J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Feb;40(1):43-47. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.43.
Eagle's syndrome: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ojyoung81@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1960972
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.43
Abstract
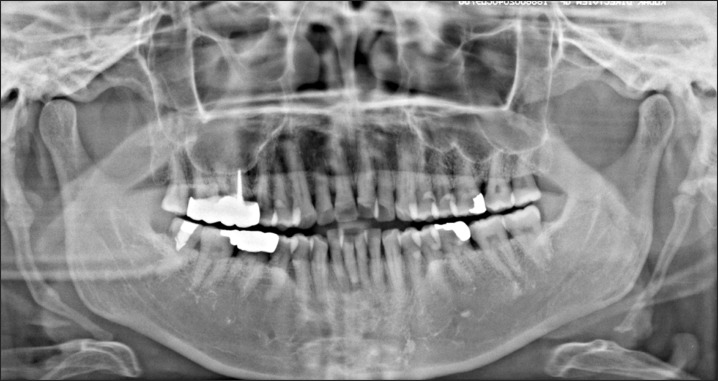
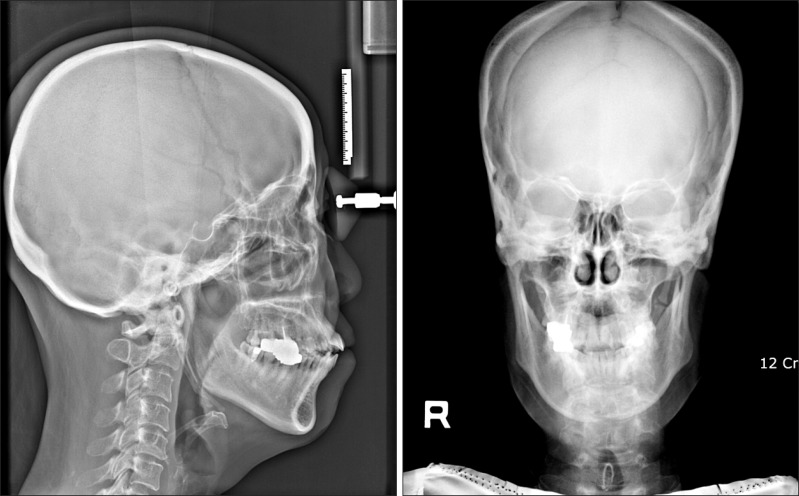
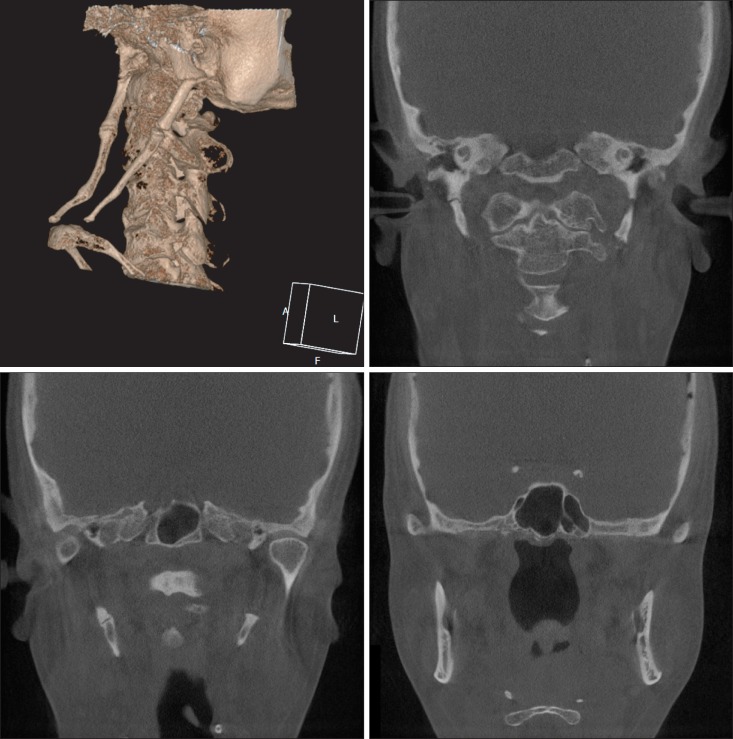
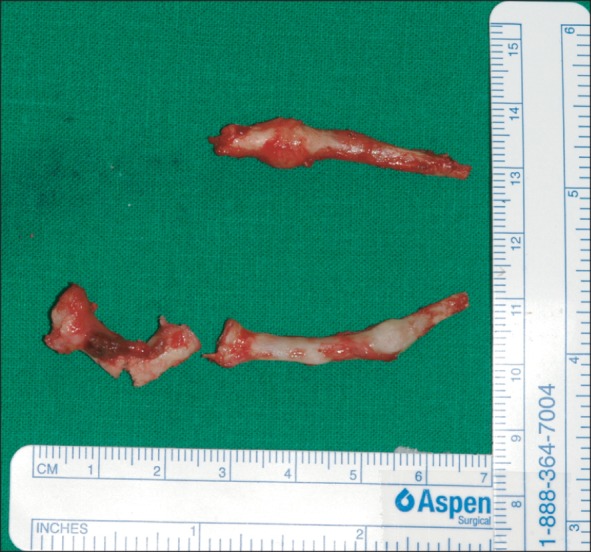
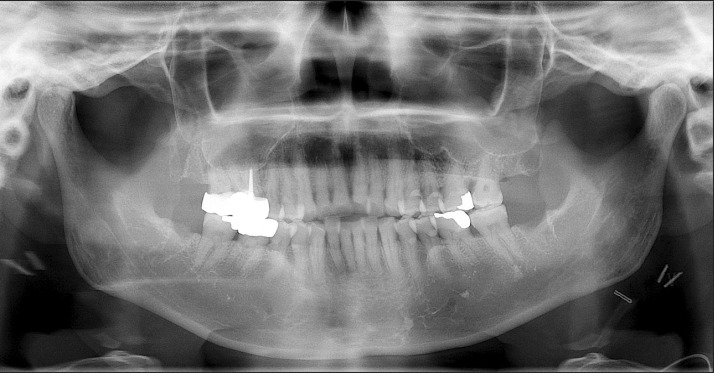
- Eagle's syndrome is a disease caused by an elongated styloid process or calcified stylohyoid ligament. Eagle defined the disorder in 1937 by describing clinical findings related to an elongated styloid process, which is one of the numerous causes of pain in the craniofacial and cervical region. The prevalence of individuals with this anatomic abnormality in the adult population is estimated to be 4% with 0.16% of these individuals reported to be symptomatic. Eagle's syndrome is usually characterized by neck, throat, or ear pain; pharyngeal foreign body sensation; dysphagia; pain upon head movement; and headache. The diagnosis of Eagle's syndrome must be made in association with data from the clinical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Patients with increased symptom severity require surgical excision of the styloid process, which can be performed through an intraoral or an extraoral approach. Here, we report a rare case of stylohyoid ligament bilaterally elongated to more than 60 mm in a 51-year-old female. We did a surgery by extraoral approach and patient's symptom was improved.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Nonsurgical treatment of stylohyoid (Eagle) syndrome: a case report
Arman Taheri, Shahram Firouzi-Marani, Masoud Khoshbin
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;40(5):246-249. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.5.246.
