Surgical Treatment of Root Injury after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bongseng Memorial Hospital, Pusan, Korea. heojkos@hitel.net
- KMID: 1897091
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2002.9.1.54
Abstract
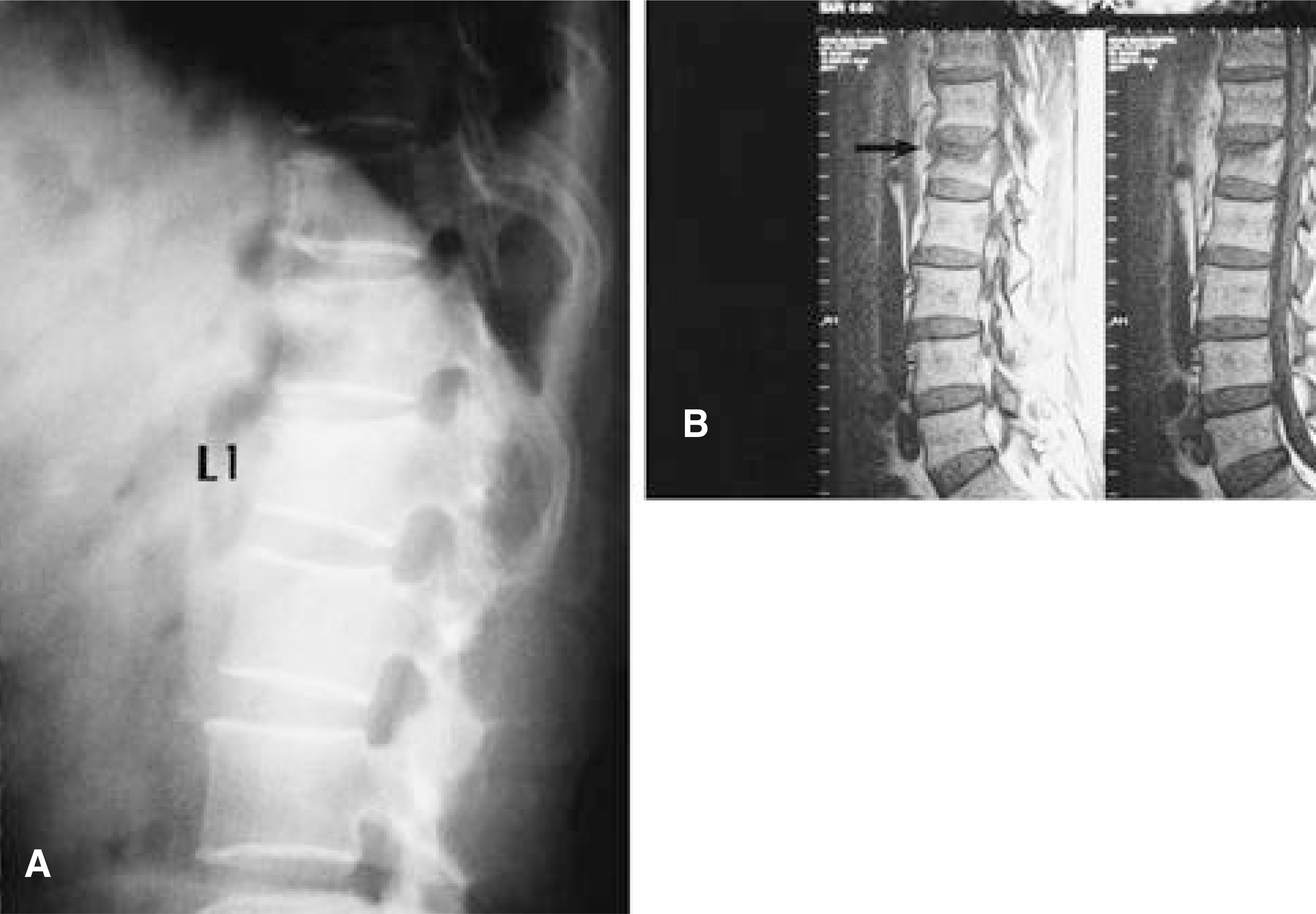
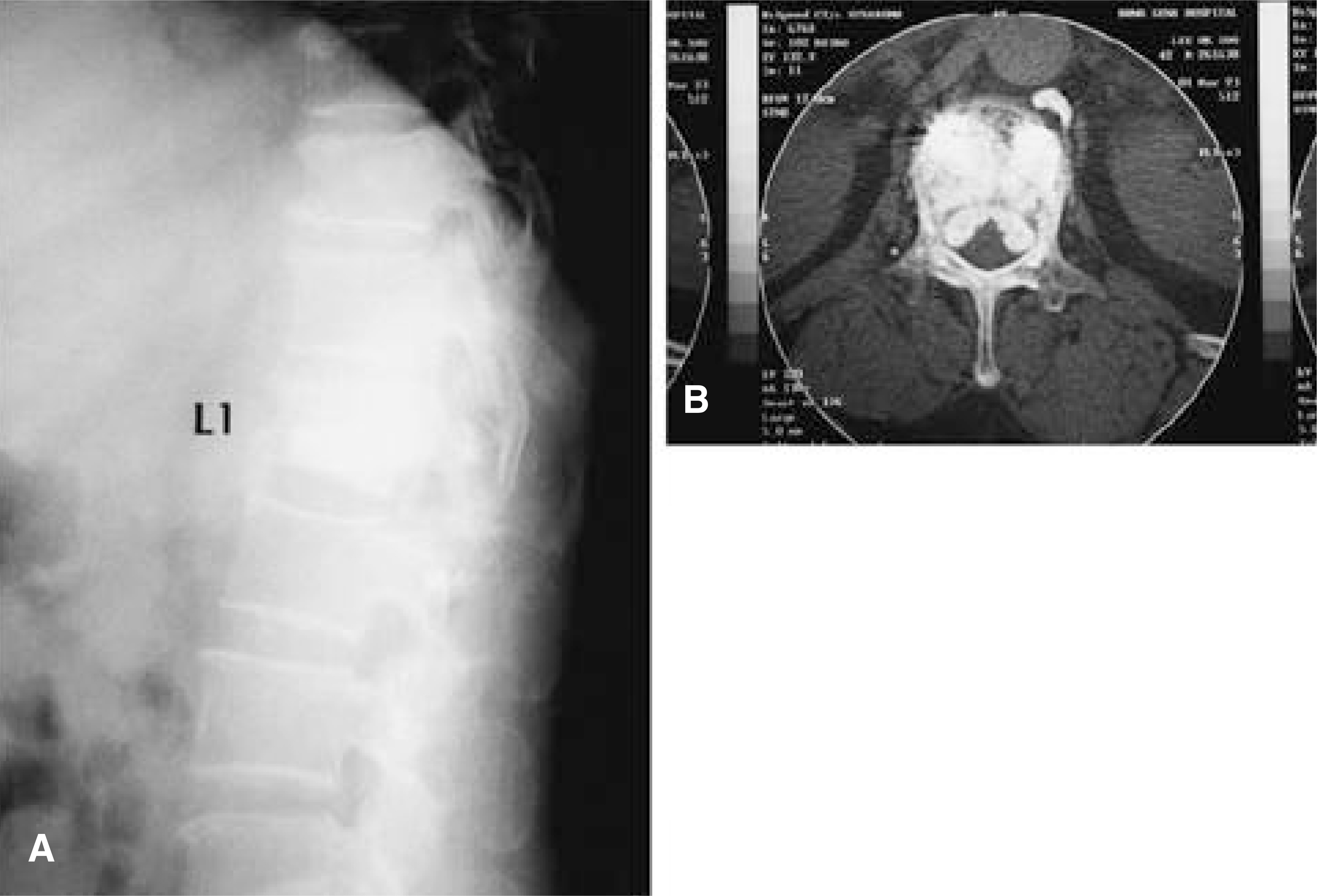
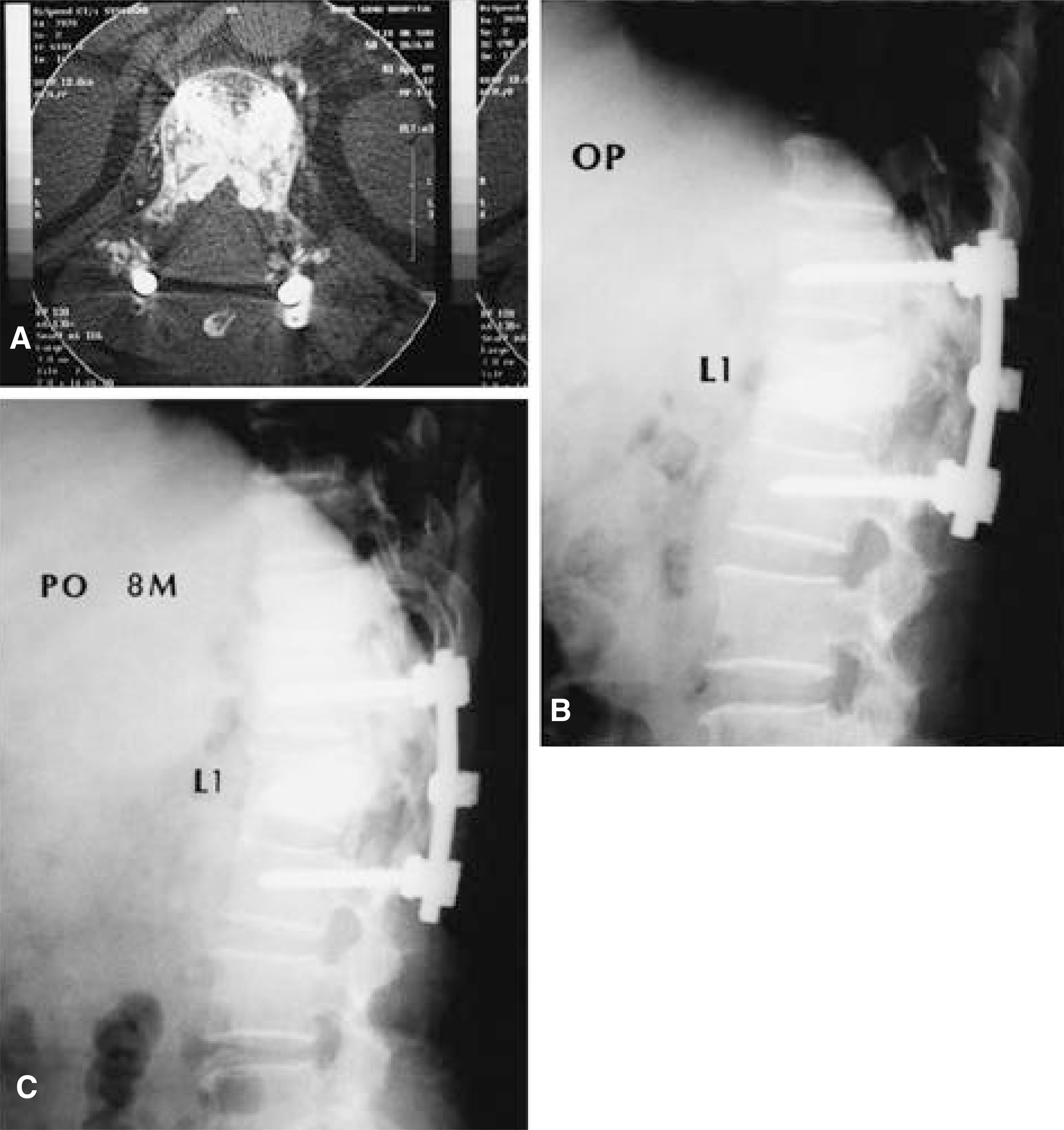
- Percutaneous vertebroplasty using PMMA was first performed in France by Deramond in 1984. It was later used to treat vertebral compression fractures caused by osteoporosis. With osteoporotic compression fractures, reported complication were few and minor. However, the principal risk of such a percutaneous technique is the leak of PMMA into the spinal canal or neural foramina. Despite being uncommon, major neurologic complications demand surgical interventions that prevent permanent neurologic dysfunction. We experienced a case of root compression during percutaneous vertebroplasty, which was treated by early surgical posterior decompression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Revision Surgery after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
Kee-Yong Ha, Ki-Won Kim, Young-Hoon Kim, In-Soo Oh, Sang-Won Park
Clin Orthop Surg. 2010;2(4):203-208. doi: 10.4055/cios.2010.2.4.203.Long term outcome of Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
Chung hwan Kim, Young Joon Choi, Jae kwang Hwang, Kyung-hwan Kim, Jong ha Lee, Jung suk Song
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005;12(1):69-74. doi: 10.4184/jkss.2005.12.1.69.Long Term Results of Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
Yong Seung Oh, Kyu Yeol Lee, Jong Yeon Seo, Sun Hyo Kim
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2013;20(3):86-90. doi: 10.4184/jkss.2013.20.3.86.Cement Leakage after Vertebroplasty; Correlation with Patterns of Compression Fractures and Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Seong Wan Kim, Young joon Ahn, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi, Se Hyuk Im, Ye Hyun Lee, Sung Wook Yang, Seok Woo Nam, Hyun See Kim
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2014;21(4):146-151. doi: 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.4.146.
Reference
-
1). Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, Mccann RM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine. 25:923–928. 2000.
Article2). Cotton A, Boutry N, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics. 18:311–323. 1998.
Article3). Cotton A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical followup. Radiology. 200:525–530. 1996.
Article4). Deramond H, Depreister C, Galibert P, Gars DL. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacry -late;technique, indication, and results. Radiologic clinics of north america. 36:533–546. 1998.5). Harrington KD. Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. J Bone Joint Surg. 83:1070–1073. 2001.
Article6). Jensen ME, Avery JE, Mathis JM, Kallmess DF, Cloft HJ, Dio JE. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fracture: technical aspects. Am J Neuroradiol. 18:1897–1904. 1997.7). Liebschner MAK, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine. 26:1547–1554. 2001.
Article8). Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol. 22:373–382. 2001.9). Mathis JM, Eckel TS, Belkoff SM, Deramond H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a therapeutic option for pain associated with vertebral compression fracture. J Back Musculoskel Rehab. 13:11–17. 1999.
Article10). Ratliff J, Nguyen T, Heiss J. Root and spinal cord compression from methylmethacrylate vertebroplasty. Spine. 26:300–302. 2001.
Article11). Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E. Spinal metastasis: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology. 199:241–247. 1996.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lumbar Root Injury by the Leakage of Bone Cement after the Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A case report
- Root Injury after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Compression Fracture: Case Report
- Fatal Hemothorax Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
- Neurologic Complication after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: A Case Report
- Pyogenic Spondylitis after Vertebroplasty: A Report of Two Cases