Prog Med Phys.
2013 Dec;24(4):237-242. 10.14316/pmp.2013.24.4.237.
The Feasibility Study of MRI-based Radiotherapy Treatment Planning Using Look Up Table
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ynkang33@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Medical Physics, Kyonggi University of Korea, School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Bio Medical Engineering, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1910564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2013.24.4.237
Abstract
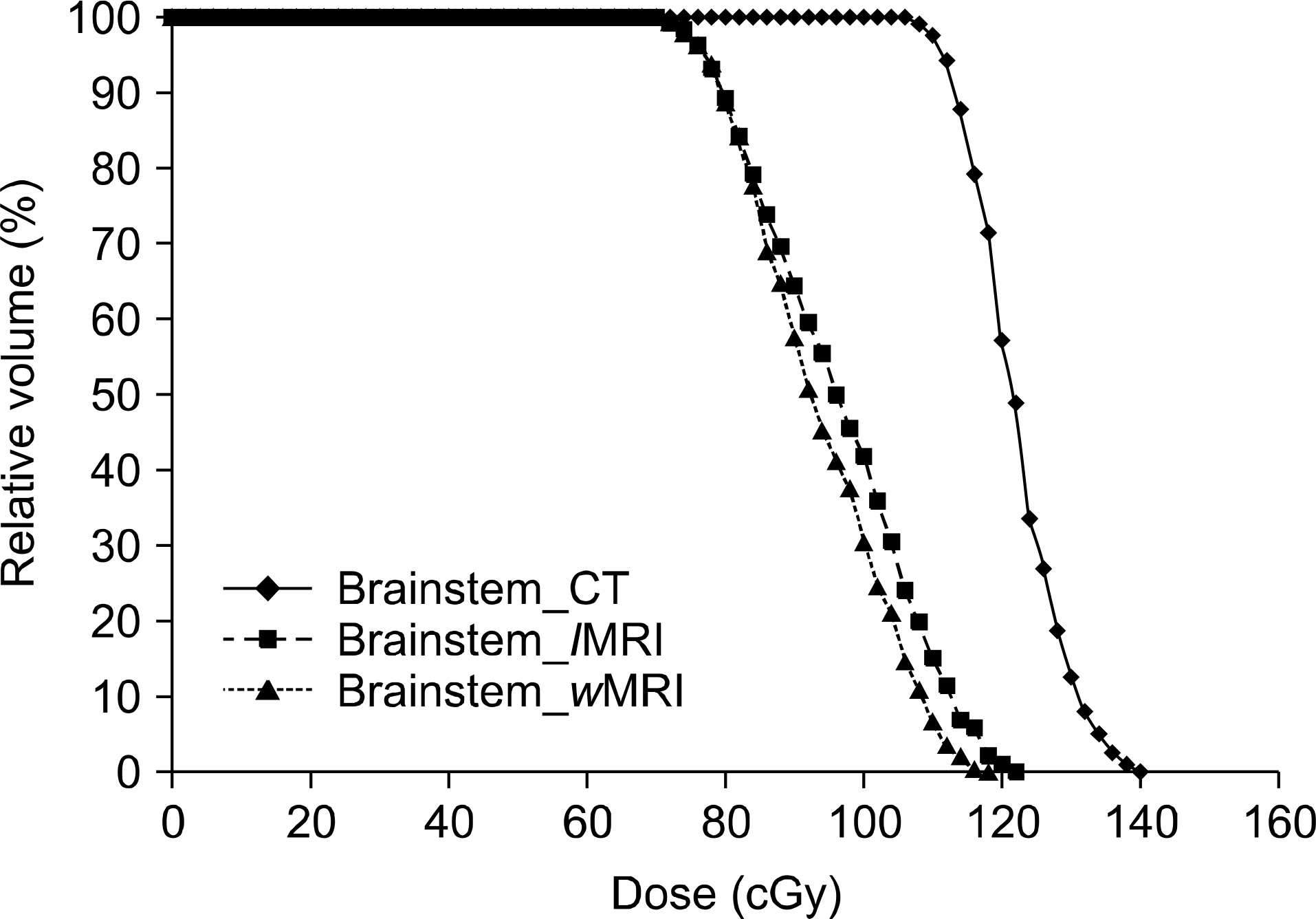
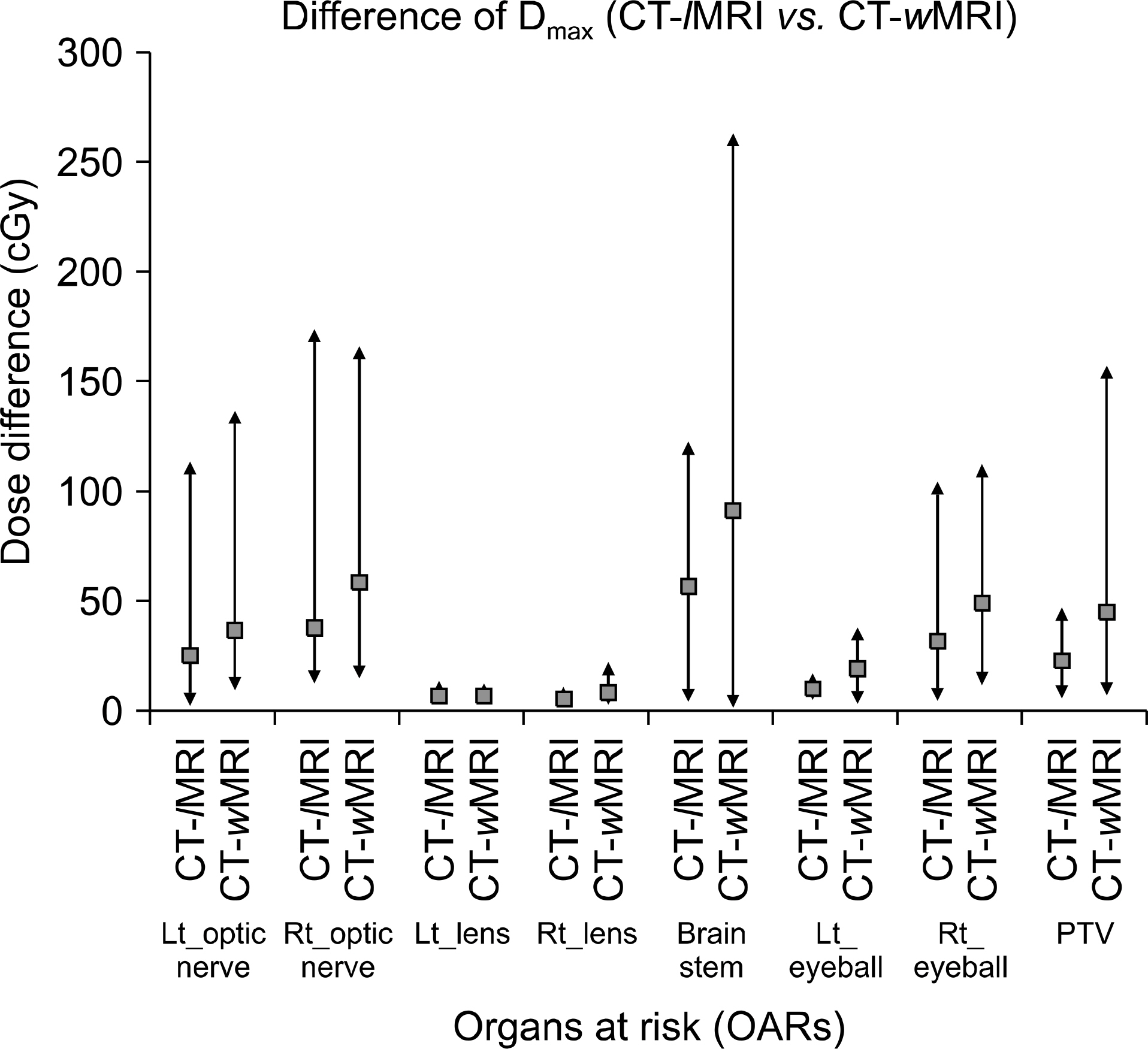
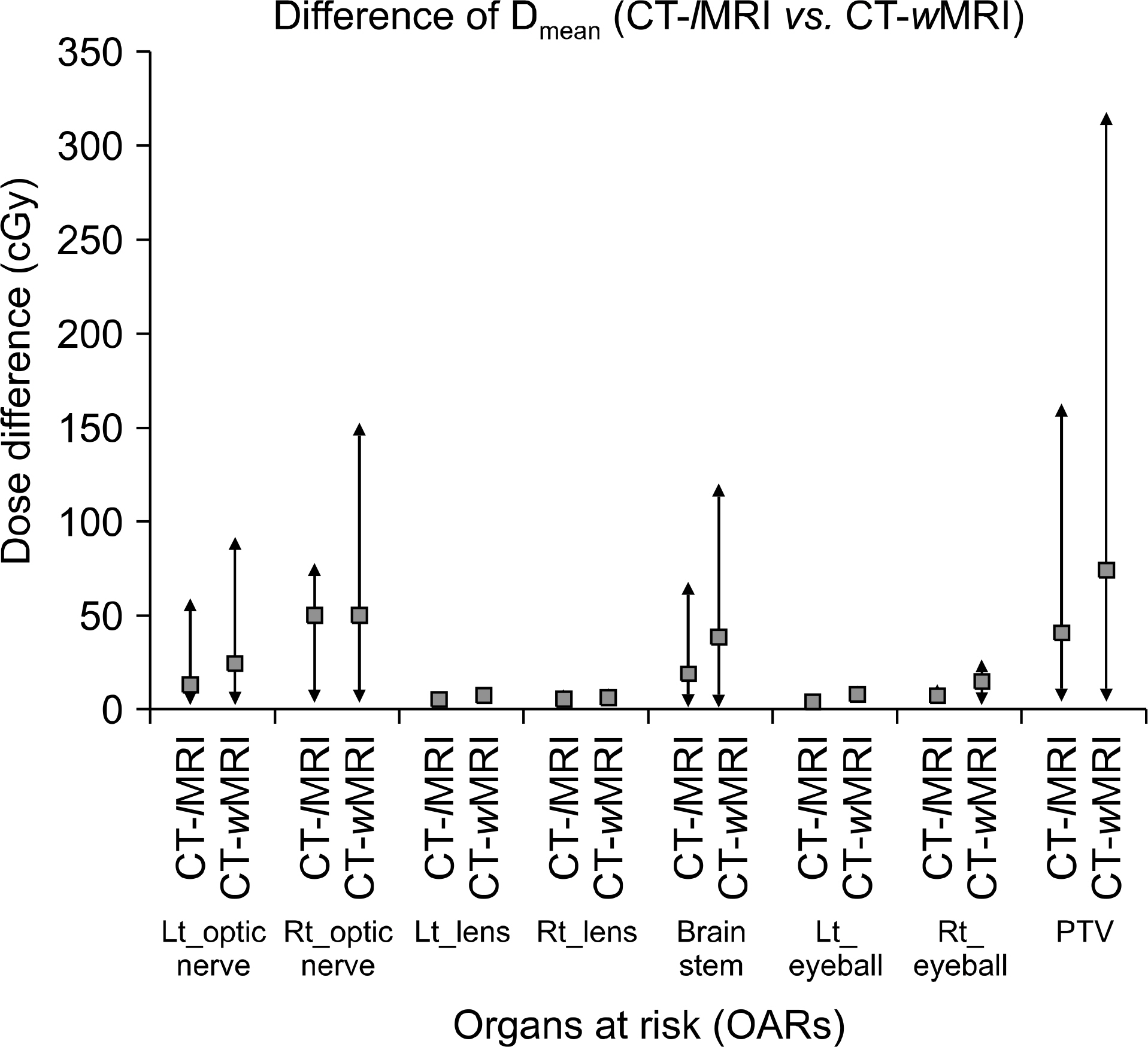
- In the intracranial regions, an accurate delineation of the target volume has been difficult with only the CT data due to poor soft tissue contrast of CT images. Therefore, the magnetic resonance images (MRI) for the delineation of the target volumes were widely used. To calculate dose distributions with MRI-based RTP, the electron density (ED) mapping concept from the diagnostic CT images and the pseudo CT concept from the MRI were introduced. In this study, the look up table (LUT) from the fifteen patients' diagnostic brain MRI images was created to verify the feasibility of MRI-based RTP. The dose distributions from the MRI-based calculations were compared to the original CT-based calculation. One MRI set has ED information from LUT (lMRI). Another set was generated with voxel values assigned with a homogeneous density of water (wMRI). A simple plan with a single anterior 6MV one portal was applied to the CT, lMRI, and wMRI. Depending on the patient's target geometry for the 3D conformal plan, 6MV photon beams and from two to five gantry portals were used. The differences of the dose distribution and DVH between the lMRI based and CT-based plan were smaller than the wMRI-based plan. The dose difference of wMRI vs. lMRI was measured as 91 cGy vs. 57 cGy at maximum dose, 74 cGt vs. 42 cGy at mean dose, and 94 cGy vs. 53 at minimum dose. The differences of maximum dose, minimum dose, and mean dose of the wMRI-based plan were lower than the lMRI-based plan, because the air cavity was not calculated in the wMRI-based plan. These results prove the feasibility of the lMRI-based planning for brain tumor radiation therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jonsson JH, Karlsson MG, Karlsson M, Nyholm T. Treatment planning using MRI data: an analysis of the dose calculation accuracy for different treatment regions. Radiat Oncol. 5:62. 2010.
Article2. Prabhakar R, Julka PK, Ganesh T, Munshi A, Joshi RC, Rath G. Feasibility of using MRI alone for 3D radiation treatment planning in brain tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 37(6):405–411. 2007.
Article3. Stanescu T, Hans-Sonke J, Stavrev P, Fallone BG. 3T MR-based treatment planning for radiotherapy of brain lesions. Radiat Oncol. 40(2):125–132. 2006.4. Chen L, Price RA Jr, Wang L, et al. MRI-based treatment planning for radiotherapy: dosimetric verification for prostate IMRT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60(2):636–647. 2004.
Article5. Wang C, Chao M, Lee L, Xing L. MRI-based treatment planning with electron density information mapped from CT. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 7(5):341–347. 2008.6. Miga MI, Boettger T, Nyholm T, et al. Radiation therapy planning and simulation with magnetic resonance images. Medical Imaging. 6918:19181C. 2008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment Planning Correction Using MRI in the Radiotherapy of Cervical Cancer
- Development of Dose Verification Method for In vivo Dosimetry in External Radiotherapy
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective
- The Role of Positron Emission Tomography(PET) in Radiation Treatment Planning
- Feasibility and Efficacy of Adaptive Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Planning according to Tumor Volume Change in Early Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy