Yonsei Med J.
2010 Jul;51(4):504-510. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.504.
The Influence of Sam-Chil-Geun (Panax Notoginseng) on the Serum Lipid Levels and Inflammations of Rats with Hyperlipidemia Induced by Poloxamer-407
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cheil General Hospital and Women's Healthcare Center, College of Medicine, Kwandong University, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2East-West Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, College of Medicine, Kwandong University, Gangneung, Korea. yeora@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1805186
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.504
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the progressive deposition of lipids and inflammatory process. We attempted to develop a chemically-induced hyperlipidemic mice model, using poloxamer-407 and evaluated the lipid lowering and anti-inflammatory effect of P. notoginseng compared with that of atorvastatin, an antihyperlipidemic drug.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
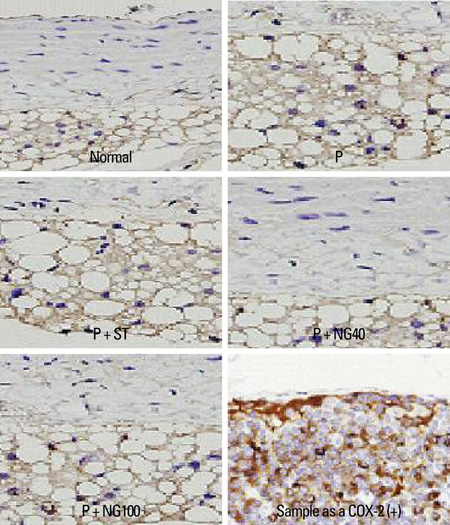
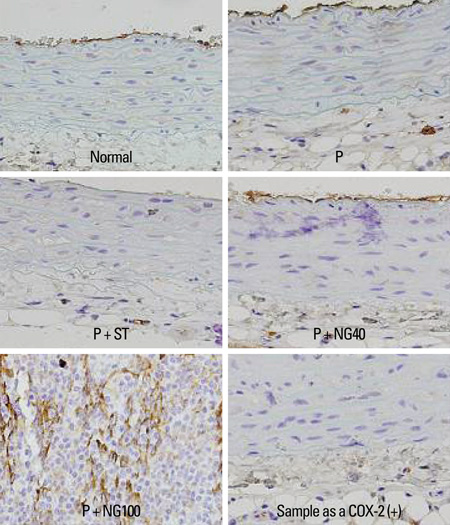
Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 5 groups: control group without any intervention (normal), poloxamer 500 mg/kg i.p. (P), poloxamer plus atorvastatin 1.34 mg/kg p.o. (P + ST), poloxamer plus P. notoginseng 40 mg/kg p.o. (P + NG40), and poloxamer plus P. notoginseng 100 mg/kg p.o. (P + NG100). After 3 weeks, we measured serum total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), triglyceride, interleukin (IL)-1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha levels, and reports of cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2 & intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) appearances in each group.
RESULTS
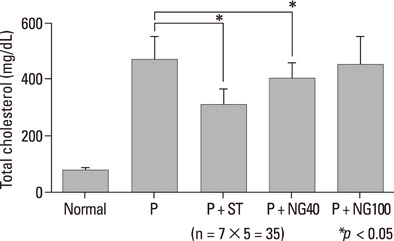
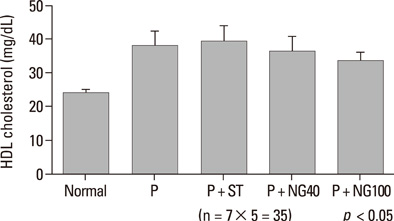
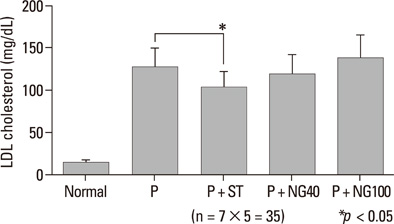
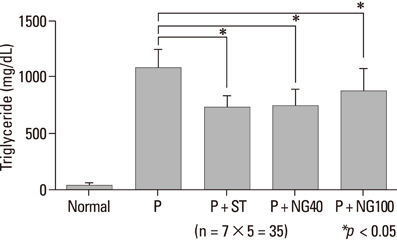
After 3 weeks, serum cholesterol levels significantly decreased in P + ST and P + NG40 groups. Significant decrease of LDL level was only noted in the P + ST group. P + ST, P + NG40, and P + NG100 also had decreased serum triglyceride levels; however, P + ST and P + NG40 showed no statistical difference of the triglyceride lowering effect. The results of IL-1 and TNF-alpha and the appearance of COX-2 and ICAM were statistically not different in each group.
CONCLUSIONS
P. notoginseng 40 mg/kg showed significantly lowering effects on serum total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. We suggest a well-designed study showing the effects of regulating blood lipids with combined administration of P. notoginseng and statin-drug.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Teng CM, Kuo SC, Ko FN, Lee JC, Lee LG, Chen SC, et al. Antiplatelet actions of panaxynol and ginsenosides isolated from ginseng. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989. 990:315–320.
Article2. Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993. 362:801–809.
Article3. Chang GT, Kang SK, Kim JH, Chung KH, Chang YC, Kim CH. Inhibitory effect of Korean herbal medicine, Dae-Jo-Whan, on platelet activating factor-induced platelet aggeregation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. 102:430–439.
Article4. Kuo SC, Teng CM, Lee JC, Ko FN, Chen SC, Wu TS. Antiplatelet components in Panax ginseng. Planta Med. 1990. 56:164–167.5. Wang G, Wang L, Xiong ZY, Mao B, Li TQ. Compound salvia pellet, a traditional Chinese medicine, for the treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris compared with nitrates: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2006. 12:SR1–SR7.6. Jin UH, Park SG, Suh SJ, Kim JK, Kim DS, Moon SK, et al. Inhibitory effect of Panax notoginseng on nitric oxide synthesase, cyclo-oxtgenase-2 and neutrophil functions. Phytother Res. 2007. 21:142–148.
Article7. Wang J, Xu J, Zhong JB. Effect of Radix notoginseng saponins on platelet activating molecule expression and aggregation in patients with blood hyperviscosity syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004. 24:312–316.8. Micallef MA, Garg ML. Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and plant sterols in hypertlipidemic individuals. Atherosclerosis. 2009. 204:476–482.9. Ridker PM, Silvertown JD. Inflammation, C-reactive protein, and atherothrombosis. J Periodontol. 2008. 79:1544–1551.
Article10. Wout ZG, Pec EA, Maggiore JA, Williams RH, Palicharla P, Johnston TP. Poloxamer 407-mediated changes in plasma cholesterol and triglycerides following intraperitoneal injection to rats. J Parenter Sci Technol. 1992. 46:192–200.11. Beckmann N, Cannet C, Babib AL, Bié FX, Zurbruegg S, Kneuer R, et al. In vivo visualization of macrophage infiltration and activity in inflammation using magnetic resonance imaging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009. 1:272–298.12. Cicero AF, Bandieri E, Arletti R. Orally administered Panax notoginseng influence on rat spontaneous behaviour. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000. 73:387–391.
Article13. Liu S, Chen JX. [Anti-arrhythmic effect of total saponins of Panax notoginseng]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1984. 5:100–103.14. Zhang WJ, Wojta J, Binder BR. Effect of notoginsenoside R1 on the synthesis of components of the fibrinolytic system in cultured smooth muscle cells of human pulmonary artery. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1997. 43:581–587.15. Park HJ, Rhee MH, Park KM, Nam KY, Park KH. Effect of non-saponin fraction from Panax ginseng on cGMP and thrombocane A2 in human platelet aggregation. J Ethnopharmacol. 1995. 49:157–162.
Article16. Taubes G. Cardiovascular disease. Does inflammation cut to the heart of the matter? Science. 2002. 296:242–245.17. Hansson GK, Libby P, Schönbeck U, Yan ZQ. Innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2002. 91:281–291.
Article18. Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002. 420:868–874.
Article19. Karin M. Inflammation-activated protein kinases as targets for drug development. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. 2:386–390.
Article20. Abate A, Oberle S, Schröder H. Lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in mouse macrophages is inhibited by chloromethylketones and a direct inhibitor of NF-kappa B translocation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 1998. 56:277–290.
Article21. Liu Y, Xie MX, Kang J, Zheng D. Studies on the interaction of total saponins of Panax notoginseng and human albumin by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2003. 59:2747–2758.22. Johnston TP, Punjabi MA, Froelich CJ. Sustained delivery of interleukin-2 form a poloxamer 407 gel matrix following intraperitoneal injection in mice. Pharm Res. 1992. 9:425–434.23. Wout ZG, Pec EA, Maggiore JA, Williams RH, Palicharla P, Johnston TP. Poloxamer 407-mediated changes in plasma cholesterol and triglycerides following intraperitoneal injections to rats. J Parenter Sci Technol. 1992. 46:192–200.24. Johnston TP, Palmer WK. Mechanism of poloxamer 407-induced hypertriglyceridemia in rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993. 46:1037–1042.25. Porter JA, Carter BL, Johnson TP, Palmer WK. Effects of pravastatin on plasma lipid concentrations in poloxamer 407-induced hyperlipidemic rats. Pharmacotherapy. 1995. 15:92–98.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Short-term Memory Impairment by Suppressing Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Poloxamer-407-Induced Hyperlipidemia Rats
- Berberine Ameliorates Brain Inflammation in Poloxamer 407-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats
- Comparison of Poloxamer-407 to Soybean Oil as an Emulsifying Agent for Propofol: Histamine Release and Plasma Lipid Levels
- Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of fermented red ginseng against high fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats
- Lipid Profile in Patients with Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head