J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Aug;56(2):121-129. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.2.121.
Does Intramedullary Signal Intensity on MRI Affect the Surgical Outcomes of Patients with Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. zunzae@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1956514
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.2.121
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
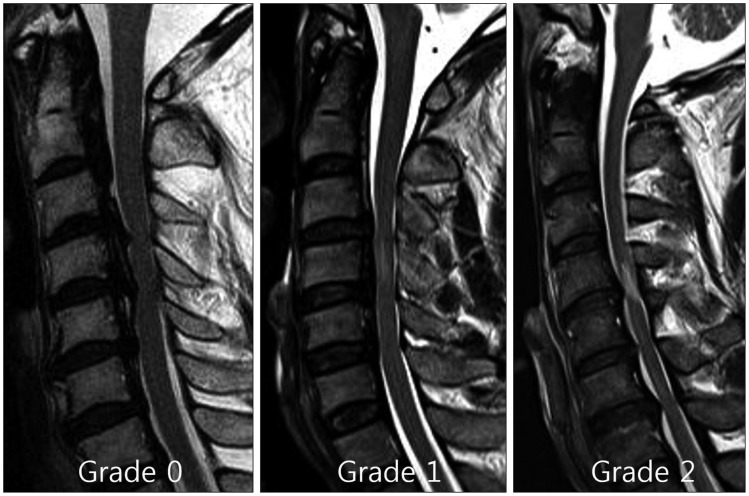
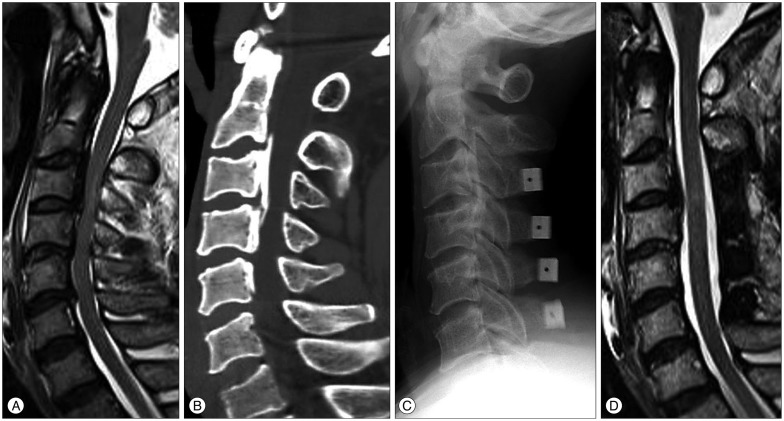
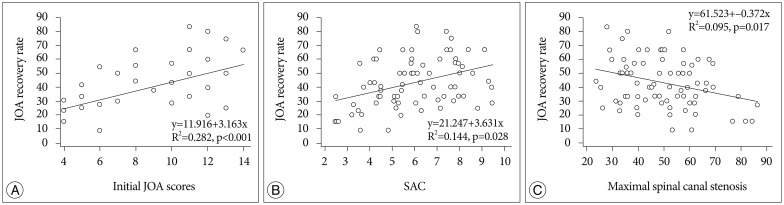
Patients with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) are susceptible to cord injury, which often develops into myelopathic symptoms. However, little is known regarding the prognostic factors that are involved in minor trauma. We evaluated the relationship between minor trauma and neurological outcome of OPLL and investigated the prognostic factors with a focus on compressive factors and intramedullary signal intensity (SI).
