Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Nov;61(5):456-462. 10.4046/trd.2006.61.5.456.
Etiology and Characteristics of Massive Pleural Effusions Investigated at One University Hospital in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. drterry@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1970251
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2006.61.5.456
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Differential diagnosis is very important in patients with pleural effusions. A few studies on the etiologies of massive pleural effusions have been reported, but these were conducted in different decades and locations. In the present study, the etiologic spectrum of massive pleural effusions in Korea, were evaluated through an investigation at one university hospital.
METHODS
Retrospective chart reviews were performed in patients having undergone thoracentesis between July 2002 and July 2005. Pleural effusions were deemed to be massive if they occurred in two thirds or more of one hemithorax. The etiologies of massive pleural effusions, pleural fluid findings, serum laboratory findings, and sputum and pleural fluid cytologies were compared.
RESULTS
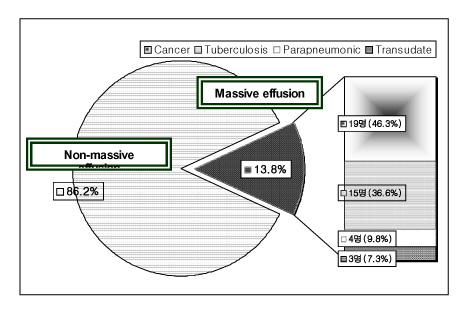
Of 298 pleural effusions cases, 41 (13.8%) had massive pleural effusions. The most frequent causes of massive pleural effusions were malignancy (19; 46.3%) followed by tuberculosis (15; 36.6%), parapneumonic effusion (4; 9.8%) and transudate (3; 7.3%). Compared with massive benign effusions, patients with massive malignant pleural effusions were more likely to have lower adenosine deaminase (ADA) activity, a higher amylase level and higher RBC count in their pleural fluids. Also, compared with non-tuberculosis effusions, patients with massive tuberculous pleural effusions were more likely to have lower RBC and neutrophil counts, but a higher lymphocyte count, adenosine deaminase (ADA) activity and protein level.
CONCLUSION
The most common etiologies of massive pleural effusions in Korea are malignancy and tuberculosis. A high ADA content favors a tuberculous condition, while bloody effusions with a relatively lower ADA content. favors malignancy. The proportion of tuberculosis in massive pleural effusions was higher than in previous reports.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Porcel JM, Vives M. Etiology and pleural fluid characteristics of large and massive effusions. Chest. 2003. 124:978–983.2. Moon JW, Han CH, Kang SM, Park MS, Hwang SY, Byun MK, et al. The relationship between age and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase activity in pleural tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 58:459–464.3. Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC, Ball WC Jr. Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates. Ann Intern Med. 1972. 77:507–513.4. Berger HW, Mejia E. Tuberculous pleurisy. Chest. 1973. 63:88–92.5. Jay SJ. Diagnostic procedures for pleural disease. Clin Chest Med. 1985. 6:33–48.6. Chernow B, Sahn SA. Carcinomatous involvement of the pleura: an analysis of 96 patients. Am J Med. 1977. 63:695–702.7. Salyer WR, Eggleston JC, Erozan YS. Efficacy of pleural needle biopsy and pleural fluid cytopathology in the diagnosis of malignant neoplasm involving the pleura. Chest. 1975. 67:536–539.8. Maher GG, Berger HW. Massive pleural effusion: malignant and nonmalignant causes in 46 patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972. 105:458–460.9. Pedro de Lelis F, Ortega Gonzalez G, Molina Boix M, Paricio Nunez P, Ferrer Puchol MD, Madrid Conesa A. Massive pleural effusion: study of 84 cases. Med Clin. 1984. 82:581–583.10. Valdes L, Alvarez D, Valle JM, Pose A, San Jose E. The etiology of pleural effusions in an area with high incidence of tuberculosis. Chest. 1996. 109:158–162.11. Liam CK, Lim KH, Wong CM. Causes of pleural exudates in a region with a high incidence of tuberculosis. Respirology. 2000. 5:33–38.12. Marel M, Zrustova M, Stasny B, Light RW. The incidence of pleural effusion in a well-defined region: epidemiologic study in central Bohemia. Chest. 1993. 104:1486–1489.13. Go WG, Lee JG, Jeong JH, Park MS, Jeong NY, Kim YS, et al. Differential diagnosis by analysis of pleural effusion. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2001. 51:559–569.14. Cheng D, Rodriguez RM, Perkett EA, Rogers J, Bienvenu G, Lappalainen U, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural fluid. Chest. 1999. 116:760–765.15. Lee GD, Shin MG, Lee KW, Jo YJ, Kim HC, Hwang YS. Clinical features in patients with amylase-rich pleural effusion. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2003. 54:563–569.16. Shin MK, Ham HS, Lee DW, Cho YJ, Jeong YY, Kim HC, et al. The diagnostic usefulness of pleural fluid adenosine deaminase with lymphocyte/neutrophil ratio in tuberculous pleural effusion. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2004. 57:132–137.17. Diacon AH, van de Wal BW, Wyser C, Smedema JP, Bezuidenhout J, Bolliger CT, et al. Diagnostic tools in tuberculous pleurisy: a direct comparative study. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:589–591.18. Perez-Rodriguez E, Jimenez Castro D. The use of adenosine deaminase and adenosine deaminase isoenzymes in the diagnosis of tuberculous pleuritis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000. 6:259–266.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Characteristics of Pleural Fluid and Blood in Mycoplasmal and Tuberculous Pleural Effusions
- Clinical Characteristics and Diagnostic Utility of Eosinophilic Pleural effusion
- A Study on Diagnostic Value of Lysozyme Activity in Various pleural effusions
- A study on lactic dehydrogenase activity of tuberculous pleural effusion
- Ferritin Assay in Pleural Effusion