Imaging Sci Dent.
2012 Mar;42(1):61-64. 10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.61.
Keratocystic odontogenic tumor: case report with CT and ultrasonography findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Ondokuz Mayis, Samsun, Turkey. psumer1970@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Ondokuz Mayis, Samsun, Turkey.
- 3Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ondokuz Mayis, Samsun, Turkey.
- 4Department of Pathology, Gulhane Military Medicine Academy, Ankara, Turkey.
- KMID: 1974409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.61
Abstract
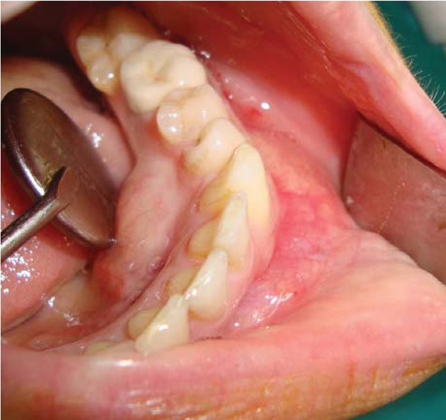
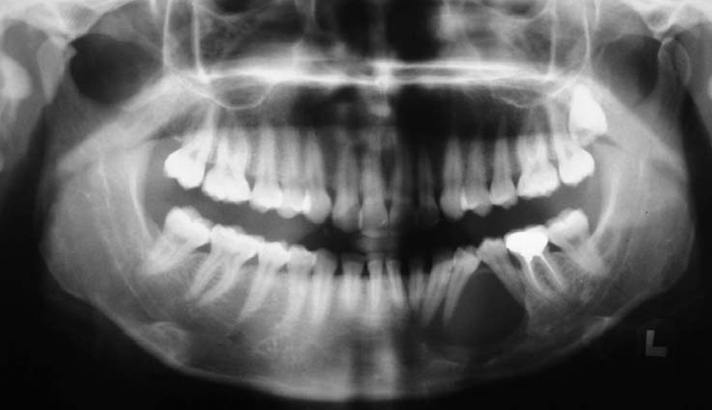
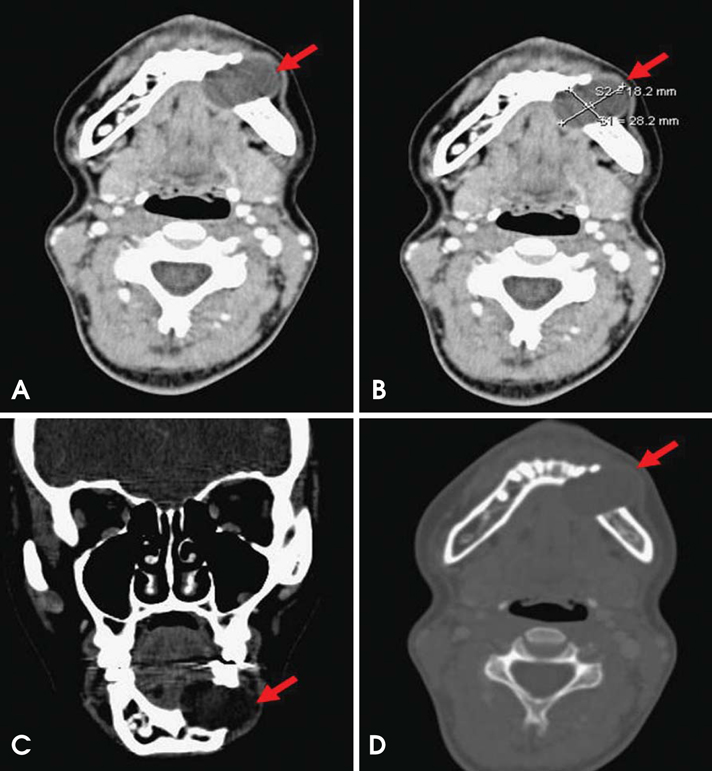
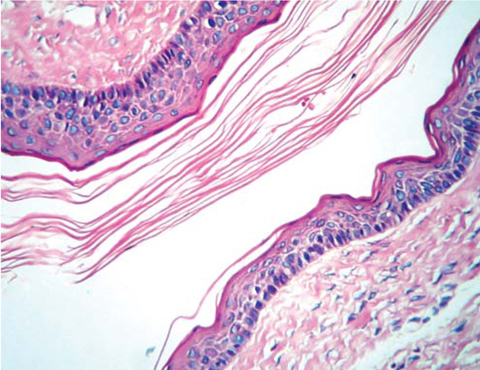
- Keratocystic odontogenic tumor (KCOT) is a benign odontogenic tumor with a potentially aggressive and infiltrative behavior. KCOT is most commonly occurred in mandible and demonstrate a unilocular, round, oval, scalloped radiolucent area, while large lesions may appear multilocular. An important characteristic of KCOT is its propensity to grow in an antero-posterior direction within medullary cavity of bone causing minimal expansion. Definitive diagnosis relies on histological examination. In this report, a KCOT that had an expansion both buccal and lingual cortical bone is described including its features in computed tomography and ultrasonographic exams. The lesion was removed surgically via an intraoral approach under local anesthesia and histologically reported as a KCOT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. 2009. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders;683–687.2. Phillpsen HP. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. Keratocystic odontogenic tumour. WHO classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumors. 2005. 3rd ed. Lyon: IARC Press;306–307.3. MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Keratocystic odontogenic tumour: systematic review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011. 40:1–23.
Article4. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 2009. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;351–355.5. Boffano P, Ruga E, Gallesio C. Keratocystic odontogenic tumor (odontogenic keratocyst): preliminary retrospective review of epidemiologic, clinical, and radiologic features of 261 lesions from University of Turin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. 68:2994–2999.
Article6. Morgan TA, Burton CC, Qian F. A retrospective review of treatment of the odontogenic keratocyst. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005. 63:635–639.
Article7. Li TJ. The odontogenic keratocyst: a cyst, or a cystic neoplasm? J Dent Res. 2011. 90:133–142.8. Cawson RA, Odell EW. Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine. 2002. 7th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone.9. Grasmuck EA, Nelson BL. Keratocystic odontogenic tumor. Head Neck Pathol. 2010. 4:94–96.
Article10. Lauria L, Curi MM, Chammas MC, Pinto DS, Torloni H. Ultrasonography evaluation of bone lesions of the jaw. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996. 82:351–357.11. Sumer AP, Danaci M, Ozen Sandikci E, Sumer M, Celenk P. Ultrasonography and Doppler ultrasonography in the evaluation of intraosseous lesions of the jaws. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009. 38:23–27.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enucleation of large keratocystic odontogenic tumor at mandible via unilateral sagittal split osteotomy: a report of three cases
- Carnoy's Solution Application for Patient Preliminarily Diagnosed with Keratocystic Odotogenic Tumor: Case Report
- Deep Neck Space Infection Caused by Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor
- Pseudoaneurysm of the Inferior Alveolar Artery after Surgical Curettage for Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report
- A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma arising from an Odontogenic Keratocyst