J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Apr;57(4):258-265. 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.4.258.
Intracranial Meningioma with Leptomeningeal Dissemination : Retrospective Study with Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jhwang@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1956423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.4.258
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purposes of this article are to present 5 cases of intracranial meningioma with leptomeningeal dissemination (LD) and investigate the characteristics of this disease.
METHODS
We present a retrospective case series of 5 females at our institutions (age ranged 21-72 years, mean 54.6 years) diagnosed with LD of an intracranial meningioma after surgery between 1998 and 2013. A database search revealed 45 cases with LD of meningioma in the English literature. Characteristic features were analyzed and compared.
RESULTS
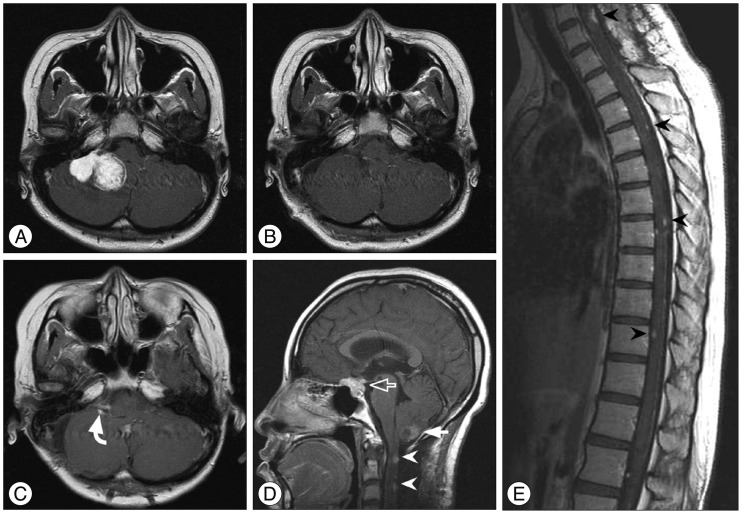
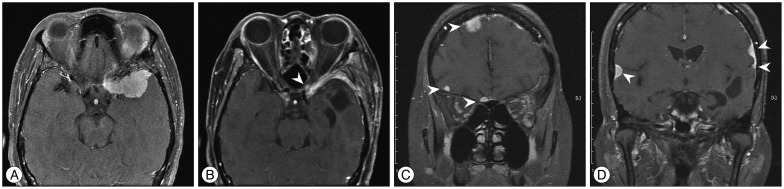
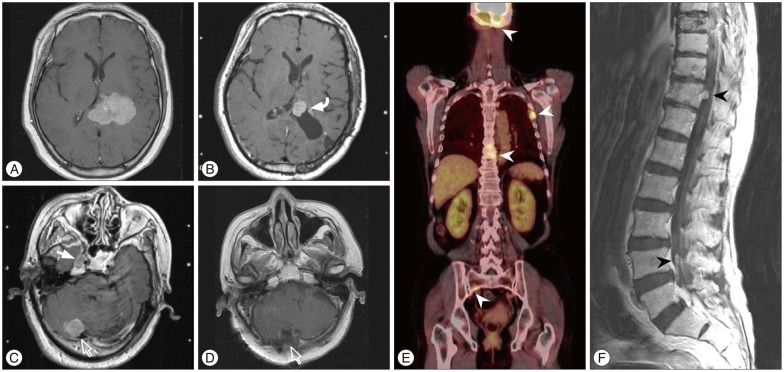
The incidence rate at our institutions of LD of meningioma was 0.9% (5/534). World Health Organization (WHO) grade was distributed as follows: I : 2, II : 2, and III : 1. Time to LD ranged from 2.5 months to 6.9 years; the patient with WHO grade III had the shortest interval to LD. The patient with an intraventricular meningioma (WHO grade II) had the second shortest interval to LD (1.7 years), and simultaneously revealed both LD and extraneuronal metastases. Four of 5 patients showed a disease progression, with the survival ranging from 1 month to 3.8 years after LD. Based on the literature, the initial tumor was an intraventricular meningioma in 9 patients, and their time to LD was shorter on average (mean 1.9 years). Histologically, 26 of 45 (58%) were initially diagnosed with a WHO grade II or III meningioma, and 6 of 19 patients (32%) with WHO grade I revealed malignant transformation.
CONCLUSION
This study shows that intraventricular location and histologically aggressive features seem to increase the chance of LD of meningioma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akimura T, Orita T, Hayashida O, Nishizaki T, Fudaba H. Malignant meningioma metastasizing through the cerebrospinal pathway. Acta Neurol Scand. 1992; 85:368–371. PMID: 1621502.
Article2. Al-Habib A, Lach B, Al Khani A. Intracerebral rhabdoid and papillary meningioma with leptomeningeal spread and rapid clinical progression. Clin Neuropathol. 2005; 24:1–7. PMID: 15696777.3. Baser ME, Poussaint TY. Age associated increase in the prevalence of chromosome 22q loss of heterozygosity in histological subsets of benign meningioma. J Med Genet. 2006; 43:285–287. PMID: 15980114.
