J Clin Neurol.
2015 Jul;11(3):262-267. 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.3.262.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Anterior-Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Eginition Hospital, University of Athens, Athens, Greece. granavan@yahoo.com
- KMID: 1894564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.3.262
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
In contrast to the posterior- and horizontal-canal variants, data on the frequency and therapeutic management of anterior-canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (AC-BPPV) are sparse. To synthesize the existing body of evidence into a systematic review regarding the incidence and treatment of AC-BPPV.
METHODS
Systematic search of medical databases employing predefined criteria, using the term "anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo."
RESULTS
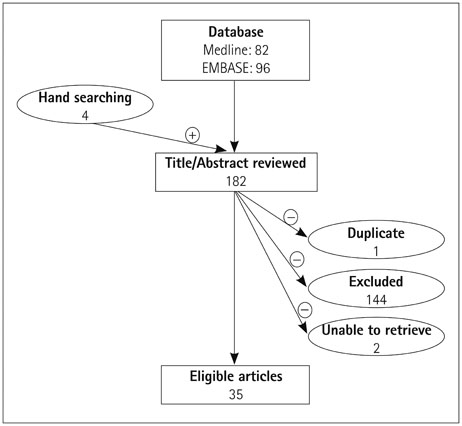
The electronic search retrieved 178 unique citations, 31 of which were considered eligible for further analysis. Analysis of the collected data revealed an estimated occurrence of AC-BPPV among benign paroxysmal positional vertigo patients of 3% (range 1-17.1%). No controlled therapeutic trials could be identified, and so the analysis was focused on uncontrolled case series. Treatment was categorized into three groups: Epley maneuver, Yacovino maneuver, and specific, nonstandard maneuvers described in individual articles. All three categories demonstrated success rates of over 75%, and the overall sample-size-weighted mean was 85.6%.
CONCLUSIONS
The present analysis demonstrated that AC-BPPV comprises about 3% of all BPPV cases. It can be treated safely using the Epley, Yacovino, and other maneuvers with rates of symptom resolution lying in the range of that reported for the other, more frequent canal variants. Multicenter controlled trials are needed in order to develop evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of AC-BPPV.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Incidence and Clinical Significance of Positional Downbeat Nystagmus in Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Eun Hye Oh, Jae-Hoon Lee, Hyo-Jung Kim, Seo-Young Choi, Kwang-Dong Choi, Jae-Hwan Choi
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(2):143-148. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.2.143.
Reference
-
1. Mizukoshi K, Watanabe Y, Shojaku H, Okubo J, Watanabe I. Epidemiological studies on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Japan. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1988; 447:67–72.
Article2. von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F, Feldmann M, Ziese T, Lempert T, et al. Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:710–715.
Article3. Helminski JO, Zee DS, Janssen I, Hain TC. Effectiveness of particle repositioning maneuvers in the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2010; 90:663–678.
Article4. Hunt WT, Zimmermann EF, Hilton MP. Modifications of the Epley (canalith repositioning) manoeuvre for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 4:CD008675.
Article5. van Duijn JG, Isfordink LM, Nij Bijvank JA, Stapper CW, van Vuren AJ, Wegner I, et al. Rapid systematic review of the epley maneuver for treating posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; 150:925–932.
Article6. von Brevern M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Semin Neurol. 2013; 33:204–211.
Article7. Fife TD, Iverson DJ, Lempert T, Furman JM, Baloh RW, Tusa RJ, et al. Practice parameter: therapies for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2008; 70:2067–2074.
Article8. Kim JS, Zee DS. Clinical practice. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1138–1147.9. van den Broek EM, van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, Bruintjes TD. Systematic review: efficacy of gufoni maneuver for treatment of lateral canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with geotropic nystagmus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; 150:933–938.10. Bertholon P, Bronstein AM, Davies RA, Rudge P, Thilo KV. Positional down beating nystagmus in 50 patients: cerebellar disorders and possible anterior semicircular canalithiasis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002; 72:366–372.
Article11. Anagnostou E, Mandellos D, Limbitaki G, Papadimitriou A, Anastasopoulos D. Positional nystagmus and vertigo due to a solitary brachium conjunctivum plaque. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006; 77:790–792.
Article12. Anagnostou E, Varaki K, Anastasopoulos D. A minute demyelinating lesion causing acute positional vertigo. J Neurol Sci. 2008; 266:187–189.
Article13. Aw ST, Todd MJ, Aw GE, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM. Benign positional nystagmus: a study of its three-dimensional spatio-temporal characteristics. Neurology. 2005; 64:1897–1905.
Article14. Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ. Complications of the canalith repositioning procedure. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 122:281–286.
Article15. Califano L, Salafia F, Mazzone S, Melillo MG, Califano M. Anterior canal BPPV and apogeotropic posterior canal BPPV: two rare forms of vertical canalolithiasis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014; 34:189–197.16. Tomaz A, Ganança MM, Ganança CF, Ganança FF, Caovilla HH, Harker L. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: concomitant involvement of different semicircular canals. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009; 118:113–117.
Article17. Kerrigan MA, Costigan MF, Blatt KJ, Mathiason MA, Domroese ME. Prevalence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in the young adult population. PM R. 2013; 5:778–785.
Article18. Perez-Fernandez N, Martinez-Lopez M, Manrique-Huarte R. Vestibulo-ocular reflex in patients with superior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Acta Otolaryngol. 2014; 134:485–490.
Article19. Balatsouras DG. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with multiple canal involvement. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012; 33:250–258.
Article20. Honrubia V, Baloh RW, Harris MR, Jacobson KM. Paroxysmal positional vertigo syndrome. Am J Otol. 1999; 20:465–470.21. Mosca F, Morano M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, incidence and treatment. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2001; 118:95–101.22. Korres S, Balatsouras DG, Kaberos A, Economou C, Kandiloros D, Ferekidis E. Occurrence of semicircular canal involvement in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2002; 23:926–932.
Article23. Rahko T. The test and treatment methods of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and an addition to the management of vertigo due to the superior vestibular canal (BPPV-SC). Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2002; 27:392–395.
Article24. Crevits L. Treatment of anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo by a prolonged forced position procedure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:779–781.
Article25. Lopez-Escamez JA, Molina MI, Gamiz M, Fernandez-Perez AJ, Gomez M, Palma MJ, et al. Multiple positional nystagmus suggests multiple canal involvement in benign paroxysmal vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005; 125:954–961.
Article26. Prokopakis EP, Chimona T, Tsagournisakis M, Christodoulou P, Hirsch BE, Lachanas VA, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: 10-year experience in treating 592 patients with canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope. 2005; 115:1667–1671.
Article27. Kim YK, Shin JE, Chung JW. The effect of canalith repositioning for anterior semicircular canal canalithiasis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2005; 67:56–60.
Article28. Cakir BO, Ercan I, Cakir ZA, Civelek S, Sayin I, Turgut S. What is the true incidence of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 134:451–454.
Article29. Lopez-Escamez JA, Molina MI, Gamiz MJ. Anterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and positional downbeating nystagmus. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006; 27:173–178.
Article30. Moon SY, Kim JS, Kim BK, Kim JI, Lee H, Son SI, et al. Clinical characteristics of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Korea: a multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:539–543.
Article31. Lorin P. Treatment of anterior semi-circular canalithiasis by a sedimentation procedure in a vertical rotatory chair. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2007; 124:184–188.
Article32. Celebisoy N, Polat F, Akyurekli O. Clinical features of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Western Turkey. Eur Neurol. 2008; 59:315–319.
Article33. Yacovino DA, Hain TC, Gualtieri F. New therapeutic maneuver for anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2009; 256:1851–1855.
Article34. Ogawa Y, Suzuki M, Otsuka K, Shimizu S, Inagaki T, Hayashi M, et al. Positional and positioning down-beating nystagmus without central nervous system findings. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 36:698–701.
Article35. Chung KW, Park KN, Ko MH, Jeon HK, Choi JY, Cho YS, et al. Incidence of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo as a function of the duration of symptoms. Otol Neurotol. 2009; 30:202–205.
Article36. Korres S, Riga M, Sandris V, Danielides V, Sismanis A. Canalithiasis of the anterior semicircular canal (ASC): treatment options based on the possible underlying pathogenetic mechanisms. Int J Audiol. 2010; 49:606–612.
