Hip Pelvis.
2013 Sep;25(3):189-196. 10.5371/hp.2013.25.3.189.
Ultrasonographic Usefulness for Diagnosis of Acetabular Labral Tear
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Bumin Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Busan Bumin Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Mirae Orthopedic Surgery Clinic, Nonsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. dshwang@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1974374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2013.25.3.189
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study evaluated the usefulness of ultrasonography for a diagnosis of acetabular labral tear in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2010 to October 2011, an ultrasonographic examination was performed in 58 patients(58 hips: 26 men and 32 women) with acetabular labral tear. The sensitivity and positive predictive value of ultrasonography were evaluated for 58 cases with acetabular labral tear confirmed by hip arthroscopy.
RESULTS
The sensitivity and positive predictive value for an acetabular labral tear using ultrasonography was 89.6% and 100%, respectively. The concordance rate of an acetabular labral tear between arthroscopy and ultrasonography was 84.6%.
CONCLUSION
Hip ultrasonography can make a significant contribution to a pathologic diagnosis and isa useful diagnostic tool for acetabular labral tears.
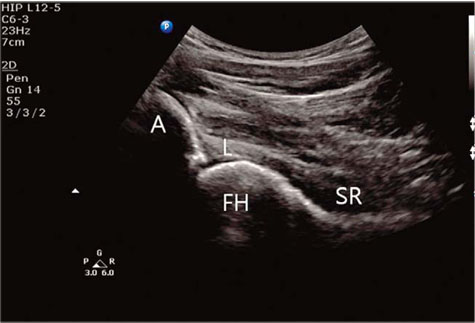
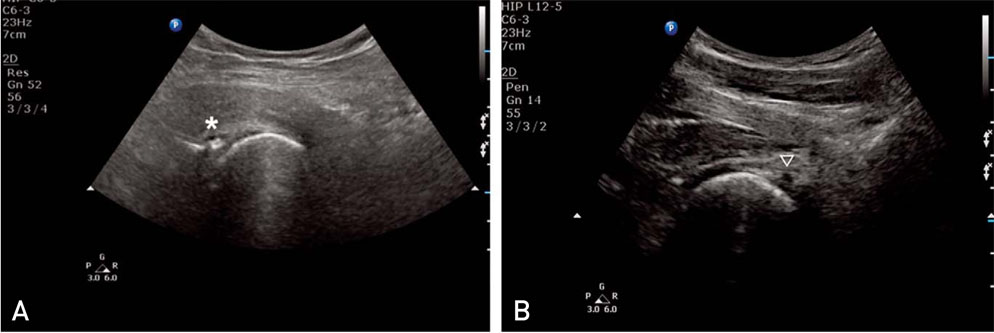
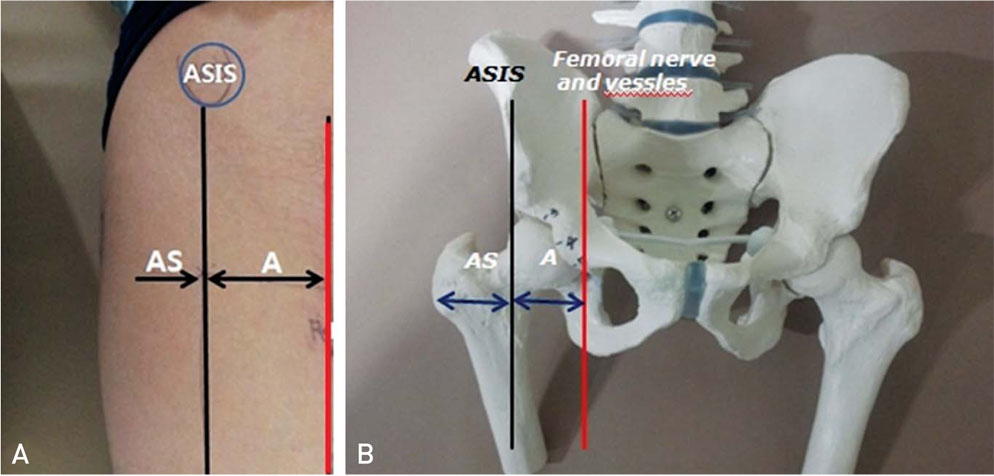
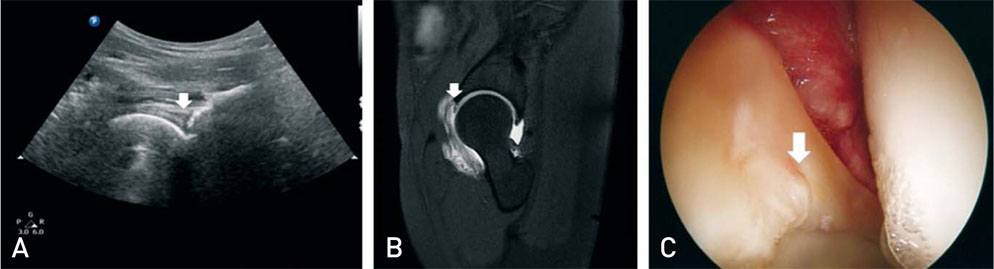
Figure
Reference
-
1. Martinoli C, Valle M, Malattia C, Beatrice Damasio M, Taqliafico A. Paediatric musculoskeletal US beyond the hip joint. Pediatr Radiol. 2011; 41:Suppl 1. S113–S124.
Article2. Connell DA, Bass C, Sykes CA, Young D, Edwards E. Sonographic evaluation of gluteus medius and minimus teninopathy. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:1339–1347.
Article3. Blankenbaker DG, Tuite MJ. The painful hip: new concepts. Skeletal Radiol. 2006; 35:352–370.
Article4. Beck M, Leuig M, Parvizi J, Boutier V, Wyss D, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: Part II. Midterm results of surgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (418):67–73.5. Troelsen A, Jacobsen S, Bolvig L, Gelineck J, Rømer L, Søballe K. Ultrasound versus magnetic resonance arthrography in acetabular labral tear diagnostics: a prospective comparison in 20 dysplastic hips. Acta Radiol. 2007; 48:1004–1010.
Article6. Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabualr impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1012–1018.7. Blankenbaker DG, De Smet AA, Keene JS, Fine JP. Classification and localization of acetabular labral tears. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:391–397.
Article8. Jamadar DA, Jacobson JA, Caoili EM, et al. Musculoskeletal sonography technique: focused versus comprehensive evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:5–9.
Article9. Troelsen A, Mechlenburg I, Gelineck J, Bolvig L, Jacobsen S, Søballe K. What is the role of clinical tests and ultrasound in acetabular labral tear diagnostics? Acta Orthop. 2009; 80:314–318.
Article10. McCarthy J, Barsoum W, Puri L, Lee JA, Murphy S, Cooke P. The role of hip arthroscopy in the elite athlete. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (406):71–74.
Article11. Tannast M, Goricki D, Beck M, Murphy SB, Siebenrock KA. Hip damage occurs at the zone of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:273–280.
Article12. Kivlan BR, Martin RL, Sekiya JK. Response to diagnostic injection in patients with femoroacetabular impingement, labral tears, chondral lesions, and extra-articular pathology. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:619–627.
Article13. Scheel AK, Schmidt WA, Hermann KG, et al. Interobserver reliability of rheumatologists performing musculosckeletal ultrasonography: results from a EULAR "Train the trainers" course. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:1043–1049.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acetabular labral tear: Diagnosis and Treatment
- Treatment of Acetabular Avulsion Fracture with Labral Tear Using Suture Anchor: A Case Report
- Arthroscopic Labral Repair Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement: Short Term 2-5 Years Follow-up Results
- Patient Satisfaction after Arthroscopic Repair of Acetabular Labral Tears
- Paralabral Cysts and Their Correlation with Acetabular Disorder