Article4. Bigner SH, Johnston WW. The cytopathology of cerebrospinal fluid. II. Metastatic cancer, meningeal carcinomatosis and primary central nervous system neoplasms. Acta Cytol. 1981; 25:461–479. PMID: 7025541.5. Chamberlain MC, Glantz MJ. Cerebrospinal fluid-disseminated meningioma. Cancer. 2005; 103:1427–1430. PMID: 15690330.
Article6. Chamberlain MC, Tsao-Wei DD, Groshen S. Temozolomide for treatment-resistant recurrent meningioma. Neurology. 2004; 62:1210–1212. PMID: 15079029.
Article7. Chuang HC, Lee HC, Cho DY. Intracranial malignant meningioma with multiple spinal metastases--a case report and literature review : case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:E1006–E1010. PMID: 17172988.8. Conrad MD, Schonauer C, Pelissou-Guyotat I, Morel C, Madarassy G, Deruty R. Recurrent lumbosacral metastases from intracranial meningioma. Report of a case and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:935–937. PMID: 11685626.
Article9. Cramer P, Thomale UW, Okuducu AF, Lemke AJ, Stockhammer F, Woiciechowsky C. An atypical spinal meningioma with CSF metastasis : fatal progression despite aggressive treatment. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 3:153–158. PMID: 16370305.
Article10. Darwish B, Munro I, Boet R, Renaut P, Abdelaal AS, MacFarlane MR. Intraventricular meningioma with drop metastases and subgaleal metastatic nodule. J Clin Neurosci. 2004; 11:787–791. PMID: 15337153.
Article11. Dogan S, Sahin S, Taskapilioglu O, Aksoy K, Adim S. Multiple metastatic malignant meningioma : a case report. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2004; 65:141–145. PMID: 15306979.
Article12. Enam SA, Abdulrauf S, Mehta B, Malik GM, Mahmood A. Metastasis in meningioma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:1172–1177. discussion 1177-1178. PMID: 8955436.
Article13. Eom KS, Kim DW, Kim TY. Diffuse craniospinal metastases of intraventricular rhabdoid papillary meningioma with glial fibrillary acidic protein expression : a case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009; 111:619–623. PMID: 19482417.
Article14. Erkutlu I, Buyukhatipoglu H, Alptekin M, Berkyurek E, Tutar E, Gok A. Spinal drop metastases from a papillary meningioma : a case report and review of the literature : utility of CSF sampling. Med Oncol. 2009; 26:242–246. PMID: 18937081.
Article15. Figueroa BE, Quint DJ, McKeever PE, Chandler WF. Extracranial metastatic meningioma. Br J Radiol. 1999; 72:513–516. PMID: 10505022.
Article16. Greenberg SB, Schneck MJ, Faerber EN, Kanev PM. Malignant meningioma in a child : CT and MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993; 160:1111–1112. PMID: 8470588.17. Kamiya K, Inagawa T, Nagasako R. Malignant intraventricular meningioma with spinal metastasis through the cerebrospinal fluid. Surg Neurol. 1989; 32:213–218. PMID: 2772810.
Article18. Kepes JJ, MacGee EE, Vergara G, Sil R. A case report. Malignant meningioma with extensive pulmonary metastases. J Kans Med Soc. 1971; 72:312–316. PMID: 5571871.19. Kim JP, Park BJ, Lim YJ. Papillary meningioma with leptomeningeal seeding. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:124–127. PMID: 21519503.
Article20. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Avakian JJ. Wallenberg syndrome caused by CSF metastasis from malignant intraventricular meningioma. Clin Neuropathol. 1985; 4:214–219. PMID: 4064387.21. Koenig MA, Geocadin RG, Kulesza P, Olivi A, Brem H. Rhabdoid meningioma occurring in an unrelated resection cavity with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:371–375. PMID: 15739568.
Article22. Kuroda H, Kashimura H, Ogasawara K, Sugawara A, Sasoh M, Arai H, et al. Malignant intracranial meningioma with spinal metastasis--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2009; 49:258–261. PMID: 19556736.23. Lee TT, Landy HJ. Spinal metastases of malignant intracranial meningioma. Surg Neurol. 1998; 50:437–441. PMID: 9842867.
Article24. Lee W, Chang KH, Choe G, Chi JG, Chung CK, Kim IH, et al. MR imaging features of clear-cell meningioma with diffuse leptomeningeal seeding. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:130–132. PMID: 10669237.25. Lee WH, Chen A, Chao DG, Harn HJ, Lin SZ. Malignant meningioma with rhabdoid transformation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2000; 63:492–497. PMID: 10925541.26. Lucey BP, Tihan T, Pomper MG, Olivi A, Laterra J. Spinal meningioma causing diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement. Neurology. 2003; 60:350–351. PMID: 12552066.
Article27. Ludwin SK, Conley FK. Malignant meningioma metastasizing through the cerebrospinal pathways. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975; 38:136–142. PMID: 1151393.
Article28. Maxwell M, Shih SD, Galanopoulos T, Hedley-Whyte ET, Cosgrove GR. Familial meningioma : analysis of expression of neurofibromatosis 2 protein Merlin. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88:562–569. PMID: 9488313.