Article37. Ganança FF, Gazzola JM, Ganança CF, Caovilla HH, Ganança MM, Cruz OL. Elderly falls associated with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 76:113–120.38. Dlugaiczyk J, Siebert S, Hecker DJ, Brase C, Schick B. Involvement of the anterior semicircular canal in posttraumatic benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2011; 32:1285–1290.
Article39. De Stefano A, Kulamarva G, Citraro L, Neri G, Croce A. Spontaneous nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011; 32:185–189.
Article40. Casani AP, Cerchiai N, Dallan I, Sellari-Franceschini S. Anterior canal lithiasis: diagnosis and treatment. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 144:412–418.41. Pérez P, Franco V, Cuesta P, Aldama P, Alvarez MJ, Méndez JC. Recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2012; 33:437–443.
Article42. Soto-Varela A, Santos-Perez S, Rossi-Izquierdo M, Sanchez-Sellero I. Are the three canals equally susceptible to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Audiol Neurootol. 2013; 18:327–334.
Article43. Prokopakis E, Vlastos IM, Tsagournisakis M, Christodoulou P, Kawauchi H, Velegrakis G. Canalith repositioning procedures among 965 patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol Neurootol. 2013; 18:83–88.
Article44. Park S, Kim BG, Kim SH, Chu H, Song MY, Kim M. Canal conversion between anterior and posterior semicircular canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2013; 34:1725–1728.
Article45. Imbaud-Genieys S. Anterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a series of 20 patients. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2013; 130:303–307.
Article46. Cambi J, Astore S, Mandalà M, Trabalzini F, Nuti D. Natural course of positional down-beating nystagmus of peripheral origin. J Neurol. 2013; 260:1489–1496.
Article47. Marques PS, Castillo R, Santos M, Perez-Fernandez N. Repositioning nystagmus: prognostic usefulness? Acta Otolaryngol. 2014; 134:491–496.
Article48. Lynn S, Pool A, Rose D, Brey R, Suman V. Randomized trial of the canalith repositioning procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995; 113:712–720.
Article49. Asawavichianginda S, Isipradit P, Snidvongs K, Supiyaphun P. Canalith repositioning for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a randomized, controlled trial. Ear Nose Throat J. 2000; 79:732–734. 736–737.
Article50. Simhadri S, Panda N, Raghunathan M. Efficacy of particle repositioning maneuver in BPPV: a prospective study. Am J Otolaryngol. 2003; 24:355–360.
Article51. Yimtae K, Srirompotong S, Srirompotong S, Sae-Seaw P. A randomized trial of the canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:828–832.
Article52. Chang AK, Schoeman G, Hill M. A randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy of the Epley maneuver in the treatment of acute benign positional vertigo. Acad Emerg Med. 2004; 11:918–924.
Article53. von Brevern M, Seelig T, Radtke A, Tiel-Wilck K, Neuhauser H, Lempert T. Short-term efficacy of Epley's manoeuvre: a double-blind randomised trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006; 77:980–982.
Article54. Chen Y, Zhuang J, Zhang L, Li Y, Jin Z, Zhao Z, et al. Short-term efficacy of Semont maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a double-blind randomized trial. Otol Neurotol. 2012; 33:1127–1130.
Article55. Mandalà M, Santoro GP, Asprella Libonati G, Casani AP, Faralli M, Giannoni B, et al. Double-blind randomized trial on short-term efficacy of the Semont maneuver for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2012; 259:882–885.
Article56. Blakley BW. A randomized, controlled assessment of the canalith repositioning maneuver. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; 110:391–396.
Article57. Kim JS, Oh SY, Lee SH, Kang JH, Kim DU, Jeong SH, et al. Randomized clinical trial for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology. 2012; 78:159–166.
Article58. Kim JS, Oh SY, Lee SH, Kang JH, Kim DU, Jeong SH, et al. Randomized clinical trial for geotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology. 2012; 79:700–707.
Article59. Mandalà M, Pepponi E, Santoro GP, Cambi J, Casani A, Faralli M, et al. Double-blind randomized trial on the efficacy of the Gufoni maneuver for treatment of lateral canal BPPV. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:1782–1786.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Clinical Characteristics of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo of the Anterior Semicircular Canal
- Canal Conversion and Reentry of Otolith in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- An Atypical Case of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo of the Anterior Semicircular Canal
- Management of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo