J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2013 Dec;19(2):156-161. 10.13029/jkaps.2013.19.2.156.
Laparoscopic-Assisted Transanal Endorectal Pull-Through for Segmental Dilatation of Rectosigmoid Colon in a Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Graduate school of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Taegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Graduate school of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Taegu, Korea. kpnugs@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1961507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2013.19.2.156
Abstract
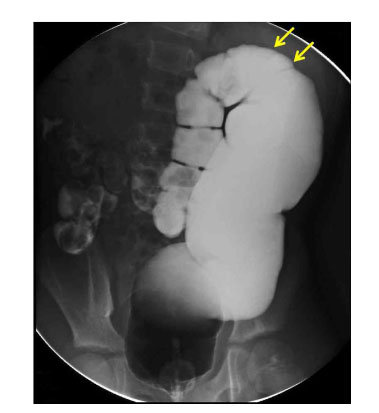
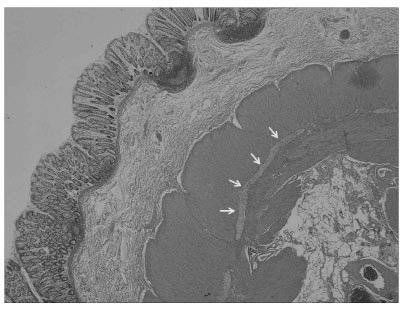
- Congenital segmental dilatation of the colon is a very rare entity of unknown etiology, characterized by a localized dilatation of a bowel segment of the colon of variable length and an abrupt transition between the normal and dilated intestine. It can affect any part of the colon, with the rectosigmoid colon being the most commonly affected site. The clinical and radiological features may resemble that of Hirschsprung disease, but differ in that the normal ganglion cells are found in the dilated and normal segment of the colon. We performed laparoscopic-assisted transanal endorectal pull-through for segmental dilatation of rectosigmoid colon in an 8-year-old boy with chronic constipation since the age of 5 months.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swenson O, Rathauser F. Segmental dilatation of the colon: a new entity. Am J Surg. 1959; 97:734–738.2. Helikson MA, Schapiro MB, Garfinkel DJ, Shermeta DW. Congenital segmental dilatation of the colon. J Pediatr Surg. 1982; 17:201–202.3. Mizote H, Oku H, Gu L, Hikita S, Tanaka Y, Kakegawa T. Congenital segmental dilatation of the colon. Kurume Med J. 1988; 35:89–93.4. AL-Salem AH, Grant C. Segmental dilatation of the colon. Report of a case and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990; 33:515–518.5. Sarin YK, Singh VP. Congenital segmental dilatation of colon. Indian Pediatr. 1995; 32:116–118.6. Ravasse P, Petit T, Cau D, Delmas P. Volvulus of the sigmoid colon as a complication of segmental dilatation of the colon. Report of two cases. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 6:375–377.7. Mathur P, Mogra N, Surana SS, Bordia S. Congenital segmental dilatation of the colon with anorectal malformation. J Pediatr Surg. 2004; 39:e18–e20.8. Kothari P, Gowrishankar , Rastogi A, Dipali R, Kulkarni B. Gowrishankar. Congenital segmental dilatation of colon with colonic atresia. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2005; 24:123–124.9. Alqahtani AR. Laparoscopic-assisted sigmoid resection for colonic ectasia in a neonate. J Pediatr Surg. 2010; 45:1714–1716.10. Mahadevaiah SA, Panjwani P, Kini U, Mohanty S, Das K. Segmental dilatation of sigmoid colon in a neonate: atypical presentation and histology. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:e1–e4.11. Irving IM, Lister J. Segmental dilatation of the ileum. J Pediatr Surg. 1977; 12:103–112.12. Mathé JC, Khairallah S, Phat Vuoung NP, Boccon-Gibod L, Rey A, Costil J. Segmental dilatation of the ileum in a neonate. Study of the myenteric plexus with a silver staining preparation (author's transl). Nouv Presse Med. 1982; 11:265–266.13. Georgeson KE, Robertson DJ. Laparoscopic-assisted approaches for the definitive surgery for Hirschsprung's disease. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2004; 13:256–262.14. Antao B, Roberts J. Laparoscopic-assisted transanal endorectal coloanal anastomosis for Hirschsprung's disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2005; 15:75–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Laparoscopic-Assisted Endorectal Pull-Through for Hirschsprung's Disease
- Laparoscopic Primary Endorectal Pull-through Procedure (Boley's) for Hirschsprung's Disease
- Treatment of a Total Obstructive Anastomosis Stricture Using a Transanal Laparoscopic Approach and Intraoperative Colonoscopic Balloon Dilatation
- Short-Term Outcomes of Transanal One-Stage Pull-Through for Hirschsprung's Disease
- Diffuse Cavernous Hemangioma of the Rectosigmoid Colon: a Case Report