J Clin Neurol.
2007 Dec;3(4):200-203. 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.200.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in AIDS: Proton MR Spectroscopy Patterns of Asynchronous Lesions Confirmed by Serial Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nmboy@unitel.co.kr
- 3Department of Neuroradiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1808557
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.200
Abstract
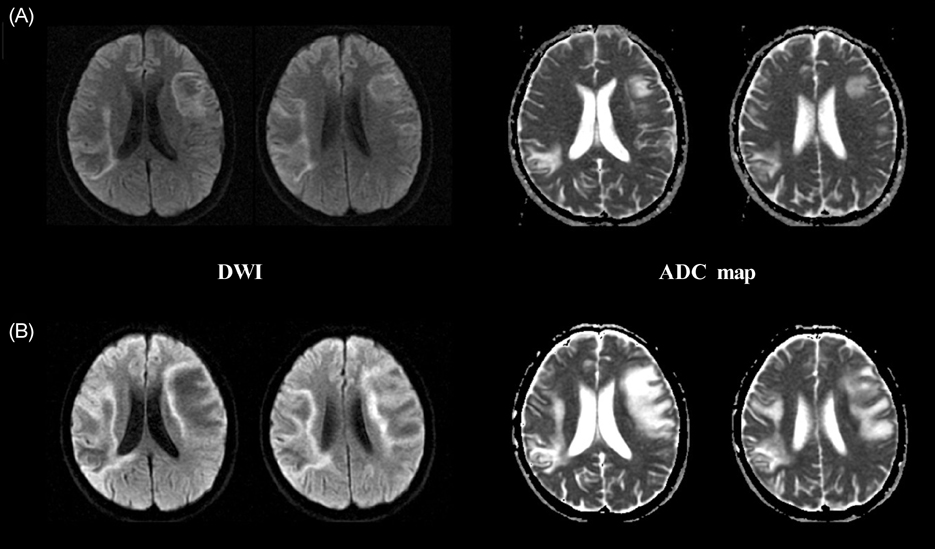
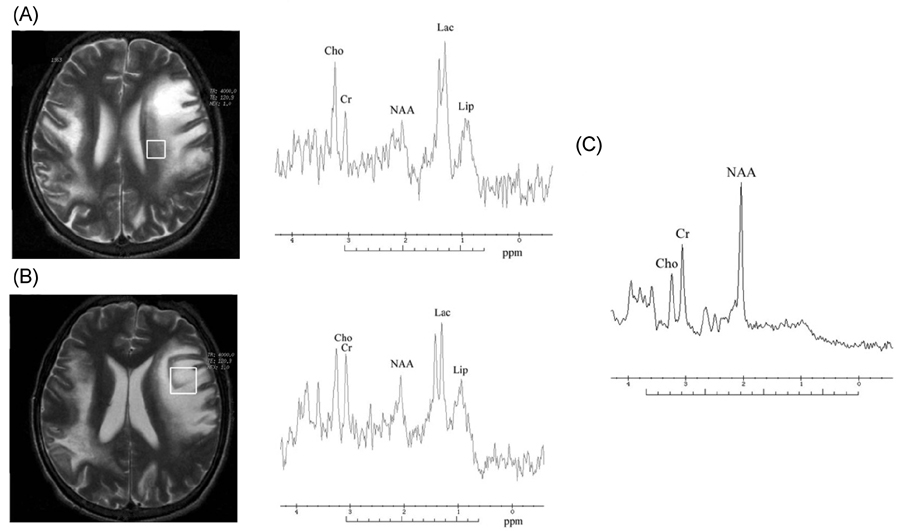
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare disease that occurs mainly in immunocompromised patients. Despite the progressive nature of the disease, the changes on MRI during the disease course - which may help in monitoring the disease process - have seldom been reported. Here we describe a patient with polymerase-chain-reaction-proven PML examined using serial diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent-diffusion-coefficient mapping. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) revealed that the demyelinating process was more active without significant neuronal loss at the newer and advancing edge of a lesion than in the older central part of the lesion. This case shows that MRI findings such as DWI and MRS may improve the diagnosis and the understanding of the pathophysiology of PML.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Stroke Mimicking Encephalopathy as an Initial Manifestation of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Jeong-Min Kim, Keun-Hwa Jung, Soon-Tae Lee, Hee-Kwon Park, Kon Chu, Jae-Kyu Roh
J Clin Neurol. 2009;5(2):97-100. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2009.5.2.97.
Reference
-
1. Wilkinson ID, Miller RF, Miszkiel KA, Paley MN, Hall-Craggs MA, Baldeweg T, et al. Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in asymptomatic HIV infection. AIDS. 1997. 11:289–295.
Article2. Henderson RD, Smith MG, Mowat P, Read SJ. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 2002. 58:1825.
Article3. Ohta K, Obara K, Sakauchi M, Obara K, Takane H, Yogo Y. Lesion extension detected by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol. 2001. 248:809–811.
Article4. Mader I, Herrlinger U, Klose U, Schmidt F, Kuker W. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: analysis of lesion development with diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology. 2003. 45:717–721.
Article5. Chang L, Ernst T, Tornatore C, Aronow H, Melchor R, Walot I, et al. Metabolite abnormalities in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology. 1997. 48:836–845.
Article6. Iranzo A, Moreno A, Pujol J, Marti-Fabregas J, Domingo P, Molet J, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy pattern of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in AIDS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999. 66:520–523.
Article7. Simone IL, Federico F, Tortorella C, Andreula CF, Zimatore GB, Giannini P, et al. Localised 1H-MR spectroscopy for metabolic characterisation of diffuse and focal brain lesions in patients infected with HIV. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. 64:516–523.
Article8. Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK, Boghi A, Geda C, Gatti G, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology. 2004. 46:22–25.
Article9. Berger JR, Koralnik IJ. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and natalizumab - unforeseen consequences. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:414–416.
Article10. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Tyler KL. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy complicating treatment with natalizumab and interferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:369–374.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Progressive Multifocal Leucoencephalopathy Isolated to Posterior Fossa in a Patient with AIDS: DWI and 1H-MRS Features
- Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Diffusion MR Imaging and Localized Proton MR Spectroscopic Findings in Two Infants
- Reversal of a Large Ischemic Lesion with Low Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value by Rapid Spontaneous Recanalization
- Clinical applications and characteristics of apparent diffusion coefficient maps for the brain of two dogs
- Serial Magnetic Resonance Images of a Right Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction : Persistent Hyperintensity on Diffusion-Weighted MRI Over 8 Months