J Korean Endocr Soc.
2008 Dec;23(6):438-443. 10.3803/jkes.2008.23.6.438.
A Case of Painful Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Successfully Treated with Total Thyroidectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam University Hwasun Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1965998
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.6.438
Abstract
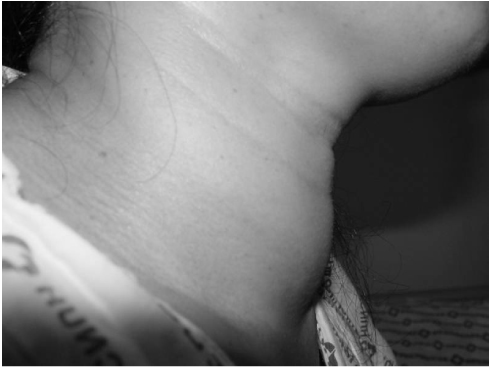
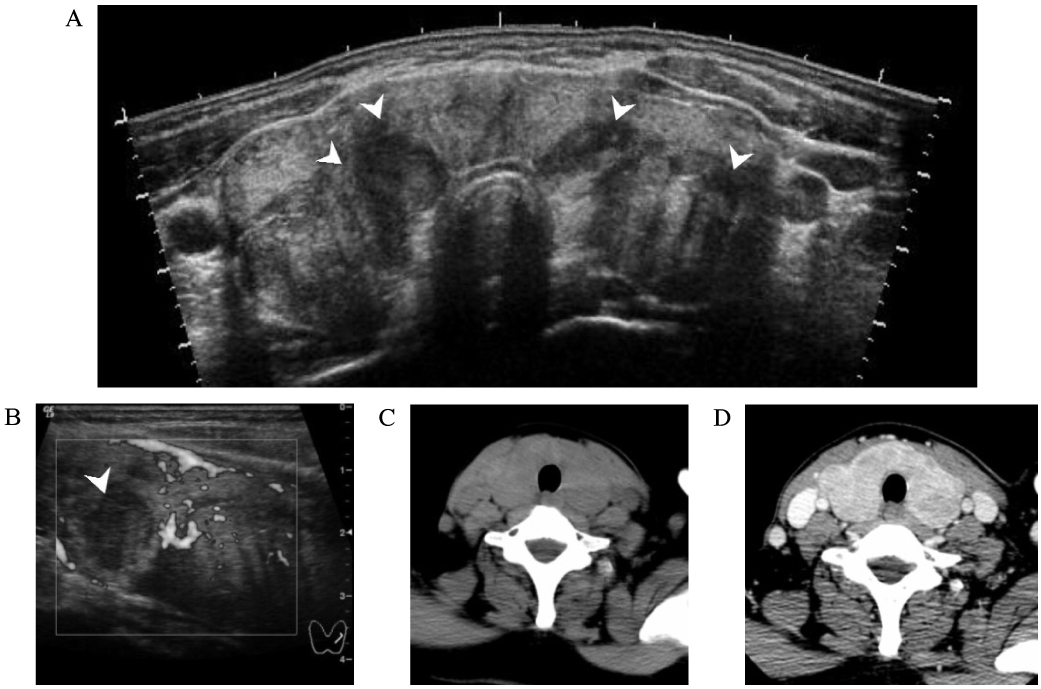
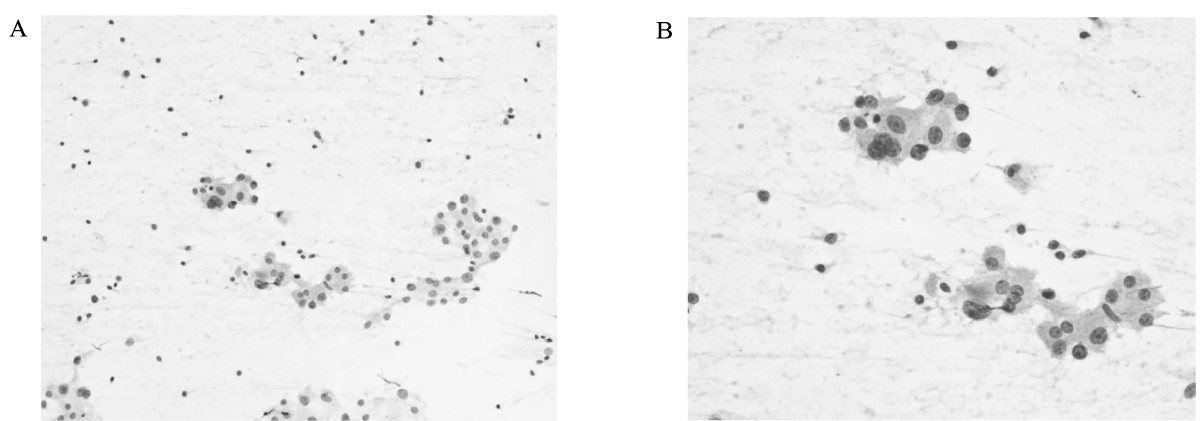
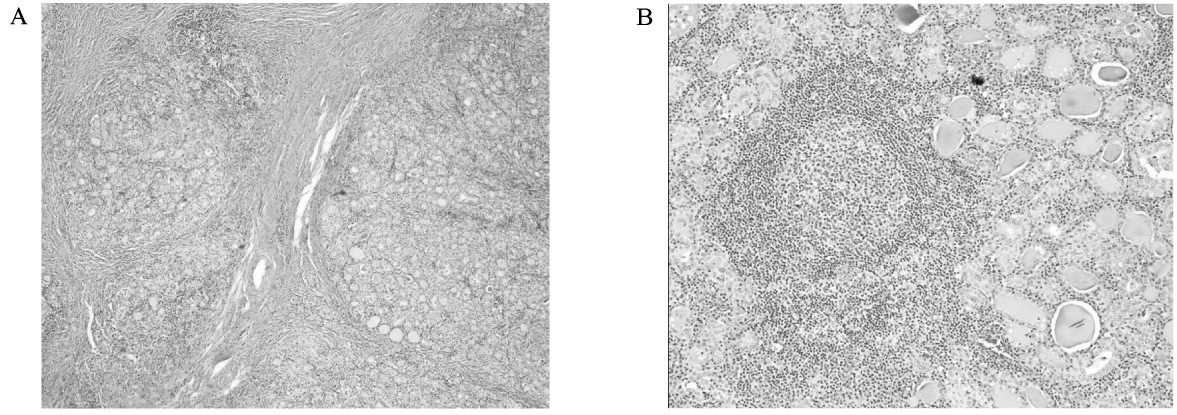
- Painful Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) is a subtype of HT characterized by thyroid pain with overt elevation in inflammatory markers and thyroid autoantibodies. The differential diagnosis of painful HT with subacute granulomatous thyroiditis is often difficult because initial clinical findings are very similar. Findings that favor the diagnosis of painful HT include preceding history of chronic goiter or autoimmune thyroid diseases, a high titer of thyroid autoantibodies, and repeated painful attacks even with chronic glucocorticoid therapy. Surgery is often needed to relieve the thyroid pain.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Case of Painful Hashimoto Thyroiditis that Mimicked Subacute Thyroiditis
Hye Mi Seo, Miyeon Kim, Jaeseok Bae, Jo-Heon Kim, Jeong Won Lee, Sang Ah Lee, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee
Chonnam Med J. 2012;48(1):69-72. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2012.48.1.69.Clinical Features of Patients Who Undergo Thyroidectomy with and without Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Mi-Jin Lee M.D., Yang-Soo Lim M.D.
Korean J Endocr Surg. 2011;11(4):242-247. doi: 10.16956/kjes.2011.11.4.242.
Reference
-
1. Dayan CM, Daniels GH. Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:99–107.2. Pearce EN, Farwell AP, Braverman LE. Thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:2646–2655.3. Meier DA, Nagle CE. Differential diagnosis of a tender goiter. J Nucl Med. 1996. 37:1745–1747.4. Doniach D, Hudson RV, Roitt IM. Human auto-immune thyroiditis: clinical studies. Br Med J. 1960. 1:365–373.5. Ishihara T, Mori T, Waseda N, Ikekubo K, Akamizu T, Imura H. Pathological characteristics of acute exacerbation of Hashimoto's thyroiditis--serial changes in a patient with repeated episodes. Endocrinol Jpn. 1986. 33:701–712.6. Zimmerman RS, Brennan MD, McConahey WM, Goellner JR, Gharib H. Hashimoto's thyroiditis. An uncommon cause of painful thyroid unresponsive to corticosteroid therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1986. 