Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 May;66(5):390-395. 10.4046/trd.2009.66.5.390.
A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinomatous Lung Abscess with Multiple Metastatic Abscesses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sekyukim@yuhs.ac
- 2The Institute of Chest Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1846404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2009.66.5.390
Abstract
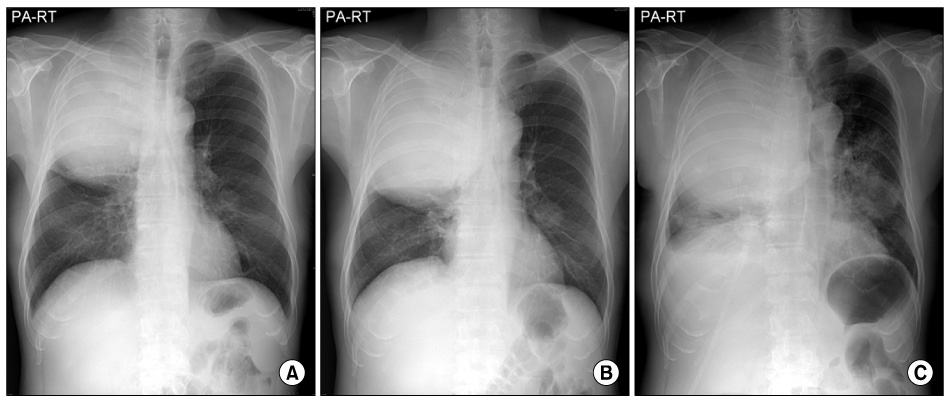
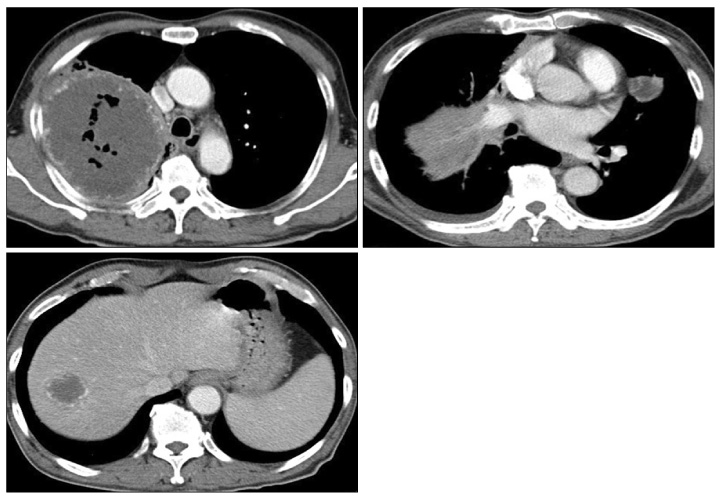
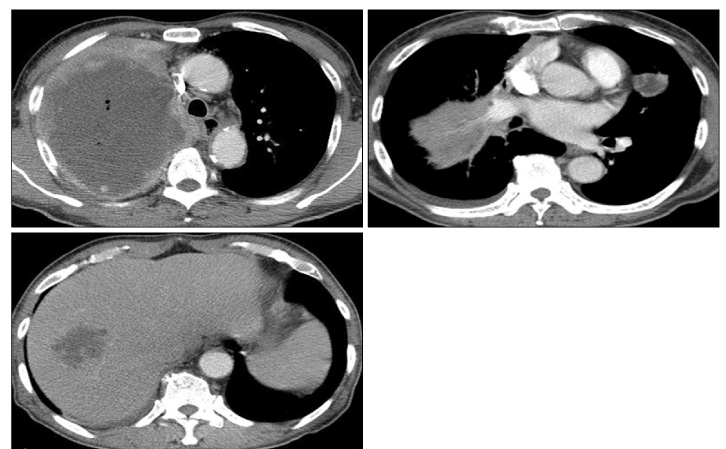
- Among the bronchogenic carcinomas, especially squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma frequently present with cavitation, which may result from tumor necrosis. Cavitary lesions of the tumor are occasionally associated with infection and misdiagnosed as benign lung abscess owing to the partial responsiveness to antibiotics. It is very difficult to distinguish the carcinomatous abscess from the benign lung abscess, because of their similar clinical and radiologic features. Delay in diagnosis of underlying lung cancer may result in poor outcome. Therefore, clinicians should remember that the patients with highly suspicious carcinoma of the lung should undergo further precise examinations to find out malignant cells.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fishman AP. Fishman JA, editor. Chapter 112. Approach to the patient with pulmonary infection. Fishman's pulmonary diseases and disorders. 2008. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical;1988–1989.2. Bernhard WF, Malcolm JA, Wylie RH. The carcinomatous abscess: a clinical paradox. N Engl J Med. 1962. 266:914–919.3. Stewart CE, Winer-Muram HT, Jennings SG, Dowdeswell I, Meyer CA. Necrotic mass-like upper lobe opacity. Chest. 2003. 123:277–279.4. Liao WY, Liaw YS, Wang HC, Chen KY, Luh KT, Yang PC. Bacteriology of infected cavitating lung tumor. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1750–1753.5. Sosenko A, Glassroth J. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy in the evaluation of lung abscesses. Chest. 1985. 87:489–494.6. Kurihara Y, Nakajima Y, Niimi H, Arakawa H, Ishikawa T, Kojima K, et al. Cavitary lung cancer producing granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: a mimicker of lung abscess. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998. 22:425–426.7. Schiza S, Siafakas NM. Clinical presentation and management of empyema, lung abscess and pleural effusion. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006. 12:205–211.8. Wallace RJ Jr, Cohen A, Awe RJ, Greenberg D, Hadlock F, Park SK. Carcinomatous lung abscess: diagnosis by bronchoscopy and cytopathology. JAMA. 1979. 242:521–522.9. Sokhandon F, Sparschu RA, Furlong JW. Best cases from the AFIP: bronchogenic squamous cell carcinoma. Radiographics. 2003. 23:1639–1643.10. Mathew BS, Jayasree K, Gangadharan VP, Nair MK, Rajan B. Renal metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Australas Radiol. 1998. 42:159–160.11. Akduman B, Altun R, Yesilli C, Yenidunya S, Ozdemir H, Mungan NA. Symptomatic renal metastasis 5 years after the management of a squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Int J Urol. 2004. 11:421–423.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Multiple Bowen's Disease
- Roentgenogram of the Issue : Huge abscess Cavity in right lower lung
- Lower Leg Abscess in Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Syndrome Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Case Report
- Hybrid verrucous squamous cell carcinoma of sinonasal tract: a case report
- A Case of Multiple Large Renal Abscesses Completely Resolved by Conservative Antibiotics Administration