J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2014 Mar;18(1):14-18. 10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.1.14.
Measurement of Normal Calcaneus in Korean Cadavers: A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. ortho1@hanmail.net
- 2Medical Department of 3821th Unit, Korea Army, Gangwon-do, Korea.
- KMID: 1958733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.1.14
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this report is to evaluate the measured values of normal Korean calcaneus by conduct of a cadaveric study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
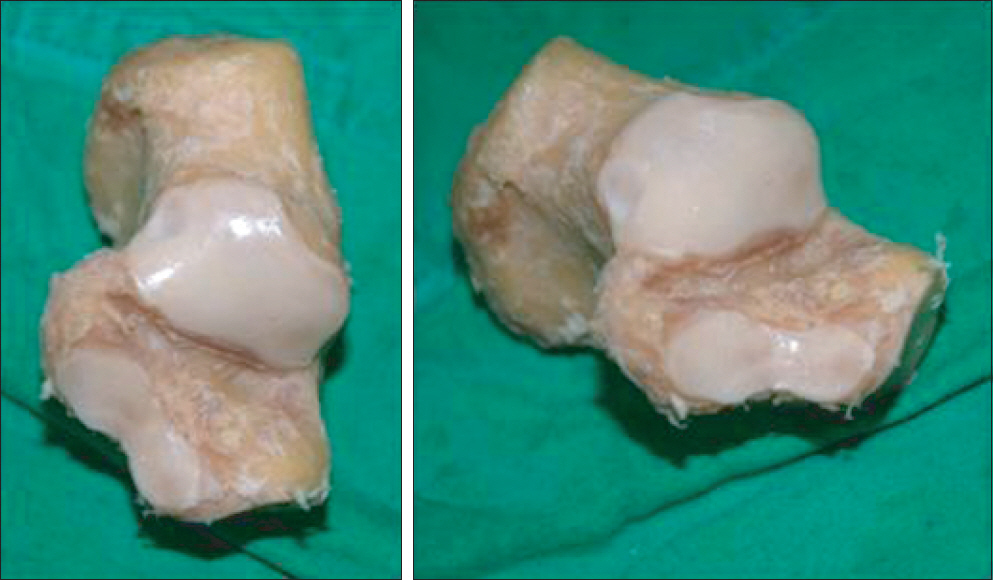
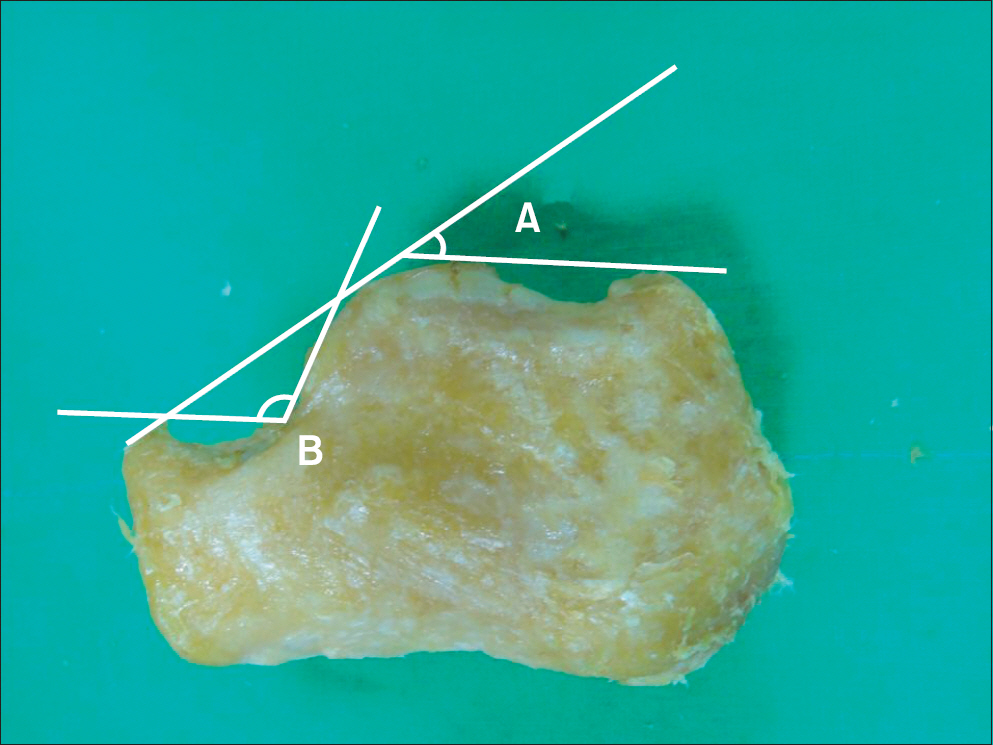
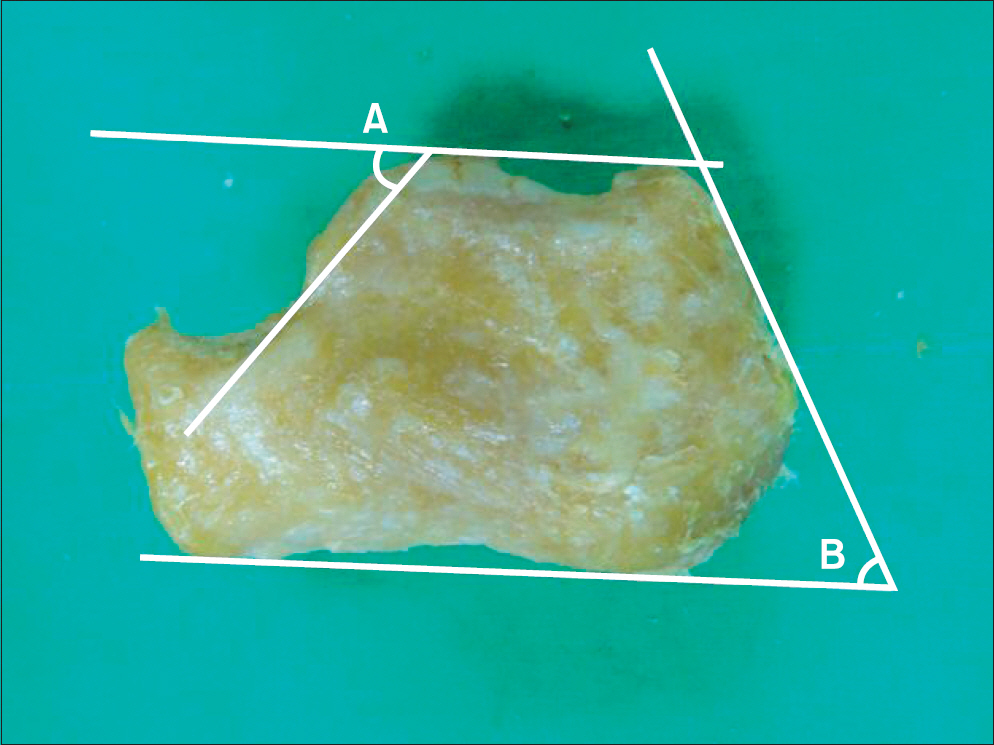
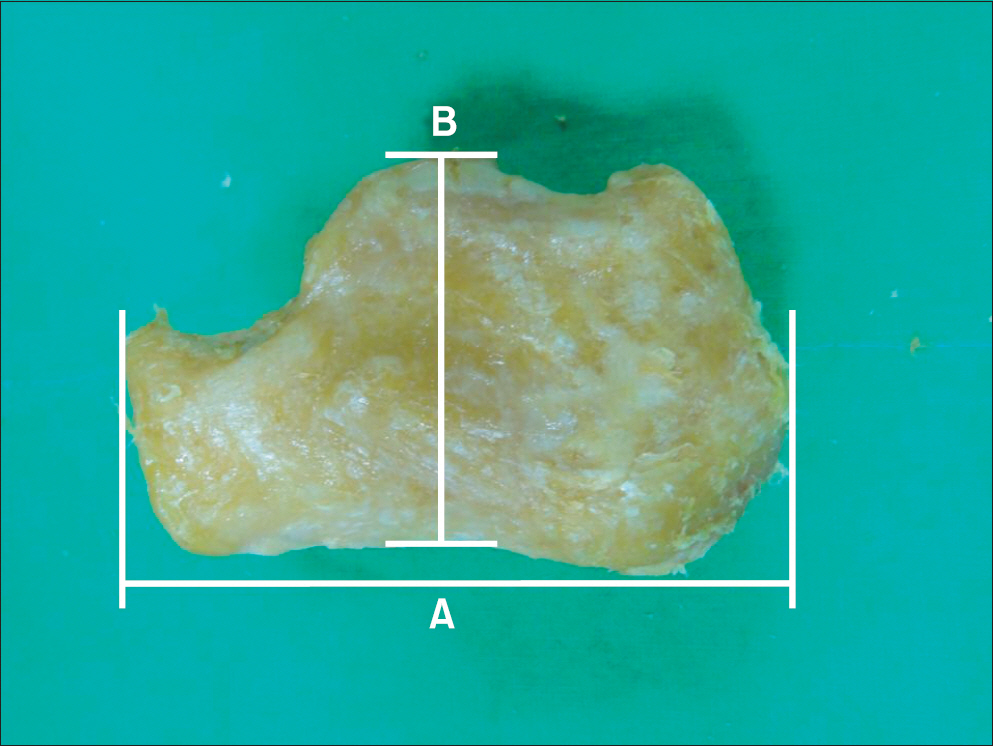
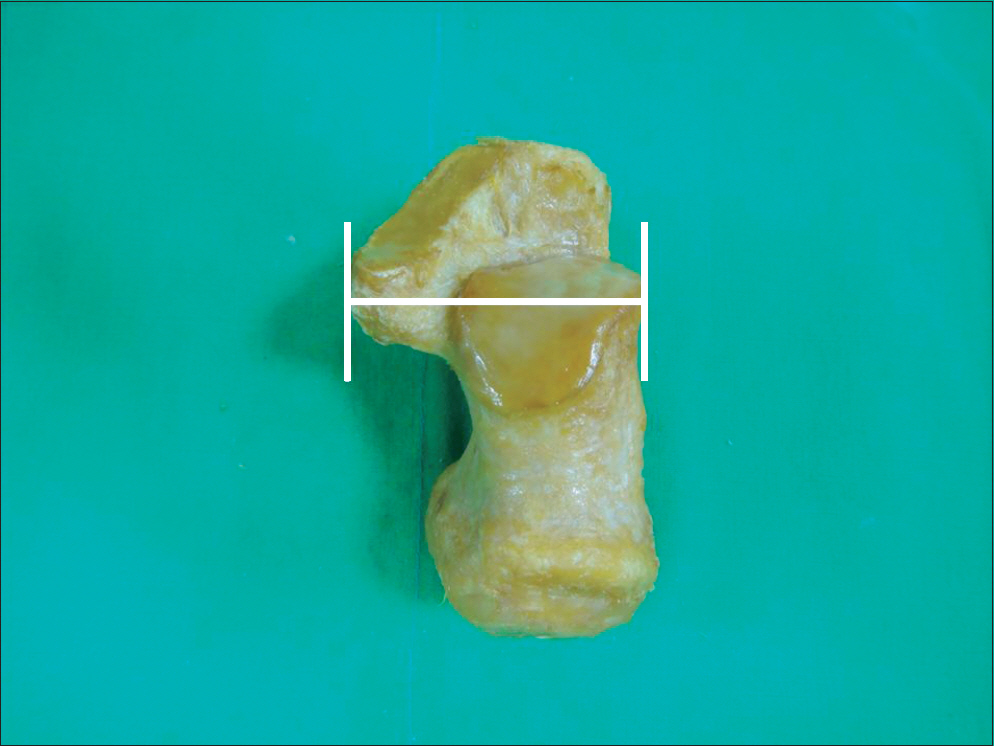
A total of 42 calcanei were obtained from Korean cadavers. A digital goniometer was used for measurement of Bohler's angle, Gissane angle, posterior facet articular inclination angle, and Fowler-Philip angle of calcaneus. A vernier caliper was used for measurement of the maximal antero-posterior length, maximal transverse width, and maximal height of calcaneus.