104:355–357.7. Ishihara T, Mori T, Waseda N, Ikekubo K, Akamizu T, Imura H. Histological, clinical and laboratory findings of acute exacerbation of Hashimoto's thyroiditis-comparison with those of subacute granulomatous thyroiditis. Endocrinol Jpn. 1987. 34:831–841.8. Leung AK, Hegde K. Hashimoto's thyroiditis simulating De Quervain's thyroiditis. J Adolesc Health Care. 1988. 9:434–435.9. Shigemasa C, Ueta Y, Mitani Y, Taniguchi S, Urabe K, Tanaka T, Yoshida A, Mashiba H. Chronic thyroiditis with painful tender thyroid enlargement and transient thyrotoxicosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. 70:385–390.10. Gourgiotis L, Al-Zubaidi N, Skarulis MC, Papanicolaou DA, Libutti SK, Alexander HR Jr, Merino MJ, Sarlis NJ. Successful outcome after surgical management in two cases of the "painful variant" of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Endocr Pract. 2002. 8:259–265.11. Kon YC, DeGroot LJ. Painful Hashimoto's thyroiditis as an indication for thyroidectomy: clinical characteristics and outcome in seven patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:2667–2672.12. Ohye H, Fukata S, Kubota S, Sasaki I, Takamura Y, Matsuzuka F, Amino N, Kuma K, Miyauchi A, Kakudo K. Successful treatment for recurrent painful Hashimoto's thyroiditis by total thyroidectomy. Thyroid. 2005. 15:340–345.13. Kasagi K. Painful Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Intern Med. 2006. 45:351–352.14. Thomas CG Jr, Rutledge RG. Surgical intervention in chronic (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis. Ann Surg. 1981. 193:769–776.15. Rotondi M, Chiovato L, Romagnani S, Serio M, Romagnani P. Role of chemokines in endocrine autoimmune diseases. Endocr Rev. 2007. 28:492–520.16. Schafers M, Sorkin L. Effect of cytokines on neuronal excitability. Neurosci Lett. 2008. 437:188–193.17. Nishihara E, Ohye H, Amino N, Takata K, Arishima T, Kudo T, Ito M, Kubota S, Fukata S, Miyauchi A. Clinical characteristics of 852 patients with subacute thyroiditis before treatment. Intern Med. 2008. 47:725–729.18. Yeh HC, Futterweit W, Gilbert P. Micronodulation: ultrasonographic sign of Hashimoto thyroiditis. J Ultrasound Med. 1996. 15:813–819.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Patients Who Undergo Thyroidectomy with and without Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Ultrasonographic Findings of Papillary Thyroid Cancer with or without Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- A case of Hashimoto's thyroiditis coexisting with thyroid papillary and follicular carcinoma
- Malignant Lymphoma Associated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Characteristics of Hypoparathyroidism after Total Thyroidectomy with or without Hashimoto Thyroiditis