Reference
-
1. Eagle WW. Elongated styloid processes: report of two cases. Arch Otolaryngol. 1937; 25:584–587.
Article2. Dunn-Ryznyk LR, Kelly CW. Eagle syndrome: a rare cause of dysphagia and head and neck pain. JAAPA. 2010; 23:2831–32. 48PMID: 21229834.3. Yavuz H, Caylakli F, Erkan AN, Ozluoglu LN. Modified intraoral approach for removal of an elongated styloid process. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 40:86–90. PMID: 21303608.4. Colby CC, Del Gaudio JM. Stylohyoid complex syndrome: a new diagnostic classification. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 137:248–252. PMID: 21422308.5. Johnson GM, Rosdy NM, Horton SJ. Manual therapy assessment findings in patients diagnosed with Eagle's Syndrome: a case series. Man Ther. 2011; 16:199–202. PMID: 21030289.
Article6. Costantinides F, Vidoni G, Bodin C, Di Lenarda R. Eagle's syndrome: signs and symptoms. Cranio. 2013; 31:56–60. PMID: 23461263.
Article7. Ghosh LM, Dubey SP. The syndrome of elongated styloid process. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1999; 26:169–175. PMID: 10214896.
Article8. Valerio CS, Peyneau PD, de Sousa AC, Cardoso FO, de Oliveira DR, Taitson PF, et al. Stylohyoid syndrome: surgical approach. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:e138–e140. PMID: 22446450.9. Murtagh RD, Caracciolo JT, Fernandez G. CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1401–1402. PMID: 11498437.10. Steinmann EP. Styloid syndrome in absence of an elongated process. Acta Otolaryngol. 1968; 66:347–356. PMID: 5734501.
Article11. Camarda AJ, Deschamps C, Forest D. I. Stylohyoid chain ossification: a discussion of etiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989; 67:508–514. PMID: 2497419.
Article12. Leclerc JE. Eagle syndrome: teaching the intraoral surgical approach with a 30 degrees endoscope. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 37:727–729. PMID: 19128684.