J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2012 Sep;14(3):170-174. 10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.170.
Stereotactic Burr Hole Aspiration Surgery for Spontaneous Hypertensive Cerebellar Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. kangsd@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 1808451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.170
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
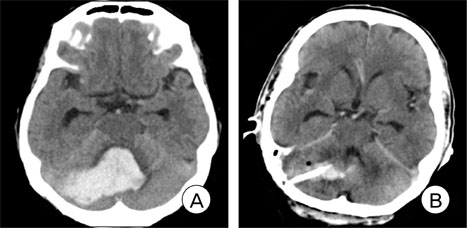
Patients with severe spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage typically undergo treatment with suboccipital craniectomy and hematoma evacuation. However, this is a stressful procedure for patients due to the long operating time and operation-induced tissue damage. In addition, the durotomy can result in pseudomeningocele. We investigated the efficacy of stereotactic or navigation-guided burr hole aspiration surgery as a treatment for spontaneous hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage (SHCH).
METHODS
Between January 2002 and December 2011, 26 patients with SHCH underwent surgery using the stereotactic or navigation-guided burr hole aspiration and catheter insertion technique in our institution.
RESULTS
Mean hematoma volume was 21.8 +/- 5.8 cc at admission and 13.1 +/- 5.4 cc immediately following surgery. Preoperative Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score was 12.5 +/- 1.3 and postoperative GCS score was 13.1 +/- 1.2. Seven days after surgery, the mean hematoma volume was 4.3 +/- 5.6 cc, and there was no occurrence of surgery-related complications during the six-month follow-up period. The mean operation time for catheter insertion was 43.1 +/- 8.9 min, and a mean 31.3 +/- 6.0 min was also added for extra-ventricular drainage. The mean Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) score after six months was 4.6 +/- 1.0.
CONCLUSION
Stereotactic burr hole aspiration surgery for treatment of SHCH is less time-consuming and invasive than other interventions, and resulted in no surgery-related complications. Therefore, we suggest that this surgical method could be a safe and effective treatment option for selected patients with SHCH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brennan RW, Bergland RM. Acute cerebellar hemorrhage. Analysis of clinical findings and outcome in 12 cases. Neurology. 1977. 06. 27(6):527–532.
Article2. Broderick JP, Adams HP Jr, Barsan W, Feinberg W, Feldmann E, Grotta J, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 1999. 04. 30(4):905–915.3. Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E, Hanley D, Kase C, Krieger D, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Circulation. 2007. 10. 116(16):e391–e413.4. Chin D, Carney P. Acute cerebellar hemorrhage with brainstem compression in contrast with benign cerebellar hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 1983. 05. 19(5):406–409.
Article5. Donauer E, Loew F, Faubert C, Alesch F, Schaan M. Prognostic factors in the treatment of cerebellar hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1994. 131(1-2):59–66.6. Firsching R, Huber M, Frowein RA. Cerebellar hemorrhage: Management and prognosis. Neurosurg Rev. 1991. 14(3):191–194.7. Heros RC. Cerebellar hemorrhage and infarction. Stroke. 1982. Jan-Feb. 13(1):106–109.
Article8. Kobayashi S, Sato A, Kageyama Y, Nakamura H, Watanabe Y, Yamaura A. Treatment of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage-Surgical or conservative management? Neurosurgery. 1994. 02. 34(2):246–250. discussion 250-1.
Article9. Koziarski A, Frankiewicz E. Medical and surgical treatment of intracerebellar hematomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991. 110(1-2):24–28.10. Lui TN, Fairholm DJ, Shu TF, Chang CN, Lee ST, Chen HR. Surgical treatment of spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 1985. 06. 23(6):555–558.
Article11. Mezzadri JJ, Otero JM, Ottino CA. Management of 50 spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhages. Importance of obstructive hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993. 122(1-2):39–44.12. Mohadjer M, Eggert R, May J, Mayfrank L. CT-guided stereotactic fibrinolysis of spontaneous and hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage: long term results. J Neurosurg. 1990. 08. 73(2):217–222.13. Niizuma H, Suzuki J. Computed tomography-guided stereotactic aspiration of posterior fossa hematomas: a supine lateral retromastoid approach. Neurosurgery. 1987. 09. 21(3):422–427.
Article14. Norris JW, Eisen AA, Branch CL. Problems in cerebellar hemorrhage and infarction. Neurology. 1969. 11. 19(11):1043–1050.
Article15. Salazar J, Vaquero J, Martinez P, Santos H, Martinez R, Bravo G. Clinical and CT scan assessment of benign versus fatal spontaneous cerebellar hematomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1986. 79(2-4):80–86.16. Taneda M, Hayakawa T, Mogami H. Primary cerebellar hemorrhage. Quadrigeminal cistern obliteration on CT scans as a predictor of outcome. J Neurosurg. 1987. 10. 67(4):545–552.17. Winn HR. Youmans Neurological Surgery. 2011. ed 6. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co;3712.18. Yanaka K, Meguro K, Fujita K, Narushima K, Nose T. Immediate surgery reduces mortality in deeply comatose patients with spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2000. 06. 40(6):295–299. discussion 299-300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Supratentorial Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Delayed Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Supratentorial Burr-Hole Drainage
- Stereotactic Management of Spontaneous Infratenorial Hemorrhage: Part II: Transtentorial Stereotactic Approach for Spontaneous Intracerebellar Hemorrhage
- Safe and time-saving treatment method for acute cerebellar infarction: Navigation-guided burr-hole aspiration – 6-years single center experience
- Risk Factors in Patients with Rebleeding after CT-Guided Stereotactic Burr Hole Aspiration for Hypertensive Intracerebral Hematoma