J Clin Neurol.
2005 Oct;1(2):174-176. 10.3988/jcn.2005.1.2.174.
Cortical Laminar Necrosis associated with Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. salee@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1808488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2005.1.2.174
Abstract
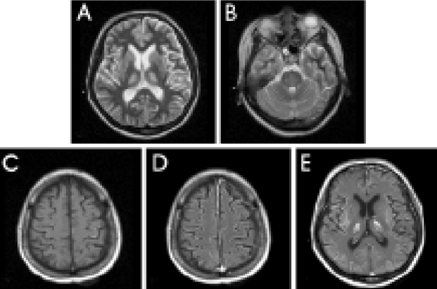
- Cortical laminar necrosis has been rarely observed in osmotic demyelination syndrome. We report a 32-year-old female patient who became comatose after the rapid correction of hyponatremia. There were high signal intensities in the pons and bilateral deep gray nuclei on T2-weighted MRI images, and linear hyperintensities along the cerebral cortices on T1-weighted images with a diffuse gyriform enhancement. MR spectroscopic findings showed a decrease of the N-acetyl aspartate peak and an increase in those of the lipid and lactate complex. The case demonstrates that a severe form of osmotic demyelination syndrome accompanying cortical laminar necrosis can result from the rapid correction of hyponatremia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute Marchiafava-Bignami Disease with Widespread Callosal and Cortical Lesions
Min-Jeong Kim, Jong-Kuk Kim, Bong-Goo Yoo, Kwang-Soo Kim, Young Duk Jo
J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22(5):908-911. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.908.
Reference
-
1. Shoji M, Kimura T, Ota K, Ohta M, Sato K, Yamamoto T, et al. Cortical laminar necrosis and central pontine myelinolysis in a patient with Sheehan syndrome and severe hyponatremia. Intern Med. 1996. 35:427–431.
Article2. Susa S, Daimon M, Morita Y, Kitagawa M, Hirata A, Manaka H, et al. Acute intermittent porphyria with central pontine myelinolysis and cortical laminar necrosis. Neuroradiology. 1999. 41:835–839.
Article3. Calakos N, Fischbein N, Baringer JR, Jay C. Cortical MRI findings associated with rapid correction of hyponatremia. Neurology. 2000. 55:1048–1051.
Article4. Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain. 1979. 102:361–385.
Article5. Vexler ZS, Ayus JC, Roberts TPL, Fraser CL, Kucharczyk J, Arieff AI. Hypoxic and ischemic hypoxia exacerbate brain injury associated with metabolic encephalopathy in laboratory animals. J Clin Invest. 1994. 93:256–264.
Article6. Ayus JC, Arieff AI. Pulmonary complications of hyponatremic encephalopathy. Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and hypercapnic respiratory failure. Chest. 1995. 107:517–521.
Article7. Okeda R, Kitano M, Sawabe M, Yamada I, Yamada M. Distribution of demyelinating lesions in pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis -- three autopsy cases including one case devoid of central pontine myelinolysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 1986. 69:259–266.
Article8. Norenberg MD. A hypothesis of osmotic endothelial injury. A pathogenetic mechanism in central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol. 1983. 40:66–69.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cortical Laminar Necrosis in an Infant with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
- Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Resulting from an Unexpected Response to Tolvaptan in a Patient with Heart Failure
- MRI Findings of Cortical Laminar Necrosis
- Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome with Recent Chemotherapy in Normonatremic Patient: A Case Report
- Initial Transient Neurologic Recovery Followed by Delayed Deterioration of Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome: A Case Report