Clin Endosc.
2015 Jul;48(4):340-344. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.340.
Single Cavernous Hemangioma of the Small Bowel Diagnosed by Using Capsule Endoscopy in a Child with Chronic Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. kskang@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 1964280
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.340
Abstract
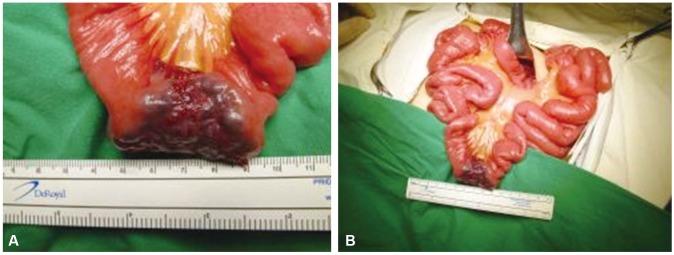
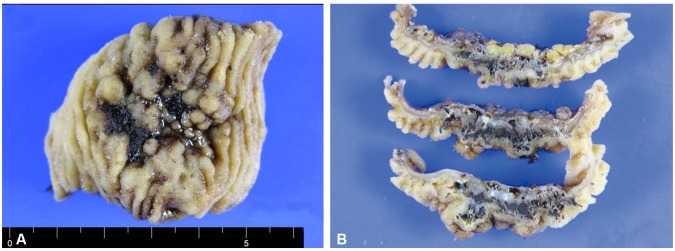
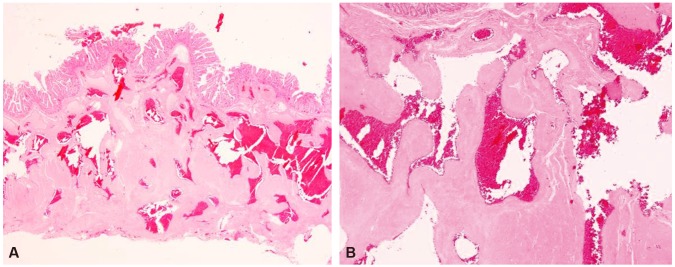
- Cavernous hemangiomas of the gastrointestinal tract are extremely rare. In particular, the diagnosis of small bowel hemangiomas is very difficult in children. A 13-year-old boy presented at the outpatient clinic with dizziness and fatigue. The patient was previously diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia at 3 years of age and had been treated with iron supplements continuously and pure red cell transfusion intermittently. Laboratory tests indicated that the patient currently had iron-deficiency anemia. There was no evidence of gross bleeding, such as hematemesis or bloody stool. Laboratory findings indicated no bleeding tendency. Gastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy results were negative. To obtain a definitive diagnosis, the patient underwent capsule endoscopy. A purplish stalked mass was found in the jejunum, and the mass was excised successfully. We report of a 13-year-old boy who presented with severe and recurrent iron-deficiency anemia caused by a cavernous hemangioma in the small bowel without symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Magnano A, Privitera A, Calogero G, Nanfito L, Basile G, Sanfilippo G. Solitary hemangioma of the small intestine: an unusual cause of bleeding diagnosed at capsule endoscopy. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40:e25–e27. PMID: 16226971.
Article2. Huber A, Abdel Samie A, Kychenko D, Theilmann L. A rare cause of recurrent iron-deficiency anemia: cavernous hemangioma of the small intestine. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2012; 21:343. PMID: 23256111.3. Handra-Luca A, Montgomery E. Vascular malformations and hemangiolymphangiomas of the gastrointestinal tract: morphological features and clinical impact. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011; 4:430–443. PMID: 21738815.4. Morgan DR, Mylankal K, el Barghouti N, Dixon MF. Small bowel haemangioma with local lymph node involvement presenting as intussusception. J Clin Pathol. 2000; 53:552–553. PMID: 10961181.
Article5. Willert RP, Chong AK. Multiple cavernous hemangiomas with iron deficiency anemia successfully treated with double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:765–767. PMID: 18155208.
Article6. Chen CH, Jones J, McGowan P. Profound iron deficiency anemia caused by a small-intestinal cavernous hemangioma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1392–1393. PMID: 19481664.
Article7. Triester SL, Leighton JA, Leontiadis GI, et al. A meta-analysis of the yield of capsule endoscopy compared to other diagnostic modalities in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:2407–2418. PMID: 16279893.
Article8. Sakaguchi M, Sue K, Etoh G, et al. A case of solitary cavernous hemangioma of the small intestine with recurrent clinical anemic attacks in childhood. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998; 27:342–343. PMID: 9740209.
Article9. Watari I, Oka S, Tanaka S, et al. Is occult obscure gastrointestinal bleeding a definite indication for capsule endoscopy? A retrospective analysis of diagnostic yield in patients with occult versus overt bleeding. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013; 2013:915463. PMID: 24324488.
Article10. Hartmann D, Schmidt H, Bolz G, et al. A prospective two-center study comparing wireless capsule endoscopy with intraoperative enteroscopy in patients with obscure GI bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:826–832. PMID: 15933683.
Article11. Park J. Large cavernous hemangioma in the jejunum of a 2-year-old boy treated by laparoscopy-assisted resection. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2012; 18:24–29.
Article12. Raju GS, Gerson L, Das A, Lewis B. American Gastroenterological Association. American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute technical review on obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1697–1717. PMID: 17983812.
Article13. Goddard AF, James MW, McIntyre AS, Scott BB. British Society of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for the management of iron deficiency anaemia. Gut. 2011; 60:1309–1316. PMID: 21561874.
Article14. Pera M, Marquez L, Dedeu JM, et al. Solitary cavernous hemangioma of the small intestine as the cause of long-standing iron deficiency anemia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:2288–2290. PMID: 22875598.
Article15. Kye BH, Kim SH, Lee JI, et al. Hemorrhage from a jejunal polypoid hemangioma: single incisional laparoscopic approach. J Korean Surg Soc. 2011; 80:362–366. PMID: 22066061.
Article16. Liu W, Xu C, Zhong J. The diagnostic value of double-balloon enteroscopy in children with small bowel disease: report of 31 cases. Can J Gastroenterol. 2009; 23:635–638. PMID: 19816629.
Article17. Oikawa-Kawamoto M, Sogo T, Yamaguchi T, et al. Safety and utility of capsule endoscopy for infants and young children. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:8342–8348. PMID: 24363526.
Article18. Bar-Meir S, Eliakim R, Nadler M, et al. Second capsule endoscopy for patients with severe iron deficiency anemia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:711–713. PMID: 15557946.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Refractory Iron Deficiency Anemia as a Manifestation of Cavernous Hemangioma of the Small Intestine
- A Case of Capillary Hemangioma in the Jejunum Detected by Single Balloon Enteroscopy in a Patient with Anemia
- A Case of Small Bowel Polyp Bleeding Diagnosed by Capsule Endoscopy
- Meckel's Diverticulum Diagnosed in a Child with Suspected Small Bowel Crohn's Disease
- Laparoscopy-assisted Surgical Removal of a Retained Wireless Capsule Endoscopy: A case report