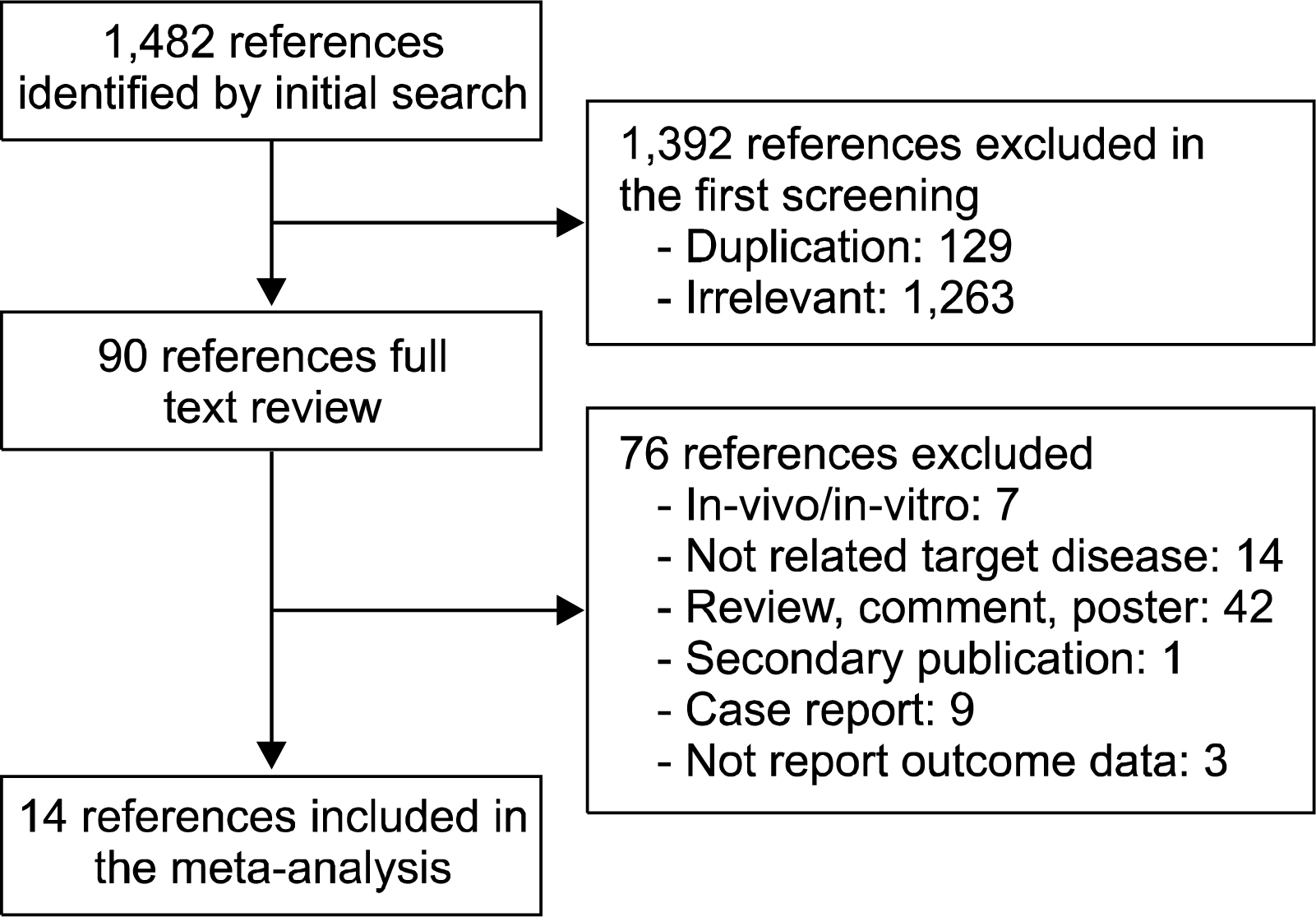
We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane database for studies of stem cell therapy in patients with stroke from its inception through July 2014. The articles included in the search were restricted to the English language, studies with at least 5 patients, and those using cell-based therapies for treating stroke.
RESULTS
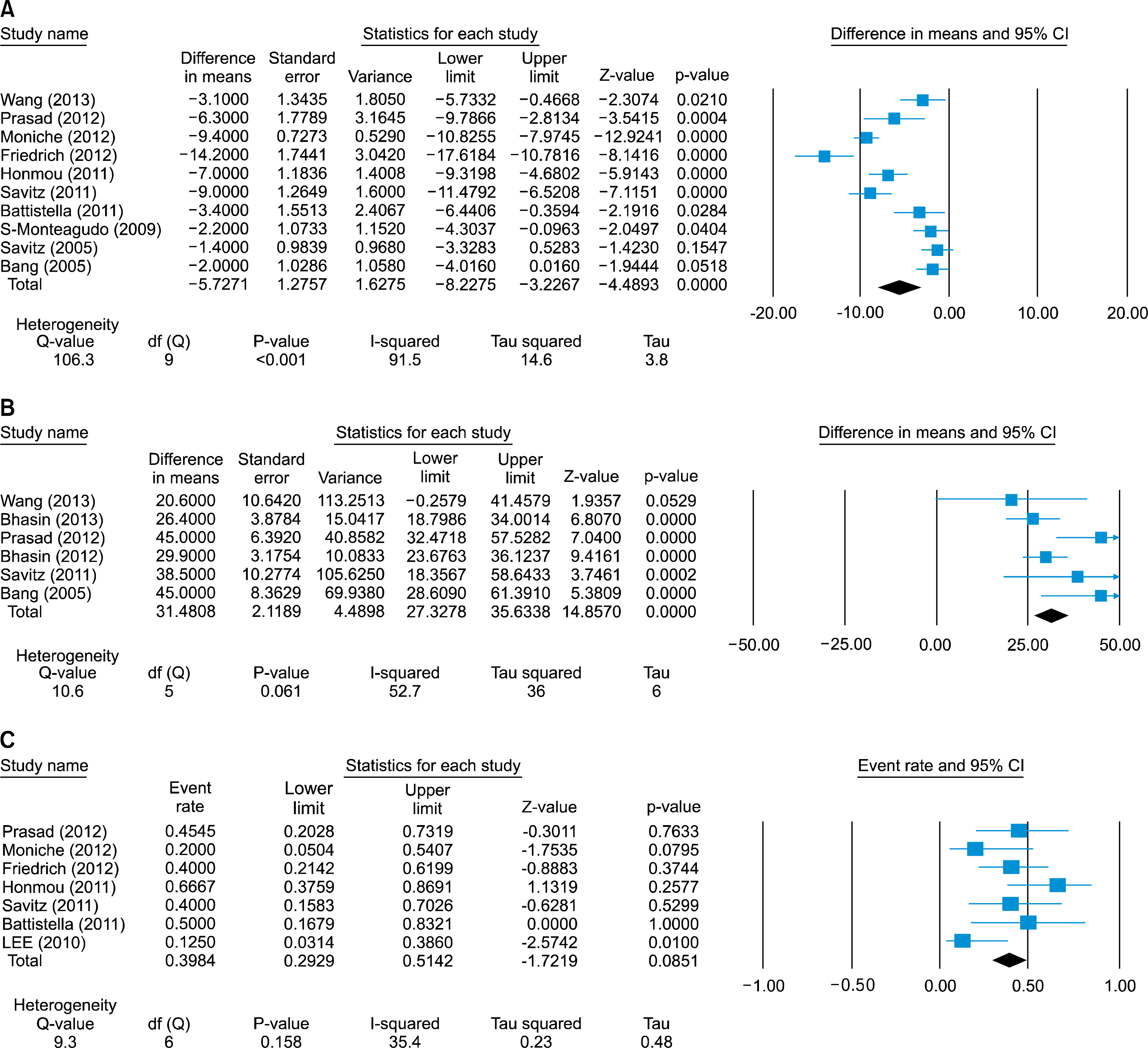
Fourteen studies included in the meta-analysis. The pooled mean difference in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores from baseline to follow-up points was 5.7 points (95%CI: -8.2 to -3.2, I2=91.5%) decreased. Also the pooled mean difference in modified Bathel index (BI) score was increased by 31.5 points (95%CI: 35.6~14.9, I2=52.7%) and the pooled incidence rate to achieve on modified Rankin score (mRS)< or =2 was 40% (95% CI: 30%~51%, I2=35.4%) at follow-up points. The pooled incidence rates of death, seizure, and infection were 13% (95%CI, 8~23%), 15% (95%CI, 8~25%), and 15% (95%CI, 8~23%), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The published data suggest that stem cell-based therapy for patients with stroke can be judged as effective based on single arm clinical studies. However, clinical benefits of stem cell therapy for patients with stroke need further investigation and reevaluation to test the clinical efficacy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Neurogenin-1 Overexpression Increases the Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Enhanced Engraftment in an Ischemic Rat Brain
Gyu-Hee Kim, Marasini Subash, Jeong Seon Yoon, Darong Jo, Jihun Han, Ji Man Hong, Sung-Soo Kim, Haeyoung Suh-Kim
Int J Stem Cells. 2019;13(1):127-141. doi: 10.15283/ijsc19111.Effects and Mechanisms of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke in Hypertensive Rats
Yulin Liu, Ying Zhao, Yu Min, Kaifeng Guo, Yuling Chen, Zhen Huang, Cheng Long
Int J Stem Cells. 2021;15(2):217-226. doi: 10.15283/ijsc21136.
Reference
-
References
1. Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, O’Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C; Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2010 (GBD 2010) and the GBD Stroke Experts Group. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014. 383:245–254.
Article2. Molina CA. Reperfusion therapies for acute ischemic stroke: current pharmacological and mechanical approaches. Stroke. 2011. 42(1 Suppl):S16–S19.3. Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, Kaste M, von Kummer R, Broderick JP, Brott T, Frankel M, Grotta JC, Haley EC Jr, Kwiatkowski T, Levine SR, Lewandowski C, Lu M, Lyden P, Marler JR, Patel S, Tilley BC, Albers G, Bluhmki E, Wilhelm M, Hamilton S; ATLANTIS Trials Investigators; ECASS Trials Investigators; NINDS rt-PA Study Group Investigators. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet. 2004. 363:768–774.
Article4. Mora-Lee S, Sirerol-Piquer MS, Gutiérrez-Pérez M, Gomez-Pinedo U, Roobrouck VD, López T, Casado-Nieto M, Abizanda G, Rabena MT, Verfaille C, Prósper F, García-Verdugo JM. Therapeutic effects of hMAPC and hMSC transplantation after stroke in mice. PLoS One. 2012. 7:e43683.
Article5. Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version5.1.0 (updated March 2011). Cochrane Collaboration;2011.
Article6. Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs.7. Huedo-Medina TB, Sánchez-Meca J, Marín-Martínez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods. 2006. 11:193–206.8. Moniche F, Gonzalez A, Gonzalez-Marcos JR, Carmona M, Piñero P, Espigado I, Garcia-Solis D, Cayuela A, Montaner J, Boada C, Rosell A, Jimenez MD, Mayol A, Gil-Peralta A. Intra-arterial bone marrow mononuclear cells in ischemic stroke: a pilot clinical trial. Stroke. 2012. 43:2242–2244.
Article9. Friedrich MA, Martins MP, Araújo MD, Klamt C, Vedolin L, Garicochea B, Raupp EF, Sartori El Ammar J, Machado DC, Costa JC, Nogueira RG, Rosado-de-Castro PH, Mendez-Otero R, Freitas GR. Intra-arterial infusion of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in patients with moderate to severe middle cerebral artery acute ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant. 2012. 21(Suppl 1):S13–S21.
Article10. Savitz SI, Misra V, Kasam M, Juneja H, Cox CS Jr, Alderman S, Aisiku I, Kar S, Gee A, Grotta JC. Intravenous autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells for ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2011. 70:59–69.
Article11. Honmou O, Houkin K, Matsunaga T, Niitsu Y, Ishiai S, Onodera R, Waxman SG, Kocsis JD. Intravenous administration of auto serum-expanded autologous mesenchymal stem cells in stroke. Brain. 2011. 134:1790–1807.
Article12. Rabinovich SS, Seledtsov VI, Banul NV, Poveshchenko OV, Senyukov VV, Astrakov SV, Samarin DM, Taraban VY. Cell therapy of brain stroke. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005. 139:126–128.
Article13. Savitz SI, Dinsmore J, Wu J, Henderson GV, Stieg P, Caplan LR. Neurotransplantation of fetal porcine cells in patients with basal ganglia infarcts: a preliminary safety and feasibility study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005. 20:101–107.
Article14. Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH, Lee G. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005. 57:874–882.
Article15. Suárez-Monteagudo C, Hernández-Ramírez P, Alvarez-González L, García-Maeso I, de la Cuétara-Bernal K, Castillo-Díaz L, Bringas-Vega ML, Martínez-Aching G, Morales-Chacón LM, Báez-Martín MM, Sánchez-Catasús C, Carballo-Barreda M, Rodríguez-Rojas R, Gómez-Fernández L, Alberti-Amador E, Macías-Abraham C, Balea ED, Rosales LC, Del Valle Pérez L, Ferrer BB, González RM, Bergado JA. Autologous bone marrow stem cell neurotransplantation in stroke patients. An open study. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2009. 27:151–161.
Article16. Battistella V, de Freitas GR, da Fonseca LM, Mercante D, Gutfilen B, Goldenberg RC, Dias JV, Kasai-Brunswick TH, Wajnberg E, Rosado-de-Castro PH, Alves-Leon SV, Mendez-Otero R, Andre C. Safety of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with non-acute ischemic stroke. Regen Med. 2011. 6:45–52.
Article17. Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, Lee PH, Ahn YH, Bang OY; STARTING collaborators. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010. 28:1099–1106.
Article18. Wang L, Ji H, Li M, Zhou J, Bai W, Zhong Z, Li N, Zhu D, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Wu M. Intrathecal Administration of Autologous CD34 Positive Cells in Patients with Past Cerebral Infarction: A Safety Study. ISRN Neurol. 2013. 2013:128591.
Article19. Bhasin A, Srivastava MV, Mohanty S, Bhatia R, Kumaran SS, Bose S. Stem cell therapy: a clinical trial of stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013. 115:1003–1008.
Article20. Prasad K, Mohanty S, Bhatia R, Srivastava MV, Garg A, Srivastava A, Goyal V, Tripathi M, Kumar A, Bal C, Vij A, Mishra NK. Autologous intravenous bone marrow mono-nuclear cell therapy for patients with subacute ischaemic stroke: a pilot study. Indian J Med Res. 2012. 136:221–228.21. Bhasin A, Srivastava M, Bhatia R, Mohanty S, Kumaran S, Bose S. Autologous intravenous mononuclear stem cell therapy in chronic ischemic stroke. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2012. 8:181–189.
Article22. Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007. 6:182–187.
Article23. Mendez-Otero R, de Freitas GR, André C, de Mendonça ML, Friedrich M, Oliveira-Filho J. Potential roles of bone marrow stem cells in stroke therapy. Regen Med. 2007. 2:417–423.
Article24. Bliss TM, Andres RH, Steinberg GK. Optimizing the success of cell transplantation therapy for stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2010. 37:275–283.
Article25. Lees JS, Sena ES, Egan KJ, Antonic A, Koblar SA, Howells DW, Macleod MR. Stem cell-based therapy for experimental stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Stroke. 2012. 7:582–588.
Article26. Adams HP Jr, Davis PH, Leira EC, Chang KC, Bendixen BH, Clarke WR, Woolson RF, Hansen MD. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: A report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology. 1999. 53:126–131.
Article27. Grotta J. Lubeluzole treatment of acute ischemic stroke. The US and Canadian Lubeluzole Ischemic Stroke Study Group. Stroke. 1997. 28:2338–2346.28. Franke CL, Palm R, Dalby M, Schoonderwaldt HC, Hantson L, Eriksson B, Lang-Jenssen L, Smakman J. Flunarizine in stroke treatment (FIST): a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in Scandinavia and the Netherlands. Acta Neurol Scand. 1996. 93:56–60.
Article29. Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Burn J, Warlow C. Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet. 1991. 337:1521–1526.
Article30. Shah S, Vanclay F, Cooper B. Predicting discharge status at commencement of stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 1989. 20:766–769.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advances in laser and stem cell treatment: current technologies, limitations, and future prospects
- Comment on “Comparison of efficacy and safety between palonosetron and ondansetron to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis”
- The Prevalence of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in the General Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Single-Arm Meta-Analysis
- Adult Stem Cell Therapy for Stroke: Challenges and Progress
- Efficacy and Safety of Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2025;49:235-51)