J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2005 Mar;12(1):12-21. 10.4184/jkss.2005.12.1.12.
Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Our Lady of Mercy Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kang-Nam St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyh@cmc.cuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1897016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2005.12.1.12
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to investigate the differences in the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in degenerative scoliosis compared with other degenerative disc disease of the spine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The intervertebral disc materials were obtained during discectomies. Six, 13 and 12 cases of herniated nucleus pulposus, spinal stenosis and degenerative lumbar scoliosis, respectively, were included in the experimental group. The expression of MMP-3 was evaluated three times that of the means, in the immunohistochemical staining, western blotting using anti human MMP-3 antibody and RT-PCR with MMP-3 primer, respectively.
RESULTS
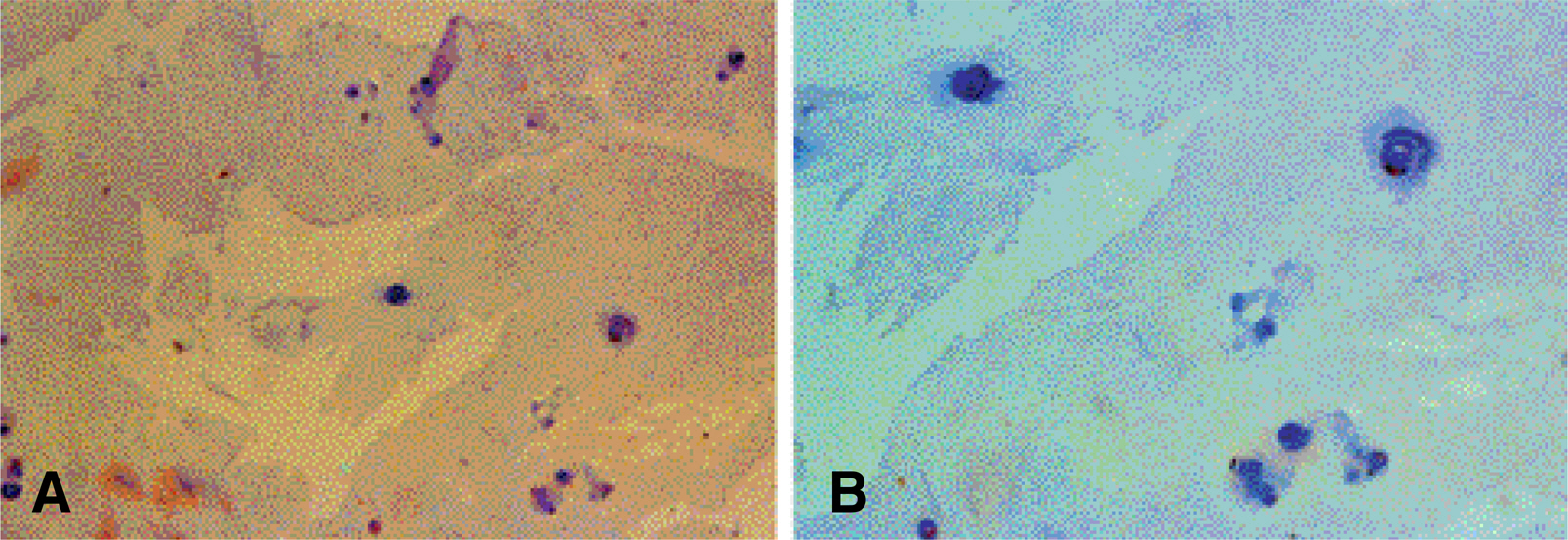
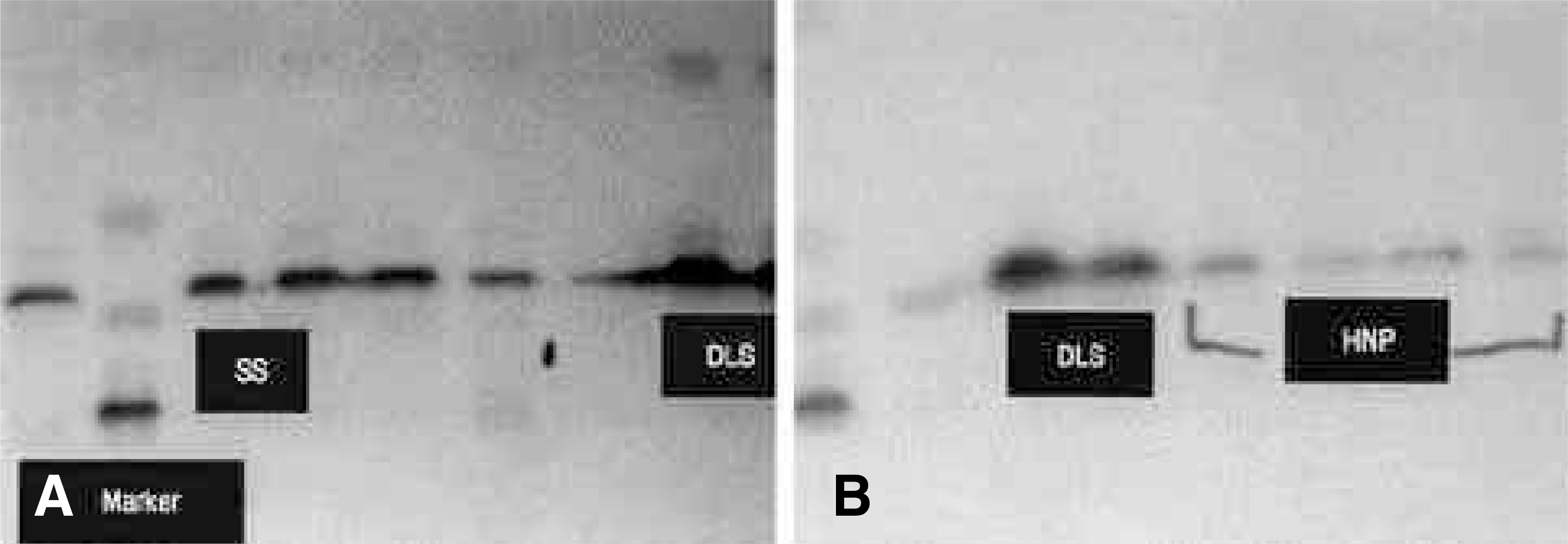
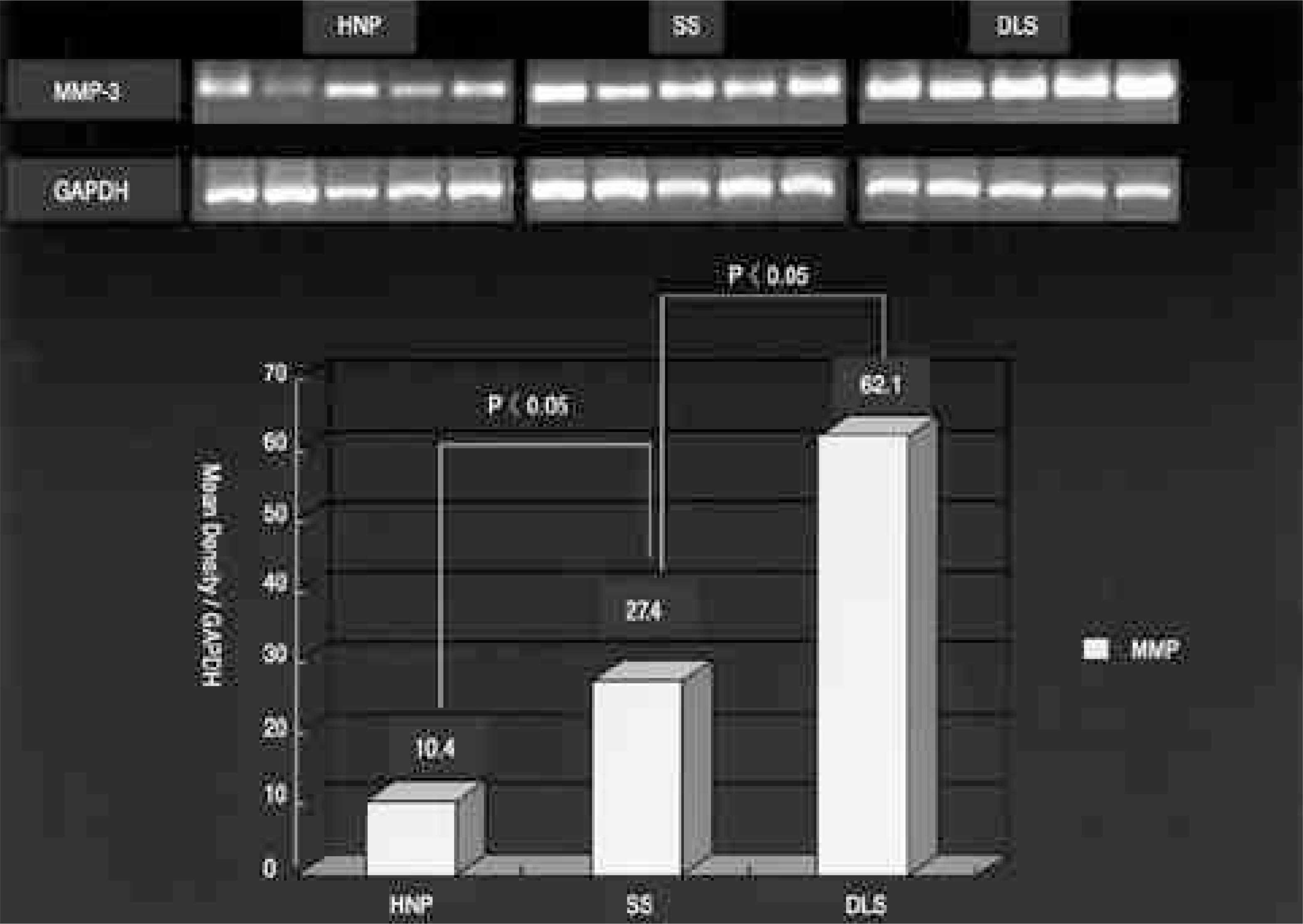
On the immunohistochemical stains, extensive and strong staining was noted in the discs of degenerative lumbar scoliosis compared to those with spinal stenosis and HNP. In the western blotting, greater expression of MMP-3 was noted in the discs of degenerative lumbar scoliosis (mean optical density: 20.68) than in other degenerative disc diseases (SS: 6.24, HNP: 2.0). In the RT-PCR, a similar result was shown (DLS: 62.1, SS: 27.4 and HNP: 10.4). There were statistically significant differences between degenerative lumbar scoliosis and degenerative disc disease (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Rapid degeneration of the intervertebral disc might be an important factor in the pathogenesis of degenerative lumbar scoliosis. MMP-3 could be a key enzyme for the rapid degeneration of the intervertebral discs, especially in degenerative lumbar scoliosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Ala-Kokko L. Genetic risk factors for lumbar disc disease. Ann Med. 2002; 34:42–47.
Article2). Crean JK, Roberts S, Jaffray DC, Eisenstein SM, Duance VC. Matrix metalloproteinase in the human intervertebral disc: Role in disc degeneration and scoliosis. Spine. 1997; 22:2877–84.3). Frymoyer JW, Cats-Baril WL. An overview of the inci -dence and costs of low back pain. Orthop Clin N Am. 1991; 22:263–271.4). Gries NC, Berlemann U, Moore RJ, Vernon-Roberts B. Early histologic changes in lower lumbar disc and facet joints and their correlation. Eur Spine J. 2000; 9:23–29.5). Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Coonard RW. Degenerative adult onset scoliosis. Spine. 1988; 13:241–245.
Article6). HA K-Y, JANG J-H, LEE J-Y. Expression of estrogen receptor on ligament flavum and facet joint capsule in degenerative spinal stenosis. J Kor Orthop Assoc. 2000; 35:263–269.7). HA K-Y, HWANG S-H, KIM Y-H, et al. Expression of estrogen receptor gene in degenerative spinal stenosis. J Kor Orthop Assoc. 2003; 38:60–65.
Article8). Handa T, Ishihara H, Ohshima H, Osada R, Tsuji H, Obata K. Effects of Hydrostatic pressure on matrix synthe -sis and matrix metalloproteinase production in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine. 1997; 22:1085–1091.9). Haro H, Crawford HC, Fingleton B, MacDougall JR, Shinomiya K, Spengler DM, Matrisian LM. Ma t rix metalloproteinase-3-dependent generation of a macrophage chemotattractant in a model of herniated disc reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 2000; 105:133–141. 2000.10). Kanemoto M, Hukuda S, Komiya Y, Katsuura A, Nish-ioka J. Immunohistochemical study of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in human intervertebral discs. Spine. 1996; 21:1–8.
Article11). Kawaguchi Y, Kanamori M, Ishihara H, Ohmori K, Matsui H, Kimura T. The association of lumbar disc disease with vitamin-D receptor gene polymorphism. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]. 2002; 84-A:2022–2028.
Article12). Liu J, Roughley PJ, Mort JS. Identification of human intervertebral disc stromelysin and its involvement in matrix degradation. J Orthop Res. 1991; 9:568–575.
Article13). Matsui Y, Maeda M, Nakagami W, Iwata H. T h e involvement of matrix metalloproteinase and inflammation in lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 1998; 23:863–869.14). Minoru D, Takako K, Takuma O, Nobuzo M. Influence of macrophage infiltration of herniated disc tissue on the production of matrix metalloproteinases leading to disc resorption. Spine. 2001; 26:1522–1527.
Article15). Mizel S, Dayer- JM, Krane SM, Mergenhagen SE. Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lympho -cyte-activating factor (interleukin-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998; 78:2474–2477.16). Modic MT, Masary TJ, Ross JS, Carter JR. Imaging of degenerative disk disease. Radiology. 1988; 168:177–186.
Article17). Mutata Y, Takahashi k, Hanaoka E, et al. Change in scoliotic curvaqture and lordotic angle during the early phase of degenerative lumbar soliosis. Spine. 2002; 27:2268–2273.18). Naylor A, Happey F, Turner RL, Shentail RD, West DC, Richardson C. Enzymic and immunological activity in the intervertebral disc. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975; 6:51–58.
Article19). Nemoto O, Yamagishi M, Yamada H, Kikuchi T, Takaishi H. Matirx metalloproteinase-3 production by human degenerated disc. J Spinal Disord. 1997; 10:493–498.20). Norcross JP, Lester GE, Weinhold P, Dahners LE. An in vivo model of degenerative disc disease. J Orth Res. 2003; 21:183–188.
Article21). Pritchett JW, Bortel DT. Degenerative symptomatic lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 1993; 18:700–703.
Article22). Robin GC, Span Y, Steinberg R. Scoliosis in the elderly: A followup study. Spine. 1982; 7:355–359.23). Takahashi M, Haro H, Wakabayashi T, Kawa-uchi T, Komori H, Shinomiya K. The association of degeneration of the intervertebral disc with 5a/6a polymorphism in the promoter of the human matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene. J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 2001; 83-B:491–495.
Article24). Videman T, Gibbons LE, Battie MC, Maravilla K, Vanninen E, Leppavuori J, Kaprio J, Peltonen L. The relative roles of intragenic polymorphism of the vitamin D receptor gene in lumbar spine degeneration and bone density. Spine. 2001; 26:7–12.25). Ye S, Eriksson P, Hamsten A, Kurkinen M, Humphries SE, Henney AM. Progression of coronary atherosclero -sis is associated with a common genetic variant of the human stromelysin-1 promoter which results in reduced gene expression. J Bio Chem. 1996; 271:13055–13060.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Differences in Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis and Spinal Stenosis
- Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Asthma
- The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1, -2 in the Degenerative Spinal Diseases
- EGCC inhibits tumor growth by inbibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 induction in UM-SCC-1 cells
- Surgical Management of Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis