Hip Pelvis.
2013 Sep;25(3):226-231. 10.5371/hp.2013.25.3.226.
Treatment of Periprosthetic Tuberculous Infection of Total Hip Arthroplasty with Long Term Medication without Implant Removal
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Jeonnam, Korea. tryoon@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1974379
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2013.25.3.226
Abstract
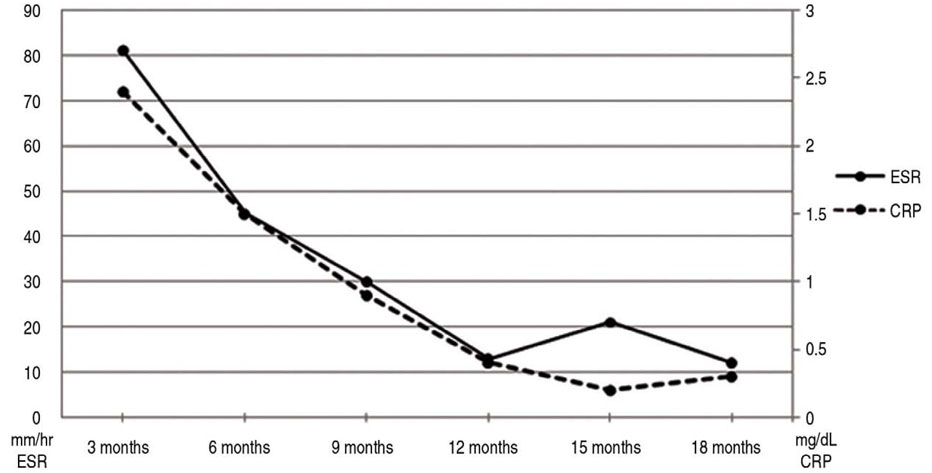
- Periprosthetic joint infection is one of the most dreaded complications of replacement arthroplasty and the incidence of periprosthetic tuberculous infections is increasing. This report presents a case of extensive periprosthetic tuberculous infections of primary total hip arthroplasty which was treated with debridement and long periods of antituberculous medication without implant removal. The patient completed 18 months of 4 drug antituberculous chemotherapy and the plain radiograph on the last review showed new bony consolidation around the prosthesis without loosening or signs of reactivation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marmor M, Parnes N, Dekel S. Tuberculosis infection complicating total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19:397–400.
Article2. Yoon TR, Rowe SM, Santosa SB, Jung ST, Seon JK. Immediate cementless total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of active tuberculosis. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:923–926.
Article3. Baldini N, Toni A, Greggi T, Giunti A. Deep sepsis from Mycobacterium tuberculosis after total hip replacement. Case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1988; 107:186–188.
Article4. Boéri C, Gauias J, Jenny JY. Total hip replacement prosthesis infected by Mycobacterium tuberculous. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2003; 89:163–166.5. Kreder HJ, Davey JR. Total hip arthroplasty complicated by tuberculous infection. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:111–114.
Article6. Besser MI. Total knee replacement in unsuspected tuberculosis of the joint. Br Med J. 1980; 280:1434.
Article7. Neogi DS, Ashok K, Yadav CS, Singh S. Delayed periprosthetic tuberculosis after total knee replacement: is conservative treatment possible? Acta Orthop Belg. 2009; 75:136–140.8. McCullough CJ. Tuberculosis as a late complication of total hip replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 1977; 48:508–510.
Article9. Khater FJ, Shamnani IQ, Mehta JB, Moorman JP, Myers JW. Prosthetic joint infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unusual case report with literature review. South Med J. 2007; 100:66–69.
Article10. Sidhu AS, Singh AP, Singh AP. Total hip replacement in active advanced tuberculous arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91:1301–1304.
Article11. Zeiger LS, Watters W, Sherk H. Scintigraphic detection of prosthetic joint and soft tissue sepsis secondary to tuberculosis. Clin Nucl Med. 1984; 9:638–639.
Article12. Wolfgang GL. Tuberculosis joint infection following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; (201):162–166.
Article13. Levin ML. Miliary tuberculosis masquerading as late infection in total hip replacement. Md Med J. 1985; 34:153–155.14. Ueng WN, Shih CH, Hseuh S. Pulmonary tuberculosis as a source of infection after total hip arthroplasty. A report of two cases. Int Orthop. 1995; 19:55–59.15. Tokumoto JI, Follansbee SE, Jacobs RA. Prosthetic joint infection due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: report of three cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1995; 21:134–136.
Article16. Lusk RH, Wienke EC, Milligan TW, Albus TE. Tuberculous and foreign-body granulomatous reactions involving a total knee prosthesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:1325–1327.
Article17. Spinner RJ, Sexton DJ, Goldner RD, Levin LS. Periprosthetic infections due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients with no prior history of tuberculosis. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:217–222.
Article18. Berbari EF, Hanssen AD, Duffy MC, Steckelberg JM, Osmon DR. Prosthetic joint infection due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a case series and review of the literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1998; 27:219–227.19. Kaya M, Nagoya S, Yamashita T, Niiro N, Fujita M. Periprosthetic tuberculous infection of the hip in a patient with no previous history of tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:394–395.
Article20. Shanbhag V, Kotwal R, Gaitonde A, Singhal K. Total hip replacement infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A case report with review of literature. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007; 73:268–274.21. Lee CL, Wei YS, Ho YJ, Lee CH. Postoperative Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection after total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2009; 16:87–89.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Fracture around a Cemented Stem in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Three Concurrent Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Hip Revision Arthroplasty
- Cementless Implant in Total Hip Arthroplasty