Article29. Meinsma-vdTuin M, Molenaar WM, Mooij JJ. Spinal papillary meningioma : a case report and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2000; 142:703–708. PMID: 10949447.30. Miller AA, Ramsden F. Malignant meningioma with extracranial metastases and seeding of the subarachnoid space and the ventricles. Pathol Eur. 1972; 7:167–175. PMID: 4635599.31. Modha A, Gutin PH. Diagnosis and treatment of atypical and anaplastic meningiomas : a review. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57:538–550. discussion 538-550. PMID: 16145534.
Article32. Morantz RA, Shain W. Trauma and brain tumors : an experimental study. Neurosurgery. 1978; 3:181–186. PMID: 703937.33. Nakane Y, Natsume A, Wakabayashi T, Oi S, Ito M, Inao S, et al. Malignant transformation-related genes in meningiomas : allelic loss on 1p36 and methylation status of p73 and RASSF1A. J Neurosurg. 2007; 107:398–404. PMID: 17695396.
Article34. Noterman J, Depierreux M, Raftopoulos C, Brotchi J. [Metastases of meningioma. Apropos of 2 cases]. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:184–189. PMID: 3614492.35. Peh WC, Fan YW. Case report : intraventricular meningioma with cerebellopontine angle and drop metastases. Br J Radiol. 1995; 68:428–430. PMID: 7795983.
Article36. Peng J, Liang ZG, Li KC. Intracranial malignant meningioma with cerebrospinal fluid dissemination : a case report. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011; 124:1597–1599. PMID: 21740827.37. Perry A, Scheithauer BW, Stafford SL, Lohse CM, Wollan PC. "Malignancy" in meningiomas : a clinicopathologic study of 116 patients, with grading implications. Cancer. 1999; 85:2046–2056. PMID: 10223247.38. Pradat PF, Hoang-Xuan K, Cornu P, Mokhtari K, Martin-Duverneuil N, Poisson M, et al. Treatment of meningeal gliomatosis. J Neurooncol. 1999; 44:163–168. PMID: 10619500.39. Ramakrishnamurthy TV, Murty AV, Purohit AK, Sundaram C. Benign meningioma metastasizing through CSF pathways : a case report and review of literature. Neurol India. 2002; 50:326–329. PMID: 12391463.40. Rosa L, Luessenhop AJ. Multiple meningiomas. In : Schmidek HH, editor. Meningiomas and Their Surgical Management. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1991. p. 83.41. Russell DS, Rubinstein LJ. Pathology of tumors of the nervous system. ed 4. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins;1977. p. 89–91.42. Santhosh K, Kesavadas C, Radhakrishnan VV, Thomas B, Kapilamoorthy TR, Gupta AK. Rhabdoid and papillary meningioma with leptomeningeal dissemination. J Neuroradiol. 2008; 35:236–239. PMID: 18325590.
Article43. Satoh T, Kageyama T, Yoshimoto Y, Kamata I, Date I, Motoi M. [Intrathecal dissemination of meningiomas; a case report]. No Shinkei Geka. 1992; 20:805–808. PMID: 1630573.44. Shintaku M, Hashimoto K, Okamoto S. Intraventricular meningioma with anaplastic transformation and metastasis via the cerebrospinal fluid. Neuropathology. 2007; 27:448–452. PMID: 18018478.
Article45. Strenger SW, Huang YP, Sachdev VP. Malignant meningioma within the third ventricle : a case report. Neurosurgery. 1987; 20:465–468. PMID: 3574625.46. Sutherland GR, Florell R, Louw D, Choi NW, Sima AA. Epidemiology of primary intracranial neoplasms in Manitoba, Canada. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987; 14:586–592. PMID: 3500769.47. Tsuda K, Akutsu H, Yamamoto T, Ishikawa E, Saito A, Nakai K, et al. Benign spinal meningioma without dural attachment presenting delayed CSF dissemination and malignant transformation. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2013; 30:185–191. PMID: 22915133.
Article48. Wakabayashi K, Suzuki N, Mori F, Kamada M, Hatanaka M. Rhabdoid cystic papillary meningioma with diffuse subarachnoid dissemination. Acta Neuropathol. 2005; 110:196–198. PMID: 15981015.
Article49. Wu YT, Ho JT, Lin YJ, Lin JW. Rhabdoid papillary meningioma : a clinicopathologic case series study. Neuropathology. 2011; 31:599–605. PMID: 21382093.50. Younis GA, Sawaya R, DeMonte F, Hess KR, Albrecht S, Bruner JM. Aggressive meningeal tumors : review of a series. J Neurosurg. 1995; 82:17–27. PMID: 7815129.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Papillary Meningioma with Leptomeningeal Seeding
- The Clinical Features of Spinal Leptomeningeal Dissemination from Malignant Gliomas
- Meningioma of the Frontal and Ethmoidal Sinus: Case Report
- Three Cases of Intracranial Hematoma Associated with Meningioma
- Primary Spinal Cord Melanoma in Thoracic Spine with Leptomeningeal Dissemination and Presenting Hydrocephalus