J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 Apr;72(4):263-270. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.4.263.
Short-Term Outcome of Fluoroscopic-Guided Steroid Injection Therapy of Lumbar Facet Cyst-Induced Radicular Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwjwkwon@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1941757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.4.263
Abstract
- PURPOSE
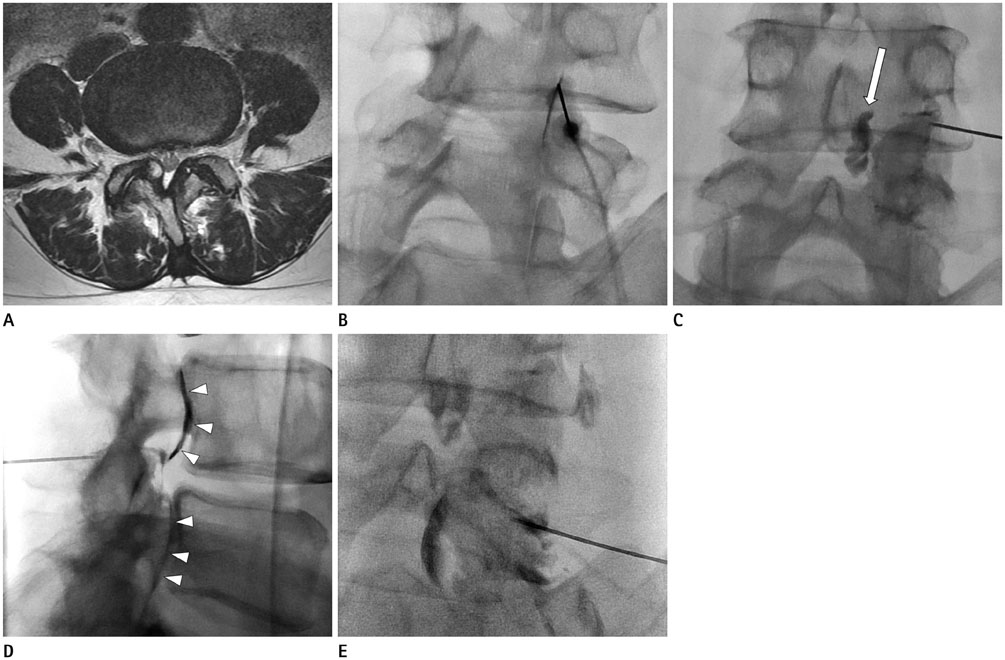
To determine the short-term effect of fluoroscopic-guided steroid injection therapy of lumbar facet cyst-induced radicular pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients with radiculopathy due to lumbar synovial cysts, who were treated with fluoroscopically guided injection, were retrospectively evaluated. All plain radiographic images and MR images before the therapy were reviewed. Five patients underwent only the facet joint injection, whereas twelve patients underwent the facet joint injection with perineural injection therapy. The clinical course of pain was evaluated on the first follow-up after therapy.
RESULTS
Effective pain relief was achieved in 11 (64.7%) of the 17 patients. Among 12 patients who underwent facet joint injection with perineural injection, 9 patients (75%) had an effective pain relief. Of 5 patients, 2 (40%) patients only took the facet joint injection and had an effective pain relief.
