J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2015 Mar;17(1):49-53. 10.7461/jcen.2015.17.1.49.
Superficial Temporal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Treated with Manual Compression Alone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. cch0102@ynu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1963150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.1.49
Abstract
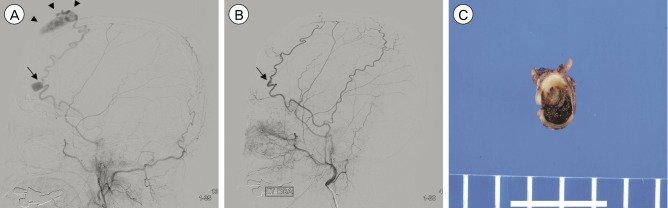
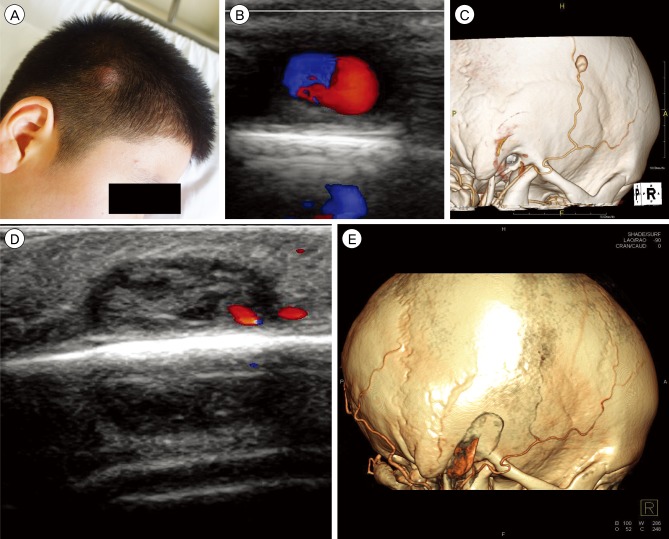
- Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the superficial temporal artery (STA) is an uncommon lesion and resection of the lesion is the treatment of choice. Three patients with traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the STA treated with only manual compression of the lesions were examined for this study. We report on an effective and safe minimally invasive technique for treatment of traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the STA.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ultrasound Guided Local Endovascular Coiling of an Iatrogenic Superficial Temporal Artery Pseudoaneurysm
Christina Huang Wright, James Wright, Anish Badjatiya, Sunil Manjila, Steven Reed, Robert Geertman
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2015;17(4):313-317. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2015.17.4.313.
Reference
-
1. Ahmad F, Turner SA, Torrie P, Gibson M. Iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysms-a review of current methods of diagnosis and treatment. Clin Radiol. 2008; 12. 63(12):1310–1316. PMID: 18996260.2. Conner WC 3rd, Rohrich RJ, Pollock RA. Traumatic aneurysms of the face and temple: a patient report and literature review, 1644 to 1998. Ann Plast Surg. 1998; 9. 41(3):321–326. PMID: 9746094.3. Cremone JC, Grosh JD. Traumatic aneurysms of the superficial temporal artery. J Trauma. 1980; 11. 20(11):986–988. PMID: 7431458.
Article4. Evans CC, Larson MJ, Eichhorn PJ, Taylor RS. Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the superficial temporal artery: two cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003; 11. 49(5 Suppl):S286–S288. PMID: 14576656.
Article5. Fox AJ, Viñuela F, Pelz DM, Peerless SJ, Ferguson GG, Drake CG, et al. Use of detachable balloons for proximal artery occlusion in the treatment of unclippable cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1987; 1. 66(1):40–46. PMID: 3783258.
Article6. Grasso RF, Quattrocchi CC, Crucitti P, Carboni G, Coppola R, Zobel BB. Superficial temporal artery pseudoaneurysm: a conservative approach in a critically ill patient. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007; Mar-Apr. 30(2):286–288. PMID: 16988876.
Article7. Han MH, Sung MW, Chang KH, Min YG, Han DH, Han MC. Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the intracavernous ICA presenting with massive epistaxis: imaging diagnosis and endovascular treatment. Laryngoscope. 1994; 3. 104(3 Pt 1):370–377. PMID: 8127196.8. Johnston KW, Rutherford RB, Tilson MD, Shah DM, Hollier L, Stanley JC. Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. Subcommittee on Reporting Standards for Arterial Aneurysms, Ad Hoc Committee on Reporting Standards, Society for Vascular Surgery and North American Chapter, International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery. J Vasc Surg. 1991; 3. 13(3):452–458. PMID: 1999868.9. Lee DH, Hur SH, Choi SJ, Jung SM, Ryu DS, Park MS, et al. A recurred carotid siphon pseudoaneurysm after detachable coil embolization successful endovascular management with detachable balloons. Interv Neuroradiol. 2002; 3. 8(1):61–65. PMID: 20594514.10. Mattens M, Hessmann M, Lesceu O, Rumbaut J. Traumatic false aneurysm of the superficial temporal artery. Acta Chir Belg. 1992; Jul-Aug. 92(4):201–203. PMID: 1414138.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Temporal Artery
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Temporal Artery due to Gardner Traction
- A Case Report of Posttraumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Temporal Artery
- Ultrasound Guided Local Endovascular Coiling of an Iatrogenic Superficial Temporal Artery Pseudoaneurysm
- A Case of Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Temporal Artery