RESULTS
The average Bohler's angle, Gissane angle, posterior facet articular inclination angle, and Fowler-Philip angle was 32.3degrees+/-5.0degrees, 114.4degrees+/-8.2degrees, 61.2degrees+/-4.4degrees, and 60.3degrees+/-7.6degrees. The average maximal antero-posterior length, maximal transverse width, and maximal height of calcaneus was 74.2+/-3.0 mm, 43.0+/-4.0 mm, and 42.5+/-3.0 mm.
CONCLUSION
The measured values of normal Korean calcaneus were lower than the values reported in the international literature. Therefore, development of appropriate instruments reflecting the anatomical characteristics of Koreans will be needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Koshy S, Vettivel S, Selvaraj KG. Estimation of length of calcaneum and talus from their bony markers. Forensic Sci Int. 2002; 129:200–4.
Article2. Sakaue K. Sex assessment from the talus and calcaneus of Japanese. Bull Natl Mus Nat Sci Ser D. 2011; 37:35–48.3. Bidmos MA, Asala SA. Sexual dimorphism of the calcaneus of South African blacks. J Forensic Sci. 2004; 49:446–50.
Article4. Zakaria MS, Mohammed AH, Habib SR, Hanna MM, Fahiem AL. Calcaneus radiograph as a diagnostic tool for sexual dimorphism in Egyptians. J Forensic Leg Med. 2010; 17:378–82.
Article5. Ari I, Kafa IM. Bone length estimation and population-specific features of calcaneus and talus bones of the late Byzantine Era. Coll Antropol. 2009; 33:613–8.6. Sohn HM, Lee JY, Ha SH, Jo SH. The comparison of radiographic parameters and clinical results after operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007; 20:227–32.
Article7. Khoshhal KI, Ibrahim AF, Al-Nakshabandi NA, Zamzam MM, Al-Boukai AA, Zamzami MM. Böhler's and Gissane's angles of the calcaneus in the Saudi population. Saudi Med J. 2004; 25:1967–70.8. Stephenson JR. Displaced fractures of the os calcis involving the subtalar joint: the key role of the superomedial fragment. Foot Ankle. 1983; 4:91–101.9. Igbigbi PS, Mutesasira AN. Calcaneal angle in Ugandans. Clin Anat. 2003; 16:328–30.
Article10. Didia BC, Dimkpa JN. The calcaneal angle in Nigerians. Relationship to sex, age, and side of the body. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1999; 89:472–4.
Article11. Chen MY, Bohrer SP, Kelley TF. Boehler's angle: a reappraisal. Ann Emerg Med. 1991; 20:122–4.
Article12. Hauser ML, Kroeker RO. Boehler's angle: a review and study. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1975; 65:517–21.
Article13. Loucks C, Buckley R. Bohler's angle: correlation with outcome in displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:554–8.
Article14. Kim JS, Cho HK, Hwang SM, Lee KW, Young KW, Lee KT. The size of calcaneus in Koreans. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2013; 17:143–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Results between Cadaveric and Radiological Measurements of Calcaneus
- Normal CT anatomy of the calcaneus
- Tibialis Anterior Tendon Transfer for Calcaneus Deformity in Children with Myelomeningocele: A Preliminary Report
- Intraosseous Lipoma in the Calcaneus: A Case report
- Enchondroma of the Calcaneus: A Case Report