Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Dec;61(6):573-577. 10.4046/trd.2006.61.6.573.
A Case of Pulmonary Metastasis of a Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ysamkim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2The Institute of Chest Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1970243
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2006.61.6.573
Abstract
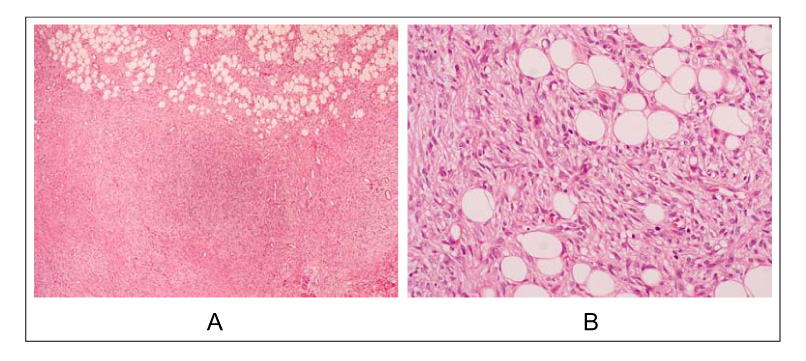
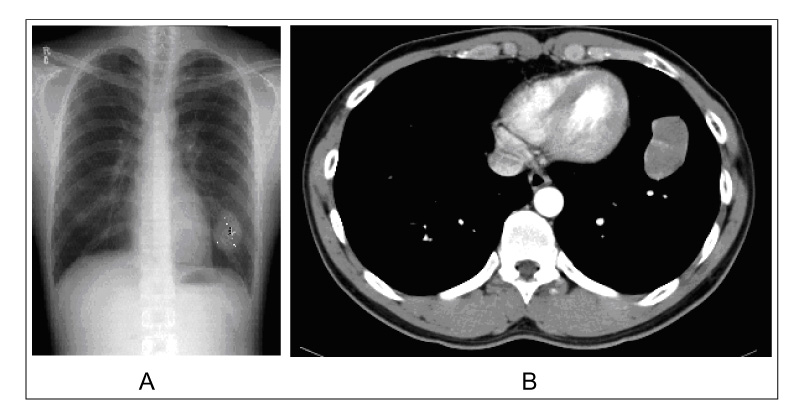
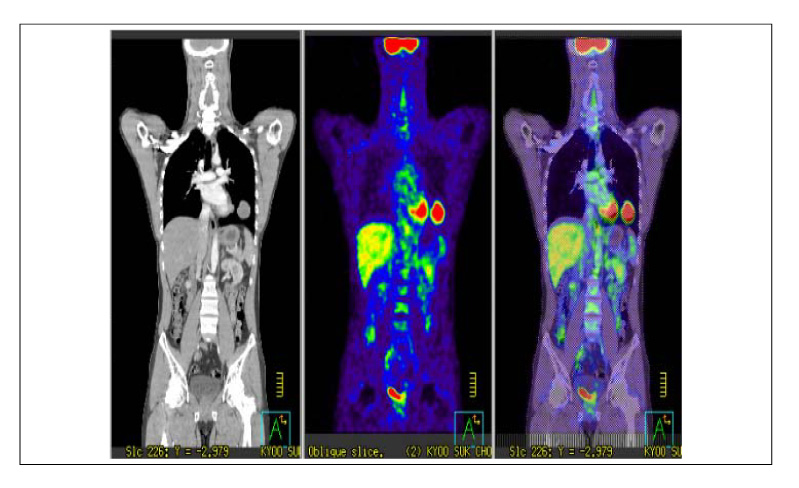
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFPS) is a locally aggressive skin tumor with a very low incidence in the general population. This tumor has a remarkable tendency to recur, However, a metastasis is rare. We report a case of DFPS with a pulmonary metastasis in 28-year-old man. The pulmonary metastasis developed 5 years after a complete resection of the primary skin tumor. We reviewed the clinical manifestations and treatment of DFPS, and highlight the need for a long-term follow-up examination for metastases after a wide excision of these lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Enzinger FM, Weiss SW. Chapter 14. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Fibrohistiocytic tumors of intermediate malignancy. Soft tissue tumors. 1995. 3rd ed. St Louis: Mosby;3235–3249.2. Barnes L, Coleman JA, Johnson JT. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol. 1984. 110:398–404.3. Kim SS, Kim JR, Lee YH, Han DS, Kim DH, Lee HK, et al. A case of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with pulmonary metastasis. Dongkooknonjib. 1993. 12:301–312.4. Kim WH, Park CK, Kim DG, Jung HW. Brain metastasis from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006. 39:148–151.5. Connelly JH, Evans HL. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a clinicopathologic review with emphasis on fibrosarcomatous areas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992. 16:921–925.6. Taylor HB, Helwig EB. Dermatofibrosarcoma probuernas: a study of 115 cases. Cancer. 1962. 15:717–725.7. Mendenhall WM, Zlotecki RA, Scarborough MT. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Cancer. 2004. 101:2503–2508.8. Klijanieko J, Caillaud JM, Lagacé R. Fine-needle aspiration of primary and recurrent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Diagn Cytopathol. 2004. 30:261–265.9. Chang CK, Jacobs IA, Salti GI. Outcomes of surgery for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004. 30:341–345.10. Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, Katz SC, Hawkins WG, Woodruff JM, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a clinicopathologicanalysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer. 2000. 88:2711–2720.11. Suit H, Spiro I, Mankin HJ, Efird J, Rosenberg AE. Radiation in management of patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Clin Oncol. 1996. 14:2365–2369.12. McPeak CJ, Cruz T, Nicastri AD. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: an analysis of 86 cases: five with metastases. Ann Surg. 1967. 166:803–816.13. Zorlu F, Yildiz F, Ertoy D, Atahan IL, Erden E. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans metastasizing to cavernous sinuses and lungs: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2001. 31:557–561.14. Turgut AT, Kosar U, Ergeneci A, Cakmak H. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans metastatic to lung without local recurrence. Tani Girisim Radyol. 2003. 9:195–198.15. Mizutani K, Tamada Y, Hara K, Tsuzuki T, Saeki H, Tamaki K, et al. Imatinib mesylate inhibits the growth of metastatic lung lesions in a patient with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Br J Dermatol. 2004. 151:235–237.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
- A Case of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Treated with Mohs Micrographic Surgery and Purse - String Suture Repair
- Comments to “Pigmented Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Presenting as a Faint Blue Macule in a Middle-aged Korean Womanâ€
- A Case of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans as a Subcutaneous Nodule without Surface Change
- A Case of Fibrosarcomatous Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans