J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 Aug;73(2):100-104. 10.3348/jksr.2015.73.2.100.
Inflammatory Pseudotumor in the Liver and Right Omentum Caused by Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. nosmokeman@naver.com
- KMID: 1964259
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.2.100
Abstract
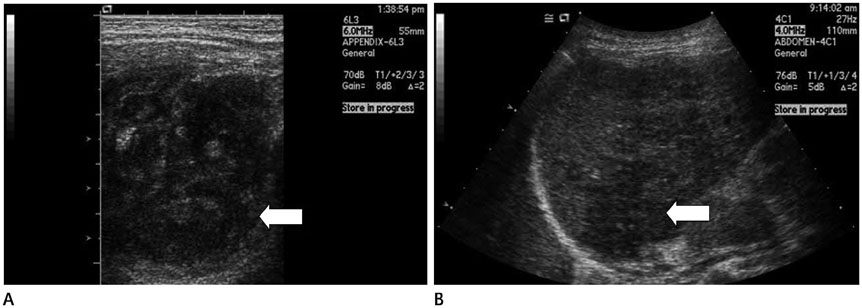
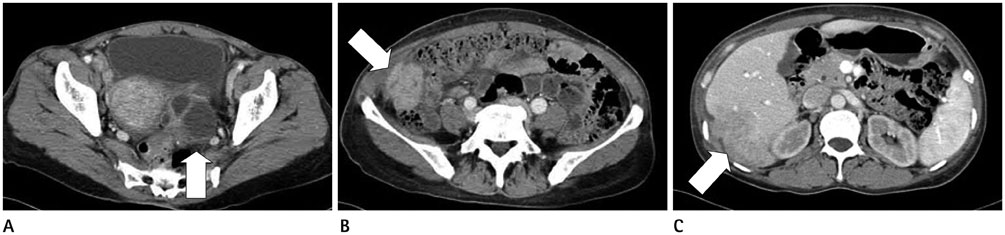
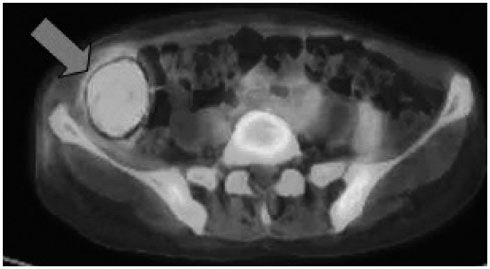
- Inflammatory pseudotumor can develop in any part of the human body. It is one of the most important tumor-mimicking lesions that require differential diagnosis. There are various causes of inflammatory pseudotumor, one of which is infection and its resultant inflammation. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) often causes perihepatitis, which is called Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome. In Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, bacteria spread along the right paracolic gutter, causing inflammation of the right upper quadrant peritoneal surfaces and the right lobe of the liver. We experienced a case of PID with accompanying inflammatory pseudotumor in the liver and the right omentum. This case identically correlates with the known intraperitoneal spreading pathway involved in Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, and hence, we present this case report.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Narla LD, Newman B, Spottswood SS, Narla S, Kolli R. Inflammatory pseudotumor. Radiographics. 2003; 23:719–729.2. Patnana M, Sevrukov AB, Elsayes KM, Viswanathan C, Lubner M, Menias CO. Inflammatory pseudotumor: the great mimicker. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:W217–W227.3. Sanders BM, West KW, Gingalewski C, Engum S, Davis M, Grosfeld JL. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the alimentary tract: clinical and surgical experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 36:169–173.4. Dehner LP. The enigmatic inflammatory pseudotumours: the current state of our understanding, or misunderstanding. J Pathol. 2000; 192:277–279.5. Wood C, Nickoloff BJ, Todes-Taylor NR. Pseudotumor resulting from atypical mycobacterial infection: a "histoid" variety of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985; 83:524–527.6. Lévy S, Sauvanet A, Diebold MD, Marcus C, Da Costa N, Thiéfin G. Spontaneous regression of an inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver presenting as an obstructing malignant biliary tumor. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:371–374.7. Rezvani M, Shaaban AM. Fallopian tube disease in the nonpregnant patient. Radiographics. 2011; 31:527–548.8. Lee JW, Kim S, Kwack SW, Kim CW, Moon TY, Lee SH, et al. Hepatic capsular and subcapsular pathologic conditions: demonstration with CT and MR imaging. Radiographics. 2008; 28:1307–1323.9. Sam JW, Jacobs JE, Birnbaum BA. Spectrum of CT findings in acute pyogenic pelvic inflammatory disease. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1327–1334.10. Berek JS. Berek & Novak's Gynecology. 14th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2007. p. 549–551.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An IgG4-Related Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Greater Omentum
- Inflammatory Pseud0tumor of the Liver: A case report
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Liver: A case report
- A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor Cerebri and Nasal Septum
- Spontaneous Regression of Inflarmmatory Pseudotumor of the Liver by Conservative Therapy