J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2007 Sep;14(3):171-177. 10.4184/jkss.2007.14.3.171.
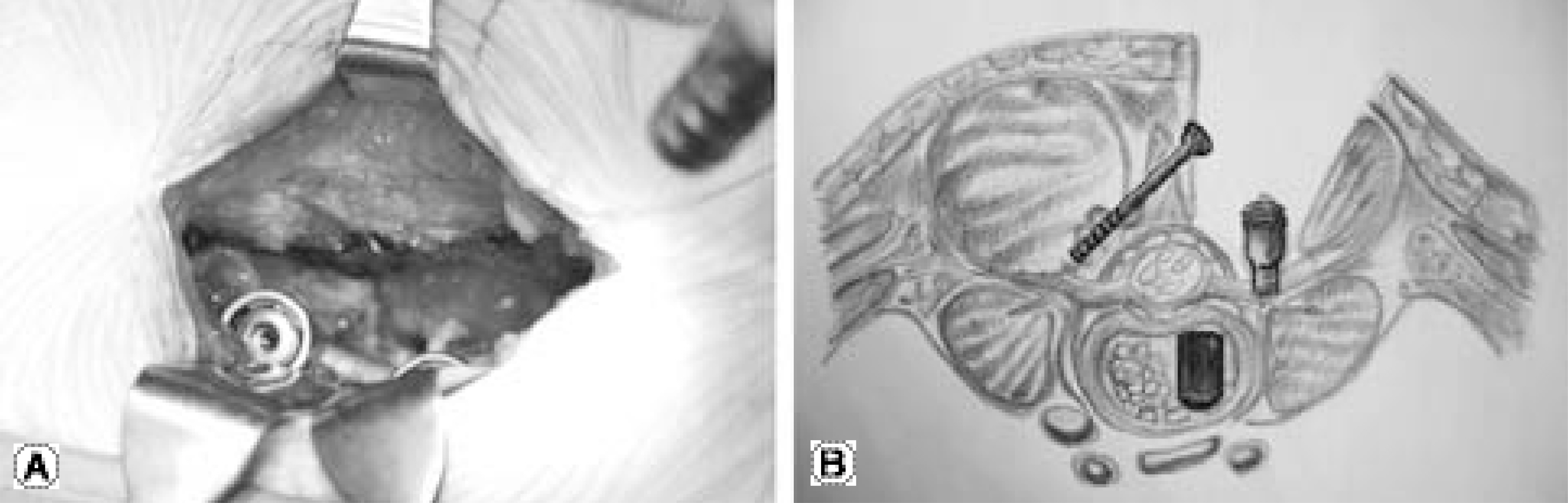
Posterior Lumbar Intebody Fusion with Unilateral Transpedicular Screw and Contralateral Translaminar Facet Screw Fixation in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kwangju Christian Hospital. stemcellchoi@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 1941649
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2007.14.3.171
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To describe the surgical procedure and assess the results of an unilateral transpedicular screw and contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation in degenerative lumbar stenosis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: A drawback of conventional lumbar fusion is the extensive soft-tissue destruction that is essential when inserting a screw and preparing the fusion bed. The development of a procedure that minimizes the tissue trauma without compromising the effectiveness of the conventional posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) should be pursued in lumbar spinal stenosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
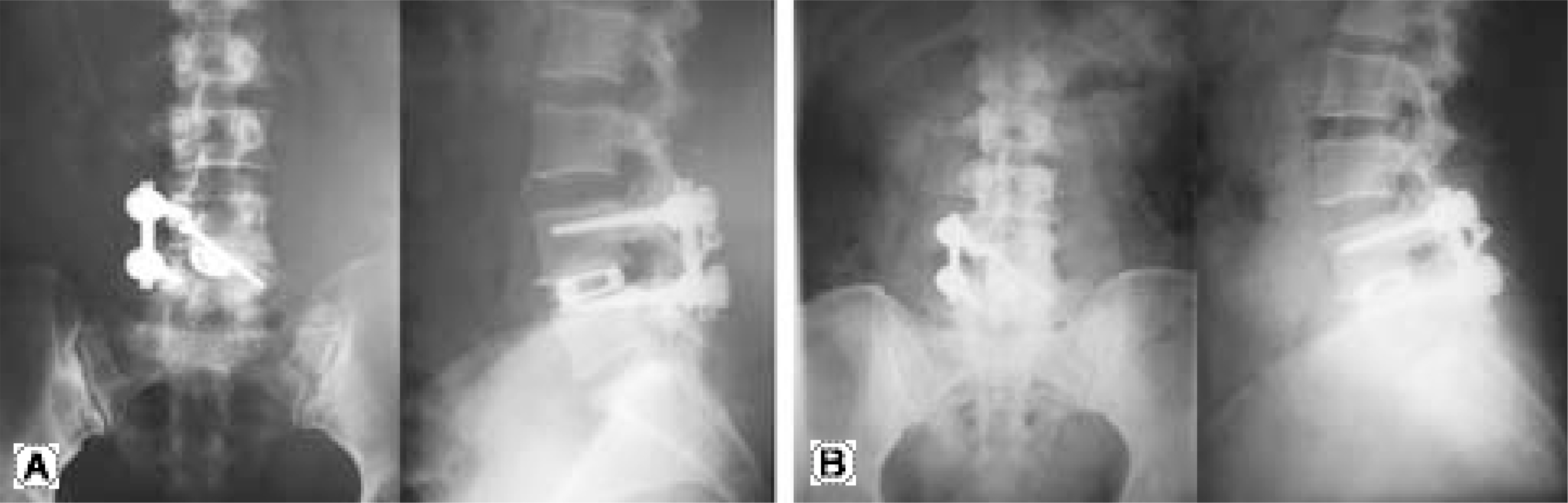
From August 2004 to November 2005, PLIF was performed on 25 consecutive patients who had lumbar spinal stenosis. Among them, 10 patients underwent with unilateral transpedicular screw and contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation (Group 1), and 15 patients underwent traditional bilateral transpedicular screw fixation (Group 2). The clinical and radiological results in the two groups were compared.
RESULTS
The mean follow-up was 17.6 and 20.5 months in Groups 1 and 2, respectively. Group 1 had less blood loss, fewer transfusion requirements (P.0.05) in the surgical procedure, and less postoperative back pain (P.0.05). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the clinical results such as the VAS score for back pain and the Kirkadly-Willis criteria at the last follow-up, and the radiological results such as the changes in the disc height and interbody fusion.
CONCLUSION
The PLIF with unilateral transpedicular screw and contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation in lumbar spinal stenosis has advantages over conventional PLIF of less soft tissue injury, and produces good clinical results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Anderson DG, Tannoury C. Minimally invasive spinal surgery. Orthopaedic knowledge update. Spine. 2006; 3:487–502.2). Fraser RD. Interbody, posterior, and combined lumbar fusions. Spine. 1995; 20:167S–177S.
Article3). Hacker RJ. Comparision of interbody fusion approaches for disabling low back pain. Spine. 1997; 22:660–665.4). Lin PM. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion technique: Complications and pitfalls. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:90–102.5). Loguidice VA, Johnson RG, Guyer RD, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 1988; 13:366–369.
Article6). Ma GW. Posterior interbody fusion with specialized instruments. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:57–63.7). Stonecipher T, Wright S. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with face-screw fixation. Spine. 1989; 14:468–471.8). Chung JY, Chung GH, Kim HS. The Result of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Transpedicular Instrumentation for the Lumbar Diseases. J Korean Spine Surg. 1996; 3:25–32.9). Chung JY, Seo HY, Kim JS. The Results &Affecting Factors of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with TPM Cages in Spondylolisthesis. J Korean Spine Surg. 2000; 7:586–596.10). Song KJ, Kim KN, Song KH, Lee JM. Comparision of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterolateral fusion in degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006; 41:623–629.11). Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, Ishihara H, Tsuji H. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery. Spine. 1999; 24:1023–1028.
Article12). Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. Part 2: Histologic and histochemical analyses in humans. Spine. 1994; 19:2598–2602.13). Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. A histologic and enzymatic analysis. Spine. 1996; 21:941–944.14). Mayer TG, Vanharanta H, Gatchel RJ, et al. Comparison of CT scan muscle measurements and isokinetic trunk strength in postoperative patients. Spine. 1989; 14:33–36.
Article15). Rantanen J, Hurme M, Falck B, et al. The lumbar multi-fidus muscle five years after surgery for a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine. 1993; 18:568–574.
Article16). Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarvi L, Airaksinen O, Parta-nen J, Tapaninaho A. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine. 1993; 18:575–581.
Article17). Styf JR, Willen J. The effects of external compression by three different retractors on pressure in the erector spine muscles during and after posterior lumbar spine surgery in humans. Spine. 1998; 23:354–358.
Article18). Foley KT, Gupta SK. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine: preliminary clinical results. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:7–12.
Article19). Foley KT, Holly LT, Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine. 2003; 28(15 Suppl):S26–S35.
Article20). Foley KT, Lefkowitz MA. Advances in minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurosurg. 2002; 49:499–517.21). Foley KT, Smith MM. Microendoscopic discectomy. Tech Neurosurg. 1997; 3:301–307.22). Guiot BH, Khoo LT, Fessler RG. A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine. 2002; 27:432–438.
Article23). Larry TK, Sylvain P, Daniel TL, Richard GF. Minimally invasive percutaneous posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurgery. 2002; 5:166–181.24). Mathews HH, Long BH. Endoscopy assisted percutaneous anterior interbody fusion with subcutaneous suprafascial internal fixation: evolution of technique and surgical considerations. Orthopaedics. 1995; 3:496–500.25). Harms J, Jeszenzky D, Stolze D, et al. The Textbook of Spinal Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphian: Lippincott-Raven;p. 1337–1347. 1997.26). Blume HG, Rojas CH. Unilateral lumbar interbody fusion (posterior approach) utilizing dowel graft. J Neurol Orthop Surg. 1981; 2:171–175.27). Lee CS, Chung SS, Chung KH. Comparision of unilateral and bilateral approaches for posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004; 39:642–647.28). Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KWE, Cauchoix J, Melvor G. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop. 1974; 99:30–50.29). Truumees E, Herkowitz HN. Lumbar spinal stenosis: treatment options. Instr Course Lect. 2001; 50:153–161.30). Guiot BH, Khoo LT, Fessler RG. A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine. 2002; 27(4):432–438.
Article31). Park Y, Ha JW, Sung SY, Oh HC, Yoo JH, Lee YT. Minimally invasive posterior lumbar interbody fusion: Comparision with traditional open surgery. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006; 41:288–296.32). Collis JS. Total disc replacement: A modified posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:64–67.33). Cloward RB. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by ventral fusion: indications, operative technique, after care. J Neurosurg. 1953; 10:154–168.34). Hutter CG. Spinal stenosis and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Orthop. 1985; 193:103–114.
Article35). Lin PM. A technical modification of Cloward's posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurgery. 1977; 1:118–124.
Article36). Slucky AV, Brodke DS, Bachus KN, Droge JA, Braun JT. Less invasive posterior fixation method following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a biomechanical analysis. Spine. 2006; 6:78–85.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Translaminar Facet Screw Fixation in Lumbar Spine Fusion
- Unilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Unilateral versus Bilateral Pedide Scrwe Fixation in Lumbar Spinal Fusion
- Follow-up Result of Transpedicular Screw Fixation in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis and Spondylolisthesis
- Metal Failure in patients with Short-segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation and Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease: Comparison Monoaxial with Polyaxial Screw