Prevalence of Diabetes and Prediabetes according to Fasting Plasma Glucose and HbA1c
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bycha@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Mitochondrial Research Group, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 9Division of Health and Nutrition Survey, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1965982
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.349
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Due to the inconvenience of performing oral glucose tolerance tests and day to day variability in glucose level, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been recommended by the American Diabetes Association as a method to diagnose diabetes. In addition, the Korean Diabetes Association has also recommended the use of HbA1c as a diagnostic test for diabetes. In this study, we evaluated the prevalence of diabetes according to fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level only or the combination of FPG and HbA1c tests.
METHODS
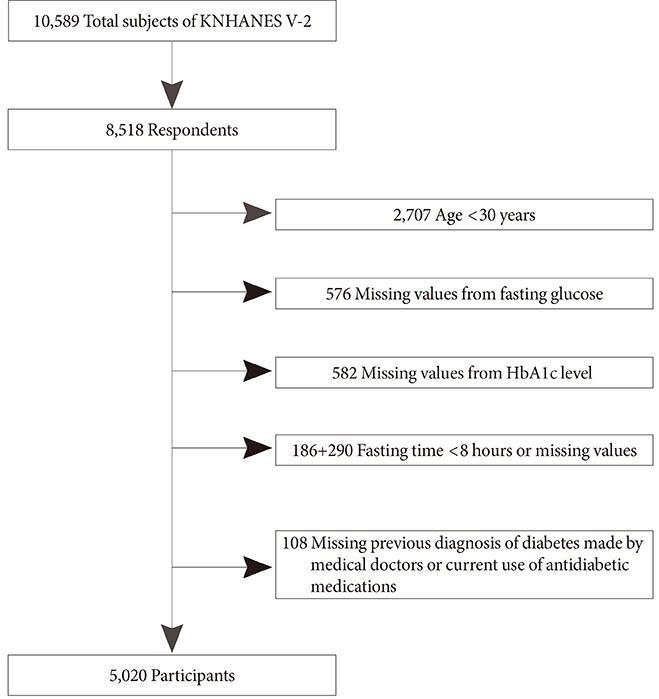
Data from the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) were analyzed. Among 5,811 subjects aged 30 years or older, 5,020 were selected after excluding the data of fasting time <8 hours, missing values from fasting glucose or HbA1c level, previous diagnosis of diabetes made by physicians, or current use of antidiabetic medications. Diabetes was defined as FPG > or =126 mg/dL, previous diagnosis of diabetes made by a medical doctor, current use of antidiabetic medications, and/or HbA1c > or =6.5%. Prediabetes was defined as FPG of 100 to 125 mg/dL and/or HbA1c of 5.7% to 6.4%.
RESULTS
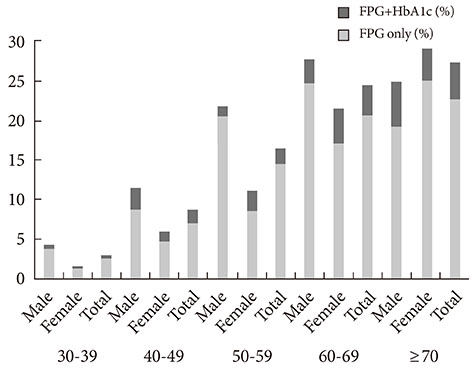
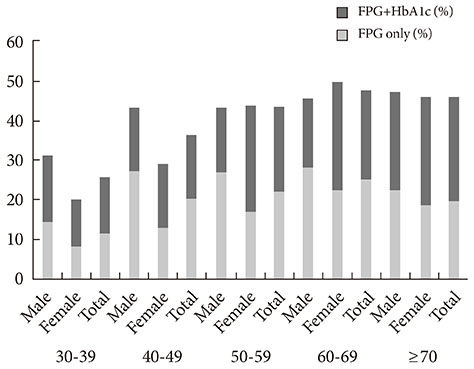
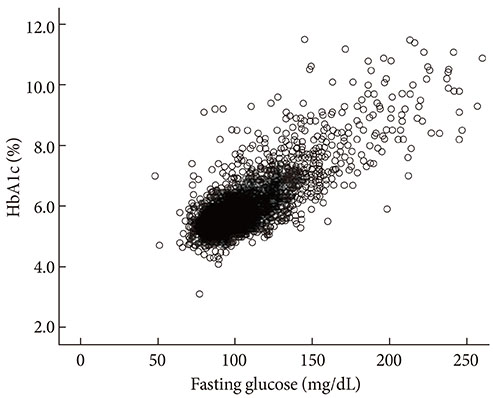
When we used FPG only, the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes were 10.5% (men, 12.6%; women, 8.5%) and 19.3% (men, 23.8%; women, 14.9%), respectively. When HbA1c was included as a diagnostic test, the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes increased to 12.4% (men, 14.5%; women, 10.4%) and 38.3% (men, 41%; women, 35.7%), respectively. Participants with HbA1c > or =6.5% and fasting glucose level <126 mg/dL were older and had lower estimated glomerular filtration rate.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that using fasting glucose level only may result in an underestimation of diabetes and prediabetes. HbA1c is an acceptable complementary diagnostic test for diabetes in Korean patients. However, national standardization is needed to order to use HbA1c as a diagnostic method of diabetes and prediabetes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 13 articles
-
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun Young Kim, Sung Rae Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, Ji-Oh Mok, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):1-10. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0254.The Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Measured by Controlled Attenuation Parameter
Young Eun Chon, Kwang Joon Kim, Kyu Sik Jung, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Jae Bock Chung, Kyeong Hye Park, Ji Cheol Bae, Kwang-Hyub Han
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):885-892. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.885.Change in Corneal Biomechanical Parameters in Diabetes Mellitus
Yeon Ggoch Park, Jin Young Rhew, Kyu Ryong Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(4):567-572. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.4.567.Changes in Indicators after Assessment of Diabetes Mellitus Adequacy Evaluation: Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service Data 2010-2015
Hyun-Soo Kang, Min-Taek Lim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Kyong-Do Han, Keun-Mi Lee, Seung-Pil Jung
Korean J Health Promot. 2020;20(4):175-181. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2020.20.4.175.Effects of Lobeglitazone, a Novel Thiazolidinedione, on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus over 52 Weeks
Soo Lim, Kyoung Min Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Doo Man Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo, Choon Hee Chung, Kyung Soo Ko, Jeong Hyun Park, Yongsoo Park, Sang Jin Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Dong Seop Choi
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):377-385. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.377.Development and Validation of the Korean Diabetes Risk Score: A 10-Year National Cohort Study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Yong-ho Lee, Sun Ok Song, Jae-woo Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Kyung-hee Cho, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):402-414. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0014.Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):415-424. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0017.Past and Current Status of Adult Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Yong-ho Lee, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Dae-Jung Kim, Chang Hee Jung, Ki-Up Lee, Kyung-Soo Ko,
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):93-100. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.93.Discrepancies between Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Plasma Glucose for Diagnosing Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Youth and Young Adults
Jieun Lee, Young Ah Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):174-182. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0046.Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
Bo-Yeon Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):487-494. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0067.Need for Diabetes Prevention Study
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2015;16(3):161-167. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2015.16.2.161.Cause-of-death statistics in the Republic of Korea, 2014
Hyun-Young Shin, Ji-Youn Lee, Juhwa Song, Seokmin Lee, Junghun Lee, Byeongsun Lim, Heyran Kim, Sun Huh
J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59(3):221-232. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.3.221.Inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation by burdock root extract
Darye Lee, Choon Young Kim
J Nutr Health. 2016;49(4):233-240. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2016.49.4.233.
Reference
-
1. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.2. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1047–1053.3. Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Lin JK, Farzadfar F, Khang YH, Stevens GA, Rao M, Ali MK, Riley LM, Robinson CA, Ezzati M. Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Glucose). National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2.7 million participants. Lancet. 2011; 378:31–40.4. International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1327–1334.5. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:Suppl 1. S62–S69.6. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–436.7. Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:881–885.8. American Diabetes Association. Postprandial blood glucose. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:775–778.9. Bonora E, Calcaterra F, Lombardi S, Bonfante N, Formentini G, Bonadonna RC, Muggeo M. Plasma glucose levels throughout the day and HbA(1c) interrelationships in type 2 diabetes: implications for treatment and monitoring of metabolic control. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:2023–2029.10. Carson AP, Reynolds K, Fonseca VA, Muntner P. Comparison of A1C and fasting glucose criteria to diagnose diabetes among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:95–97.11. Oh JY, Lim S, Kim DJ, Kim NH, Kim DJ, Moon SD, Jang HC, Cho YM, Song KH, Ahn CW, Sung YA, Park JY, Shin C, Lee HK, Park KS. Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. A report on the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycemia in Korea: a pooled analysis of four community-based cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008; 80:463–468.12. Lee ET, Howard BV, Go O, Savage PJ, Fabsitz RR, Robbins DC, Welty TK. Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes in three American Indian populations. A comparison of the 1997 American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria and the 1985 World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: the Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:181–186.13. Rodriguez BL, Abbott RD, Fujimoto W, Waitzfelder B, Chen R, Masaki K, Schatz I, Petrovitch H, Ross W, Yano K, Blanchette PL, Curb JD. American Diabetes Association. World Health Organization. The American Diabetes Association and World Health Organization classifications for diabetes: their impact on diabetes prevalence and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in elderly Japanese-American men. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:951–955.14. Wahl PW, Savage PJ, Psaty BM, Orchard TJ, Robbins JA, Tracy RP. Diabetes in older adults: comparison of 1997 American Diabetes Association classification of diabetes mellitus with 1985 WHO classification. Lancet. 1998; 352:1012–1015.15. Ministry for Health Welfare and Family Affairs. The second year of the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2). updated 2013 Jul 18. Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.16. Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976; 16:31–41.17. Bennett CM, Guo M, Dharmage SC. HbA(1c) as a screening tool for detection of Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med. 2007; 24:333–343.18. Gregg EW, Geiss L, Zhang P, Zhuo X, Williamson DF, Albright AL. Implications of risk stratification for diabetes prevention: the case of hemoglobin A1c. Am J Prev Med. 2013; 44:4 Suppl 4. S375–S380.19. Herman WH, Ma Y, Uwaifo G, Haffner S, Kahn SE, Horton ES, Lachin JM, Montez MG, Brenneman T, Barrett-Connor E. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Differences in A1C by race and ethnicity among patients with impaired gluglucose tolerance in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:2453–2457.20. Ziemer DC, Kolm P, Weintraub WS, Vaccarino V, Rhee MK, Twombly JG, Narayan KM, Koch DD, Phillips LS. Glucose-independent, black-white differences in hemoglobin A1c levels: a cross-sectional analysis of 2 studies. Ann Intern Med. 2010; 152:770–777.21. Brown AF, Gregg EW, Stevens MR, Karter AJ, Weinberger M, Safford MM, Gary TL, Caputo DA, Waitzfelder B, Kim C, Beckles GL. Race, ethnicity, socioeconomic position, and quality of care for adults with diabetes enrolled in managed care: the Translating Research Into Action for Diabetes (TRIAD) study. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:2864–2870.22. Anand SS, Razak F, Vuksan V, Gerstein HC, Malmberg K, Yi Q, Teo KK, Yusuf S. Diagnostic strategies to detect glucose intolerance in a multiethnic population. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:290–296.23. Bunn HF, Haney DN, Kamin S, Gabbay KH, Gallop PM. The biosynthesis of human hemoglobin A1c. Slow glycosylation of hemoglobin in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1976; 57:1652–1659.24. Cohen RM, LeCaire TJ, Lindsell CJ, Smith EP, D'Alessio DJ. Relationship of prospective GHb to glycated serum proteins in incident diabetic retinopathy: implications of the glycation gap for mechanism of risk prediction. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:151–153.25. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998; 352:837–853.26. Cho NH, Kim TH, Woo SJ, Park KH, Lim S, Cho YM, Park KS, Jang HC, Choi SH. Optimal HbA1c cutoff for detecting diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. Epub 2013 Jan 25. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0452-3.27. Little RR, Rohlfing CL, Wiedmeyer HM, Myers GL, Sacks DB, Goldstein DE. NGSP Steering Committee. The national glycohemoglobin standardization program: a five-year progress report. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:1985–1992.28. Shima K, Endo J, Oimomi M, Oshima I, Omori Y, Katayama Y, Kanazawa Y, Kawai T, Kawamori R, Kanno T, Kiyose H, Nakashima K, Nagamine Y, Baba S, Hoshino T, Amino N. Interlaboratory difference in HbA1c measurement in Japan: a report of the committee on an interlaboratory standardization of HbA1c determination, the Japan Diabetes Society. J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 1994; 37:855–864.29. Arnqvist H, Wallensteen M, Jeppson JO. Standards for long-term measures of blood sugar are established. Lakartidningen. 1997; 94:4789–4790.30. Manley S, John WG, Marshall S. Introduction of IFCC reference method for calibration of HbA: implications for clinical care. Diabet Med. 2004; 21:673–676.31. Hanas R, John WG. International HbA1c Consensus Committee. 2013 update on the worldwide standardization of the HbA1c measurement. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:885–886.32. Lim NK, Park SH, Choi SJ, Lee KS, Park HY. A risk score for predicting the incidence of type 2 diabetes in a middle-aged Korean cohort: the Korean genome and epidemiology study. Circ J. 2012; 76:1904–1910.33. Choi SH, Kim TH, Lim S, Park KS, Jang HC, Cho NH. Hemoglobin A1c as a diagnostic tool for diabetes screening and new-onset diabetes prediction: a 6-year community-based prospective study. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:944–949.34. Bae JC, Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Park SE, Park CY, Oh KW, Park SW, Kim SW. Optimal range of HbA1c for the prediction of future diabetes: a 4-year longitudinal study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 93:255–259.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement and Treatment Goal of Postprandial Hyperglycemia
- Lifestyle-related predictors affecting prediabetes and diabetes in 20-30-year-old young Korean adults
- The Utility of HbA1c as a Diagnostic Criterion of Diabetes
- HbA1c Cutoff for Prediabetes and Diabetes Based on Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Obese Children and Adolescents
- Discrepancies between Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Plasma Glucose for Diagnosing Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Youth and Young Adults