J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Mar;80(3):172-181. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.3.172.
Expression of c-erbB2 and p53 in Curatively Resected Gastric Cancer: Correlation with Clinicopathologic Features and Prognosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. hmjeon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1963580
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.80.3.172
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the correlation between expression of c-erbB-2 and p53 proteins and clinicopathologic features of gastric cancer to reveal prognostic factors.
METHODS
125 patient records under going curative resection for gastric carcinoma at our institution from January 2000 to June 2003 were collected. Surgical specimens embedded in paraffin block were evaluated for p53 and c-erbB-2 protein as detected by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
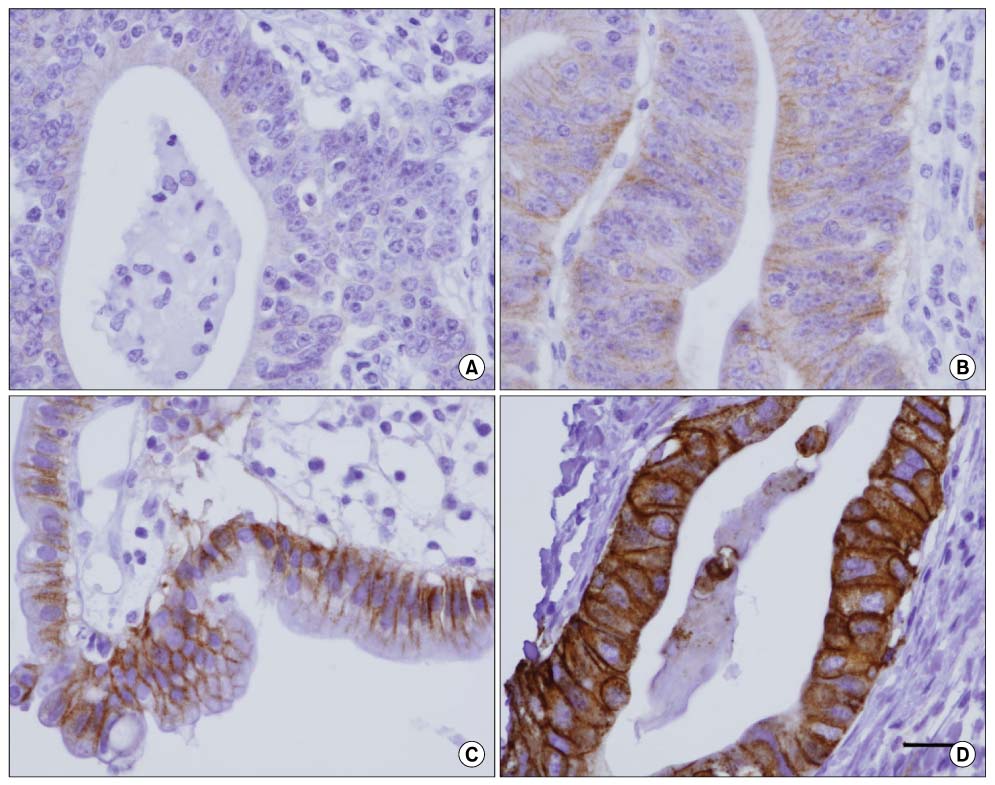
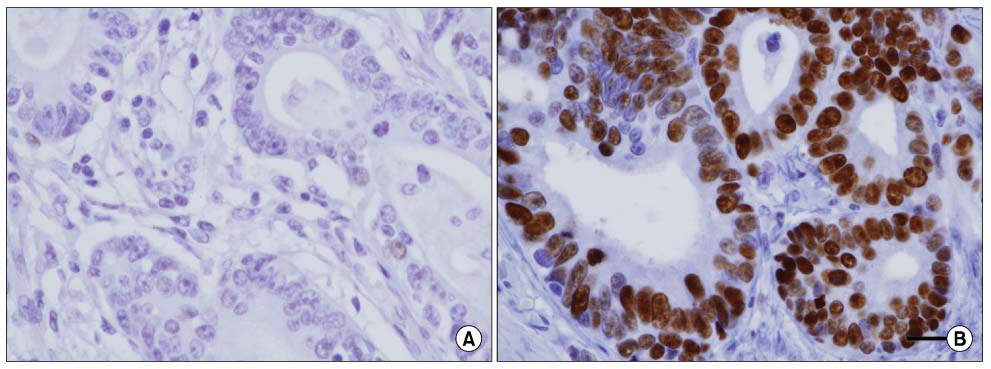
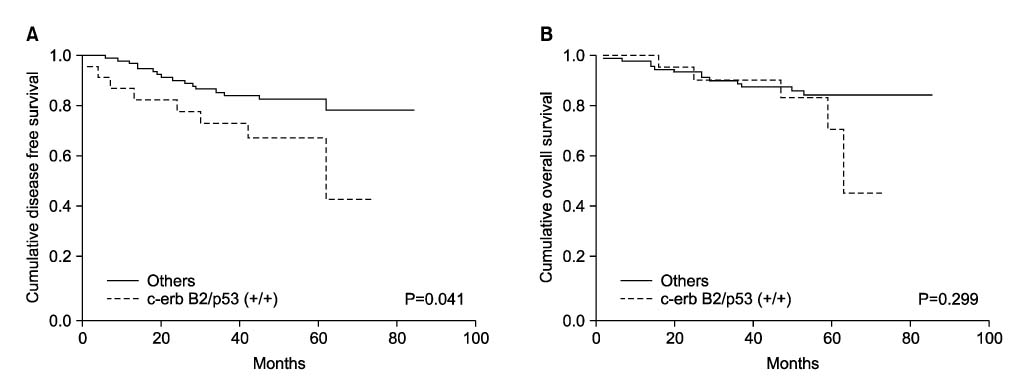
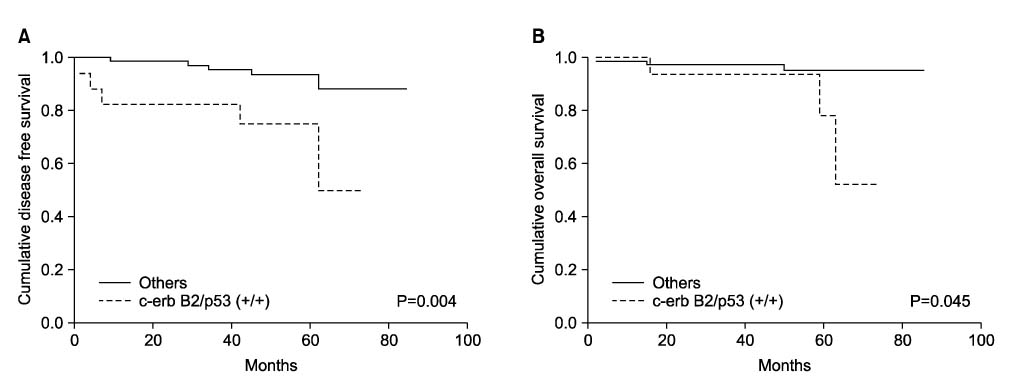
Samples from 30 cases (24.0%) of 125 patients with gastric adenocarcinomas demonstrated positive staining for c-erbB-2 and 72 patients (57.6%) showed positive nuclear staining for p53 protein. c-erbB-2 stained tumors were significantly associated with the depth of tumor invasion (P=0.022), lymph node metastasis (P=0.004) and lymphatic invasion (P=0.019). In a subgroup of patients with gastric carcinoma not exposed to serosa (n=91), expression of both c-erbB-2 and p53 significantly related with poor disease-free survival (OR=5.107) and survival (OR=4.449) in multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
When patients with gastric adenocarcinoma showed expression of c-erbB-2 with p53, they were associated with aggressive pathologic features. In the subgroup of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma that did not involve serosa, expression of c-erbB-2 combined with p53 could become a predictive factor for recurrence and survival in multivariate analysis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of eighteen major cancers in 1985. Int J Cancer. 1993. 54:594–606.2. Schechter AL, Stern DF, Vaidyanathan L, Decker SJ, Drebin JA, Greene MI, et al. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984. 312:513–516.3. Hernandez-Boussard T, Rodriguez-Tome P, Montesano R, Hainaut P. International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC p53 mutation database: a relational database to compile and analyze p53 mutations in human tumors and cell lines. Hum Mutat. 1999. 14:1–8.4. Matozaki T, Sakamoto C, Suzuki T, Matsuda K, Uchida T, Nakano O, et al. p53 gene mutations in human gastric cancer: wild-type p53 but not mutant p53 suppresses growth of human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992. 52:4335–4341.5. Hilton DA, West KP. c-erbB-2 oncogene product expression and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1992. 45:454–456.6. Ichiyoshi Y, Oiwa H, Tomisaki S, Sakaguchi Y, Ohno S, Maehara Y, et al. Overexpression of p53 is associated with growth pattern and prognosis in advanced gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997. 44:546–553.7. Ostrowski JL, Sawan A, Henry L, Wright C, Henry JA, Hennessy C, et al. p53 expression in human breast cancer related to survival and prognostic factors: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1991. 164:75–81.8. Starzynska T, Bromley M, Ghosh A, Stern PL. Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in gastric and colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1992. 66:558–562.9. Yonemura Y, Ninomiya I, Ohoyama S, Kimura H, Yamaguchi A, Fushida S, et al. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in gastric carcinoma. Immunoreactivity for c-erbB-2 protein is an independent indicator of poor short-term prognosis in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1991. 67:2914–2918.10. Yonemura Y, Ninomiya I, Yamaguchi A, Fushida S, Kimura H, Ohoyama S, et al. Evaluation of immunoreactivity for erbB-2 protein as a marker of poor short term prognosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1991. 51:1034–1038.11. Becker KF, Keller G, Hoefler H. The use of molecular biology in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Surg Oncol. 2000. 9:5–11.12. Tamura G. Genetic and epigenetic alterations of tumor suppressor and tumor-related genes in gastric cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2002. 17:323–329.13. Tamura G. Alterations of tumor suppressor and tumor-related genes in the development and progression of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:192–198.14. Christensen JG, Schreck RE, Chan E, Wang X, Yang C, Liu L, et al. High levels of HER-2 expression alter the ability of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family tyrosine kinase inhibitors to inhibit EGFR phosphorylation in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. 7:4230–4238.15. Danielsen AJ, Maihle NJ. Ligand-independent oncogenic transformation by the EGF receptor requires kinase domain catalytic activity. Exp Cell Res. 2002. 275:9–16.16. Allgayer H, Babic R, Gruetzner KU, Tarabichi A, Schildberg FW, Heiss MM. c-erbB-2 is of independent prognostic relevance in gastric cancer and is associated with the expression of tumor-associated protease systems. J Clin Oncol. 2000. 18:2201–2209.17. Jain S, Filipe MI, Gullick WJ, Linehan J, Morris RW. c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene expression and its relationship to survival in gastric carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study on archival material. Int J Cancer. 1991. 48:668–671.18. Tateishi M, Toda T, Minamisono Y, Nagasaki S. Clinicopathological significance of c-erbB-2 protein expression in human gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1992. 49:209–212.19. Hollstein M, Rice K, Greenblatt MS, Soussi T, Fuchs R, Sorlie T, et al. Database of p53 gene somatic mutations in human tumors and cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. 22:3551–3555.20. Scott N, Sagar P, Stewart J, Blair GE, Dixon MF, Quirke P. p53 in colorectal cancer: clinicopathological correlation and prognostic significance. Br J Cancer. 1991. 63:317–319.21. Ioachim E, Goussia A, Stefanou D, Agnantis NJ. Expression of p53 protein in gastric cancer: an immunohistochemical study with correlation to proliferative activity. Anticancer Res. 1997. 17:513–517.22. Chang K, Ding I, Kern FG, Willingham MC. Immunohistochemical analysis of p53 and HER-2/neu proteins in human tumors. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991. 39:1281–1287.23. Sasano H, Date F, Imatani A, Asaki S, Nagura H. Double immunostaining for c-erbB-2 and p53 in human stomach cancer cells. Hum Pathol. 1993. 24:584–589.24. Bouchet BP, de Fromentel CC, Puisieux A, Galmarini CM. p53 as a target for anti-cancer drug development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006. 58:190–207.25. Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Shilov A, Hultcrantz M, Pugacheva E, Chumakov P, et al. Restoration of the tumor suppressor function to mutant p53 by a low-molecular-weight compound. Nat Med. 2002. 8:282–288.26. Baxevanis CN, Sotiropoulou PA, Sotiriadou NN, Papamichail M. Immunobiology of HER-2/neu oncoprotein and its potential application in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004. 53:166–175.27. Ohtsu A. Chemotherapy for metastatic gastric cancer: past, present, and future. J Gastroenterol. 2008. 43:256–264.28. Nakajima T, Kinoshita T, Nashimoto A, Sairenji M, Yamaguchi T, Sakamoto J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of adjuvant uracil-tegafur versus surgery alone for serosa-negative, locally advanced gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2007. 94:1468–1476.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, c-erbB2, and p53 Protein Overexpression and Prognosis in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- Expression of p53, c-erbB2, bcl-2, Cathepsin D in Infiltrating Ductal Cancer of the Breast
- Expression of p53, c-erbB2, bcl-2, Cathepsin D in Infiltrating Ductal Cancer of the Breast
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and p53, c-erbB2, nm23 Protein Expression in Gastric Remnant Cancer
- Prognostic Significance of Immunohistochemical Expression of p53 and Retinoblastoma Gene Protein (pRB) in Curatively Resected Gastric Cancer