METHODS
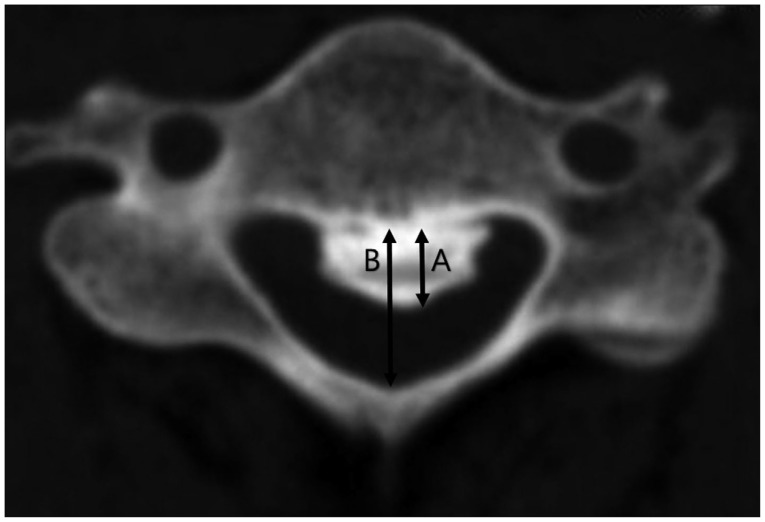
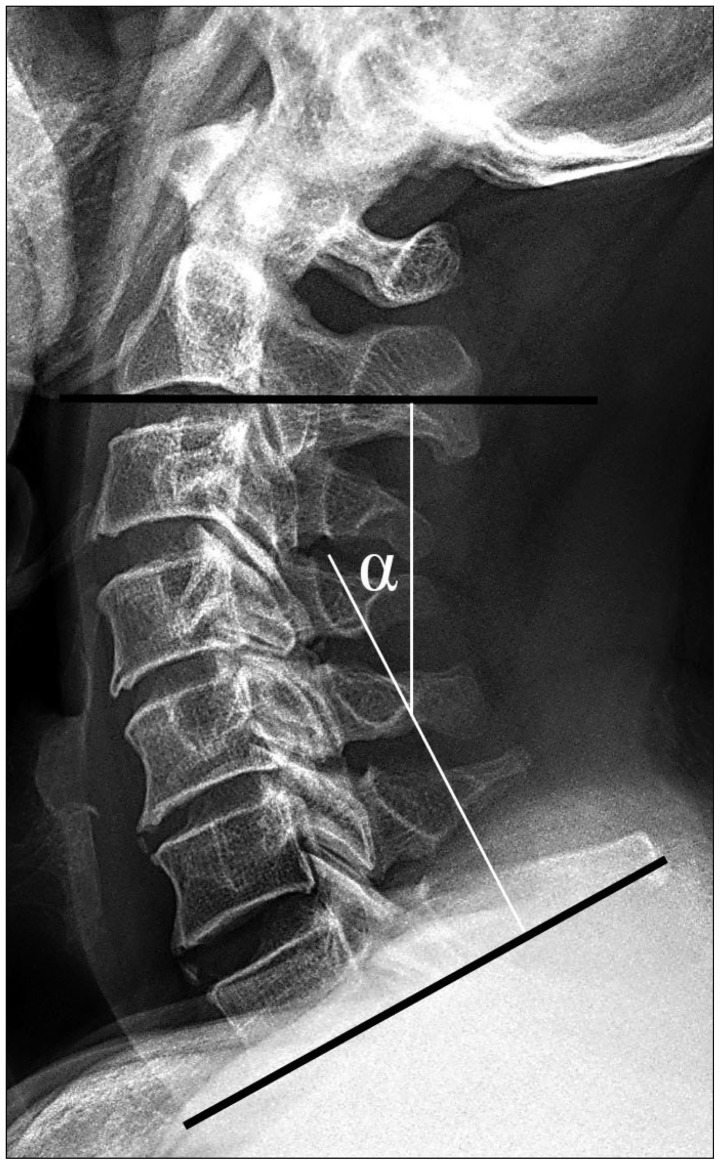
A total of 74 patients with cervical myelopathy caused by OPLL at more than three-levels were treated with posterior decompression surgeries. We surveyed the space available for spinal cord (SAC), the severity of SI change on T2-weighted image, and diabetes mellitus (DM). The neurological outcome using Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) scale was assessed at admission and at 12-month follow-up.