CONCLUSION
Fluoroscopic-guided steroid injection therapy shows a good short-term effect in patients with symptomatic lumbar facet joint synovial cysts.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hemminghytt S, Daniels DL, Williams AL, Haughton VM. Intraspinal synovial cysts: natural history and diagnosis by CT. Radiology. 1982; 145:375–376.2. Bjorkengren AG, Kurz LT, Resnick D, Sartoris DJ, Garfin SR. Symptomatic intraspinal synovial cysts: opacification and treatment by percutaneous injection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 149:105–107.3. Hsu KY, Zucherman JF, Shea WJ, Jeffrey RA. Lumbar intraspinal synovial and ganglion cysts (facet cysts). Ten-year experience in evaluation and treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:80–89.4. Parlier-Cuau C, Wybier M, Nizard R, Champsaur P, Le Hir P, Laredo JD. Symptomatic lumbar facet joint synovial cysts: clinical assessment of facet joint steroid injection after 1 and 6 months and long-term follow-up in 30 patients. Radiology. 1999; 210:509–513.5. Bureau NJ, Kaplan PA, Dussault RG. Lumbar facet joint synovial cyst: percutaneous treatment with steroid injections and distention--clinical and imaging follow-up in 12 patients. Radiology. 2001; 221:179–185.6. Allen TL, Tatli Y, Lutz GE. Fluoroscopic percutaneous lumbar zygapophyseal joint cyst rupture: a clinical outcome study. Spine J. 2009; 9:387–395.7. Martha JF, Swaim B, Wang DA, Kim DH, Hill J, Bode R, et al. Outcome of percutaneous rupture of lumbar synovial cysts: a case series of 101 patients. Spine J. 2009; 9:899–904.8. Slipman CW, Lipetz JS, Wakeshima Y, Jackson HB. Nonsurgical treatment of zygapophyseal joint cyst-induced radicular pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81:973–977.9. Sabers SR, Ross SR, Grogg BE, Lauder TD. Procedure-based nonsurgical management of lumbar zygapophyseal joint cyst-induced radicular pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:1767–1771.10. Lee SJ, Kim YK, Jung HS, Lim JB, Lee C. Percutaneous treatment with steroid injections and distension of facet synovial cyst - a case report. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:246–250.11. Shin KM, Kim MS, Ko KM, Jang JS, Kang SS, Hong SJ. Percutaneous aspiration of lumbar zygapophyseal joint synovial cyst under fluoroscopic guidance -A case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012; 62:375–378.12. Apostolaki E, Davies AM, Evans N, Cassar-Pullicino VN. MR imaging of lumbar facet joint synovial cysts. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:615–623.13. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Boos N, Hodler J. MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints. Skeletal Radiol. 1999; 28:215–219.14. Niggemann P, Kuchta J, Grosskurth D, Beyer HK, Hoeffer J, Delank KS. Spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis: impact of vertebral hypoplasia on the use of the Meyerding classification. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:358–362.15. Yang KH, Kim NK, Kim YS, Ko Y, Oh SH, Oh SJ, et al. Lumbar spinal instability and its radiologic findings. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2000; 29:78–86.16. Abdi S, Datta S, Trescot AM, Schultz DM, Adlaka R, Atluri SL, et al. Epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:185–212.17. Eyster EF, Scott WR. Lumbar synovial cysts: report of eleven cases. Neurosurgery. 1989; 24:112–115.18. Park HJ, Jeon YH, Rho MH, Lee EJ, Park NH, Park SI, et al. Incidental findings of the lumbar spine at MRI during herniated intervertebral disk disease evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:1151–1155.19. Boviatsis EJ, Stavrinou LC, Kouyialis AT, Gavra MM, Stavrinou PC, Themistokleous M, et al. Spinal synovial cysts: pathogenesis, diagnosis and surgical treatment in a series of seven cases and literature review. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:831–837.20. Khan AM, Girardi F. Spinal lumbar synovial cysts. Diagnosis and management challenge. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:1176–1182.21. Shah RV, Lutz GE. Lumbar intraspinal synovial cysts: conservative management and review of the world's literature. Spine J. 2003; 3:479–488.22. Reale C, Turkiewicz AM, Reale CA, Stabile S, Borgonuovo P, Apponi F. Epidural steroids as a pharmacological approach. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000; 18:2 Suppl 19. S65–S66.23. Manchikanti L. Role of neuraxial steroids in interventional pain management. Pain Physician. 2002; 5:182–199.24. Gray RG, Gottlieb NL. Intra-articular corticosteroids. An updated assessment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; (177):235–263.25. Sarazin L, Chevrot A, Pessis E, Minoui A, Drape JL, Chemla N, et al. Lumbar facet joint arthrography with the posterior approach. Radiographics. 1999; 19:93–104.26. Cook NJ, Hanrahan P, Song S. Paraspinal abscess following facet joint injection. Clin Rheumatol. 1999; 18:52–53.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of FluoroscopyGuided Lumbar Facet Joint Synovial Cyst Rupture with Intra-Articular Steroid Injection after Laminectomy
- Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Spine Injection for Axial and Radicular Pain: A Single Institution Early Experience
- Effect of Transforaminal Epidural Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain
- Selective Epidural Steroid Injection in a Patient with Refractory Radicular Leg Pain: A case report
- Facet joint disorders: from diagnosis to treatment