J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2013 Dec;20(4):169-177. 10.4184/jkss.2013.20.4.169.
Ideal Insertion Point and Angle of Cervical Pedicular Screws in Korean
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Korea. par73@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1896946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2013.20.4.169
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
Using computed tomography, it is to measure pedicle size of lower cervical spine in Koreas to find ideal insertion point and angle in fixating pedicular screws. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Although techniques in pedicular screw fixation and pedicle's anatomical shape in foreign populations have been well documented and studied, no anatomical study on lower cervical pedicle in Korean population has been reported.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
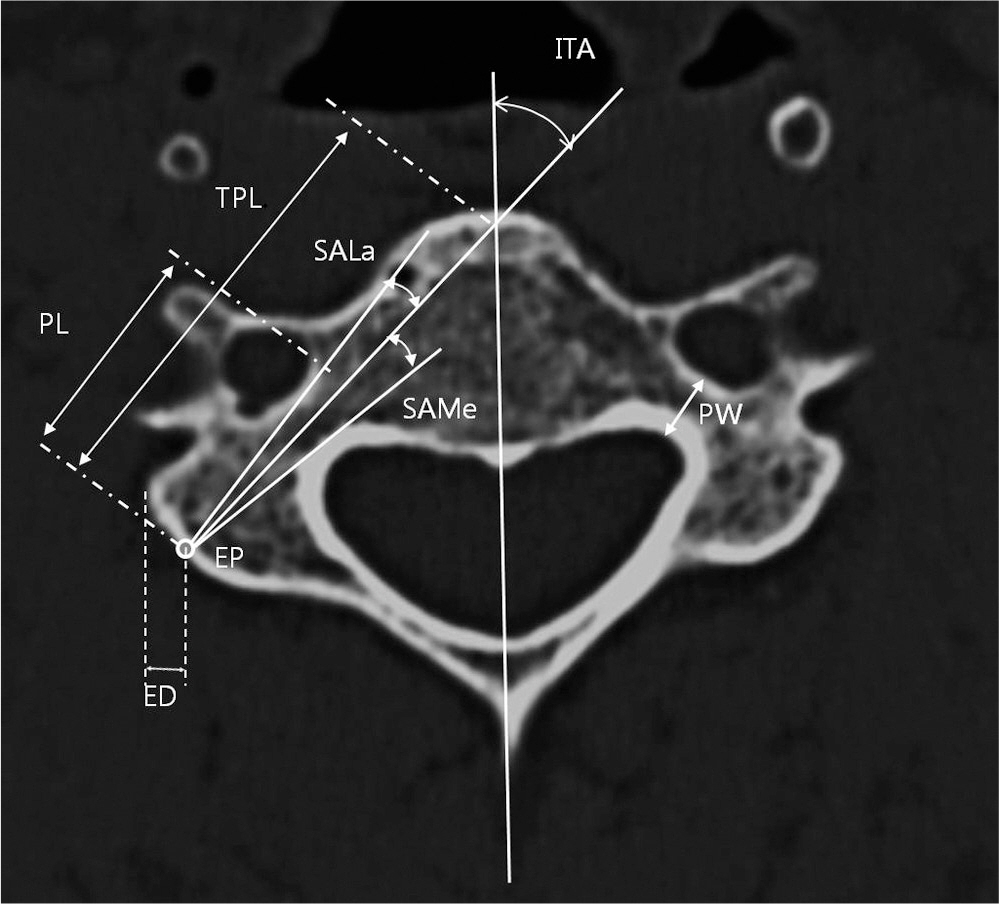
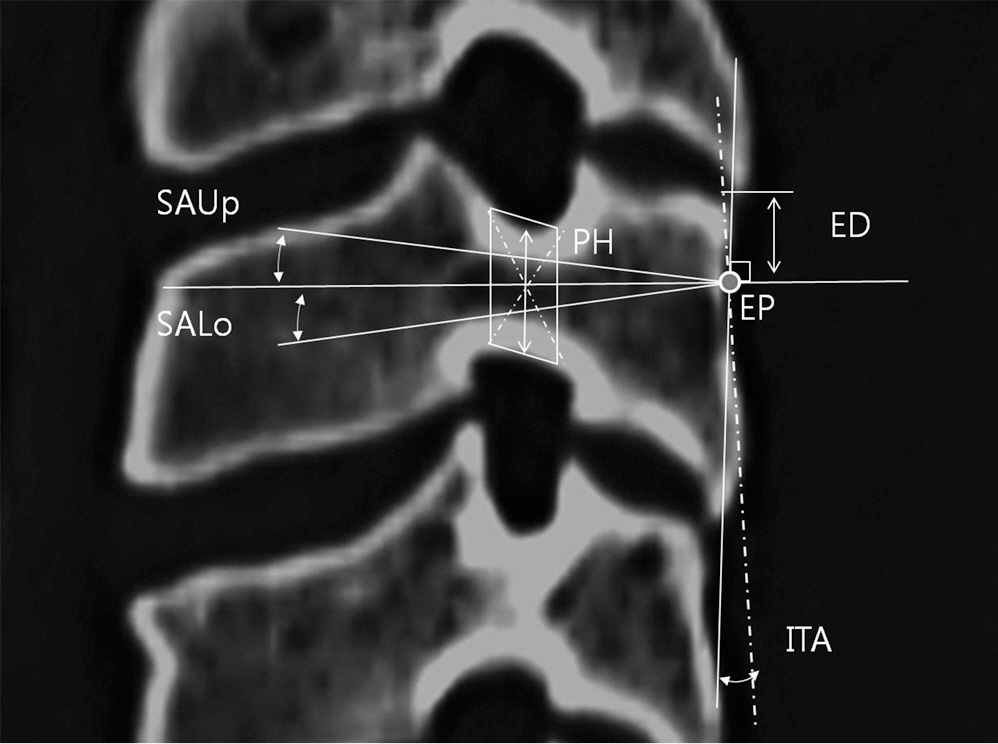
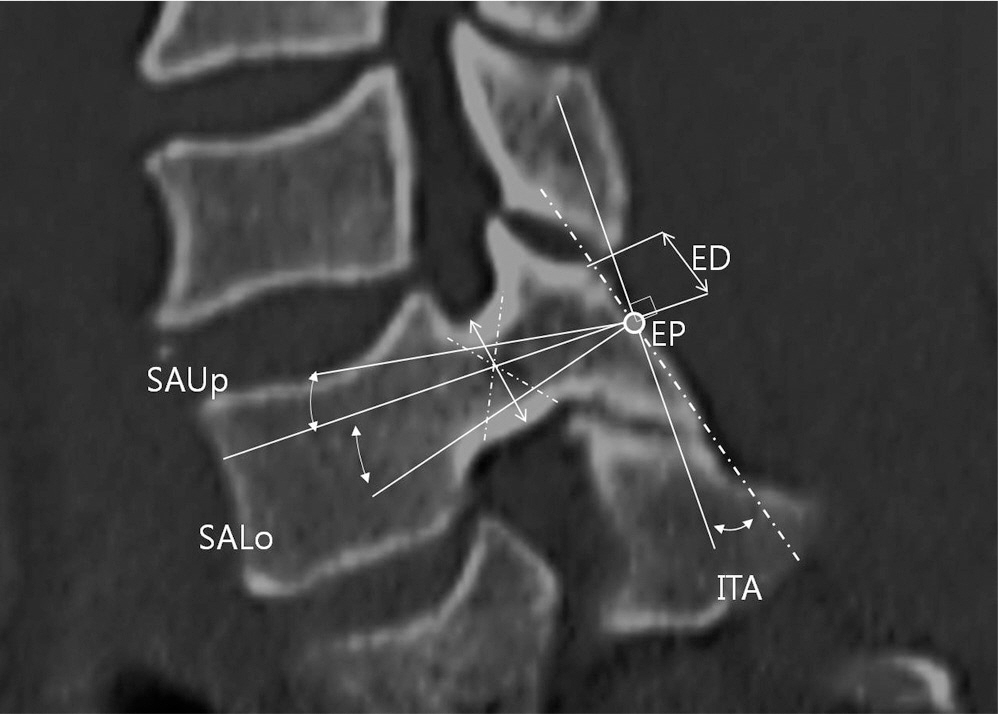
A total of 180 patients with computed tomography taken at our institution were selected for the study. Width, total length, and length of pedicle, insertion point and angle, and safe insertion angles were measured on axial view. On sagittal view, height of pedicle, insertion point and angle, and safe insertion angles were determined.
RESULTS
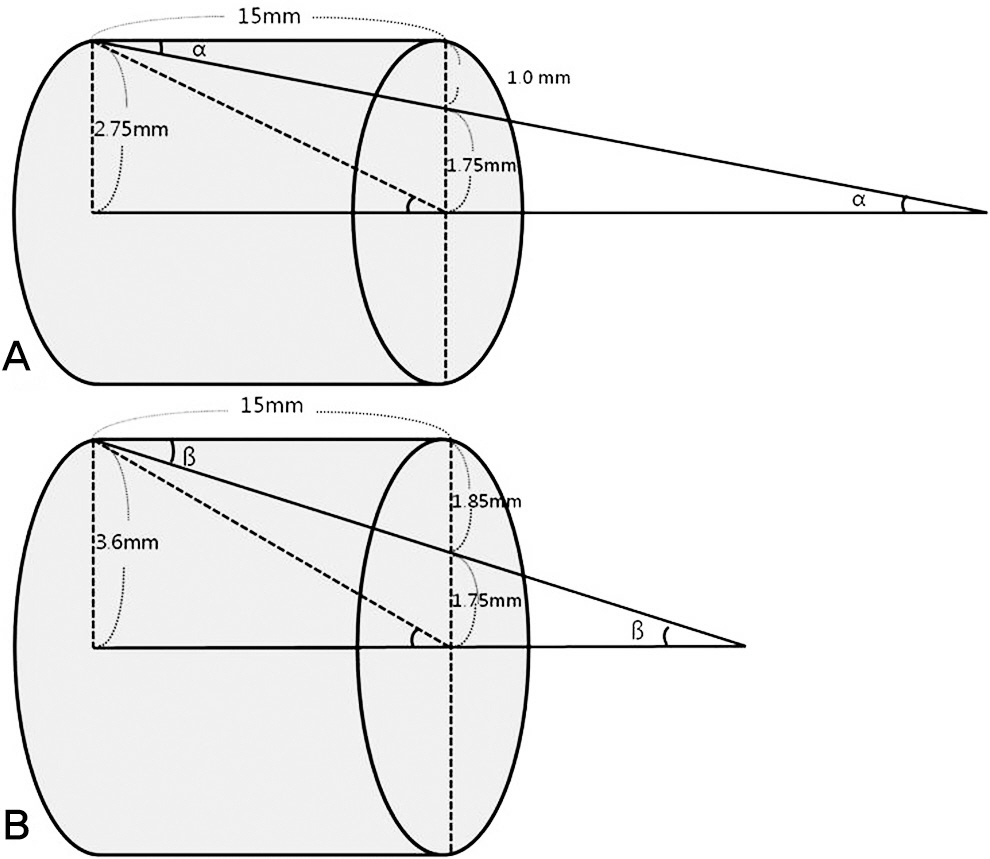
Mean height of study subject was 164.2cm. Mean width of pedicle was 5.5mm, mean height 7.2mm, mean total length 31.2mm, and mean length 14.8mm. Mean insertion point from 3rd to 7th cervical spines was medially 3.3mm from lateral mass and downward 4.7mm from margin of upper facet. Mean insertion angles from 3rd to 7th cervical spines were 41.6degrees axially and 6.4degrees sagittally. Calculated safe insertion angles were 8degrees on medial and lateral sides and 14degrees on superior and inferior sides.
CONCLUSIONS
Using computed tomography images, ideal insertion point and angle were measured for pedicular screw insertion, but, due to individual variation, preoperative measurement of insertion point and angle on computed tomography is necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Montesano PX, Jauch E, Anderson PA, Benson DR, Han-son B. Biomechanics of cervical spine internal fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991; 16(3 Suppl):10–6.
Article2. Krag MH, Weaver DL, Beynnon BD, Haugh LD. Mor-phometry of the thoracic and lumbar spine related to pedicular screw placement for surgical spinal fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13:27–32.3. Kanalziora F, Pflugmacher R, Scholz M, et al. Posterior stabilization of subaxial cervical spine trauma: indications and techniques. Injury. 2005; 36(Suppl 2):36–43.
Article4. Kotani Y, Cunningham BW, Abumi K, McAfee PC. Biomechanical analysis of cervical stabilization systems: an assessment of pedicular screw fixation in the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2529–39.5. Abumi K, Shono Y, Ito M, Taneichi H, Katani H, Kaneda K. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in reconstructive surgery of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:962–9.
Article6. Kast E, Mohr K, Richter HP, Bö rm W. Complications of pedicular screw fixation in the cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:327–34.7. Neo M, Sakamoto T, Fujibayashi S, Nakamura T. The clinical risk of vertebral artery injury from cervical pedicle screws inserted in degenerative vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2800–5.
Article8. Chazono M, Soshi S, Inoue T, Kida Y, Ushiku C. Anatomical considerations for cervical pedicle screw insertion: the use of multiplanar computerized tomography reconstruction measurements. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4:472–7.
Article9. Onibokun A, Khoo LT, Bistazzoni S, Chen NF, Sassi M. Anatomical considerations for cervical pedicle screw insertion: the use of multiplanar computerized tomography measurements in 122 consecutive clinical cases. Spine J. 2009; 9:729–34.
Article10. Miyamoto H, Uno K. Cervical pedicle screw insertion using a computed tomography cutout technique. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009; 11:681–7.
Article11. Su P, Ma R, Li C, Liu S, Huang D. Pedicle screw fixation of the cervical spine: guidance by computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 462:99–104.12. Liu J, Napolitano JT, Ebraheim NA. Systematic review of cervical pedicle dimensions and projections. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:E1373–80.
Article13. Panjabi MM, Shin EK, Chen NC, et al. Internal morphol-ogy of human cervical pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1197–205.
Article14. Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Knight T, Yeasting RA. Morphomet-ric evaluation of lower cervical pedicle and its projection. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:1–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rate of Pedicle Disruption after Screw Fixation
- Insertion Angle of Pedicle Screws in the Subaxial Cervical Spine: The Analysis of Computed Tomography-Navigated Insertion of Pedicle Screws
- Measurements of Lateral Mass of Cervical Spine Using MRI for Lateral Mass Screw Fixation
- Lateral Mass Screw Fixation in the Cervical Spine: Introducing a New Technique
- Surface Anatomical Landmark and Optimal Insertion Angle in Cervical Epidural Block