RESULTS
Among the variables tested, preoperative JOA score, severity of intramedullary SI, SAC, and DM were significantly related to neurological outcome. The mean preoperative JOA were 11.3+/-1.9 for the 41 patients who did not have histories of trauma and 8.0+/-3.1 for the 33 patients who had suffered minor traumas (p<0.05). However, there were no significant differences in the recovery ratios between those two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Initial neurological status and high intramedullary SI in the preoperative phase were related to poorer postoperative outcomes. Moreover, the patients with no histories of DM and larger SACs exhibited better improvement than did the patients with DM and smaller SACs. Although the initial JOA scores were worse for the minor trauma patients than did those who had no trauma prior to surgery, minor trauma exerted no direct effects on the surgical outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Successful Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring in Cervical Myelopathy : Related Factors and the Effect of Increased Stimulation Intensity
Hyok Ki Shim, Jae Meen Lee, Dong Hwan Kim, Kyoung Hyup Nam, Byung Kwan Choi, In Ho Han
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64(1):78-87. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0111.Inter- and Intra-Observer Variability of the Volume of Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Using Medical Image Processing Software
Dong Ah Shin, Gyu Yeul Ji, Chang Hyun Oh, Keung Nyun Kim, Do Heum Yoon, Hyunchul Shin
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(4):441-447. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.0708.014.
Reference
-
1. Baba H, Maezawa Y, Furusawa N, Imura S, Tomita K. Flexibility and alignment of the cervical spine after laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy. A radiographic study. Int Orthop. 1995; 19:116–121. PMID: 7649681.2. Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, Holford TR, Young W, Baskin DS, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of methylprednisolone or naloxone in the treatment of acute spinal-cord injury. Results of the Second National Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:1405–1411. PMID: 2278545.
Article3. Carette S, Fehlings MG. Clinical practice. Cervical radiculopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:392–399. PMID: 16049211.4. Cho WS, Chung CK, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Post-laminectomy kyphosis in patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament : does it cause neurological deterioration? J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:259–264. PMID: 19096629.
Article5. Cho YE, Shin JJ, Kim KS, Chin DK, Kuh SU, Lee JH, et al. The relevance of intramedullary high signal intensity and gadolinium (Gd-DTPA) enhancement to the clinical outcome in cervical compressive myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:2267–2274. PMID: 21779859.
Article6. Eaton SE, Harris ND, Rajbhandari SM, Greenwood P, Wilkinson ID, Ward JD, et al. Spinal-cord involvement in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Lancet. 2001; 358:35–36. PMID: 11454377.
Article7. Ebersold MJ, Pare MC, Quast LM. Surgical treatment for cervical spondylitic myelopathy. J Neurosurg. 1995; 82:745–751. PMID: 7714597.
Article8. Edwards CC 2nd, Heller JG, Murakami H. Corpectomy versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical myelopathy : an independent matched-cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:1168–1175. PMID: 12045513.9. Endo S, Shimamura T, Nakae H, Takakuwa T, Yamada Y, Kasai T, et al. Cervical spinal cord injury associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1994; 113:218–221. PMID: 7917716.
Article10. Fujimura Y, Nakamura M, Toyama Y. Influence of minor trauma on surgical results in patients with cervical OPLL. J Spinal Disord. 1998; 11:16–20. PMID: 9493765.
Article11. Hirabayashi K, Miyakawa J, Satomi K, Maruyama T, Wakano K. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1981; 6:354–364. PMID: 6792717.
Article12. Iwasaki M, Kawaguchi Y, Kimura T, Yonenobu K. Long-term results of expansive laminoplasty for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine : more than 10 years follow up. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96(2 Suppl):180–189. PMID: 12450281.
Article13. Iwasaki M, Okuda S, Miyauchi A, Sakaura H, Mukai Y, Yonenobu K, et al. Surgical strategy for cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament : Part 1 : Clinical results and limitations of laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:647–653. PMID: 17413469.
Article14. Iwasaki M, Okuda S, Miyauchi A, Sakaura H, Mukai Y, Yonenobu K, et al. Surgical strategy for cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament : Part 2 : Advantages of anterior decompression and fusion over laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:654–660. PMID: 17413470.
Article15. Kato Y, Iwasaki M, Fuji T, Yonenobu K, Ochi T. Long-term follow-up results of laminectomy for cervical myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg. 1998; 89:217–223. PMID: 9688116.
Article16. Katoh S, el Masry WS, Jaffray D, McCall IW, Eisenstein SM, Pringle RG, et al. Neurologic outcome in conservatively treated patients with incomplete closed traumatic cervical spinal cord injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:2345–2351. PMID: 8915069.
Article17. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Ishihara H, Gejo R, Yasuda T. Surgical outcome of cervical expansive laminoplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:551–555. PMID: 10749630.
Article18. Koyanagi I, Iwasaki Y, Hida K, Akino M, Imamura H, Abe H. Acute cervical cord injury without fracture or dislocation of the spinal column. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93(1 Suppl):15–20. PMID: 10879753.
Article19. Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Hayashi K, Ishidou Y, Hirotsu M, Komiya S. Trauma-induced myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97(2 Suppl):172–175. PMID: 12296674.
Article20. Minoda Y, Nakamura H, Konishi S, Nagayama R, Suzuki E, Yamano Y, et al. Palsy of the C5 nerve root after midsagittal-splitting laminoplasty of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1123–1127. PMID: 12782979.
Article21. Mizuno J, Nakagawa H, Hashizume Y. Pathology of the spinal cord damaged by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament associated with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 1999; 37:224–227. PMID: 10213337.
Article22. Morimoto T, Yamada T, Nagata K, Matsuyama T, Sakaki T. Intramedullary gadolinium-DTPA enhancement in a patient with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and an associated vascular lesion. Case report. Neurosurg Focus. 1996; 1:e3. PMID: 15096029.23. Nakamura R, Noritake M, Hosoda Y, Kamakura K, Nagata N, Shibasaki H. Somatosensory conduction delay in central and peripheral nervous system of diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1992; 15:532–535. PMID: 1499471.
Article24. Nilsson P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Norrving B, Larsson EM. The role of MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and CSF examination for the diagnosis of primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2007; 14:1292–1295. PMID: 17764461.
Article25. Okada S, Maeda T, Ohkawa Y, Harimaya K, Saiwai H, Kumamaru H, et al. Does ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament affect the neurological outcome after traumatic cervical cord injury? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1148–1152. PMID: 19444061.
Article26. Onishi E, Sakamoto A, Murata S, Matsushita M. Risk factors for acute cervical spinal cord injury associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37:660–666. PMID: 21857407.
Article27. Pavlov H, Torg JS, Robie B, Jahre C. Cervical spinal stenosis : determination with vertebral body ratio method. Radiology. 1987; 164:771–775. PMID: 3615879.
Article28. Radcliff KE, Limthongkul W, Kepler CK, Sidhu GD, Anderson DG, Rihn JA, et al. Cervical laminectomy width and spinal cord drift are risk factors for postoperative C5 palsy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014; 27:86–92. PMID: 22425890.
Article29. Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, Ishii T, Yoshikawa H. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cervical myelopathy : review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2447–2451. PMID: 14595162.30. Shin JJ, Jin BH, Kim KS, Cho YE, Cho WH. Intramedullary high signal intensity and neurological status as prognostic factors in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:1687–1694. PMID: 20512384.
Article31. Son S, Lee SG, Yoo CJ, Park CW, Kim WK. Single stage circumferential cervical surgery (selective anterior cervical corpectomy with fusion and laminoplasty) for multilevel ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with spinal cord ischemia on MRI. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:335–341. PMID: 21113361.
Article32. Suri A, Chabbra RP, Mehta VS, Gaikwad S, Pandey RM. Effect of intramedullary signal changes on the surgical outcome of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2003; 3:33–45. PMID: 14589243.
Article33. Takemitsu M, Cheung KM, Wong YW, Cheung WY, Luk KD. C5 nerve root palsy after cervical laminoplasty and posterior fusion with instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008; 21:267–272. PMID: 18525487.
Article34. Tsuyama N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; (184):71–84. PMID: 6423334.
Article35. Vinik AI. Diabetic neuropathy : pathogenesis and therapy. Am J Med. 1999; 107:17S–26S. PMID: 10484041.36. Yukawa Y, Kato F, Ito K, Horie Y, Hida T, Machino M, et al. Postoperative changes in spinal cord signal intensity in patients with cervical compression myelopathy : comparison between preoperative and postoperative magnetic resonance images. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 8:524–528. PMID: 18518672.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: 2 cases report
- Significance of Intramedullary High Signal Intensity on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
- Surgical Outcomes According to Dekyphosis in Patients with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in the Thoracic Spine
- Cervical Spine CT and MRI Findings in a Patient with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
- Does Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Progress after Fusion?