Korean J Pain.
2014 Oct;27(4):334-338. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.334.
The Effects of a Forceful Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection on Radicular Pain: A Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. ingoo97@lycos.co.kr
- KMID: 1802499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.334
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections (TFESIs) are performed to provide symptom relief in patients with radicular pain. Recent articles suggested that injected volume itself have analgesic effects and higher volumes are associated with better outcomes. To date, few studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of volume. Therefore, well-designed controlled studies were necessary to confirm the effect of volume itself on pain relief. The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of a forceful saline injection on lumbar TFESI using non-particulate steroids.
METHODS
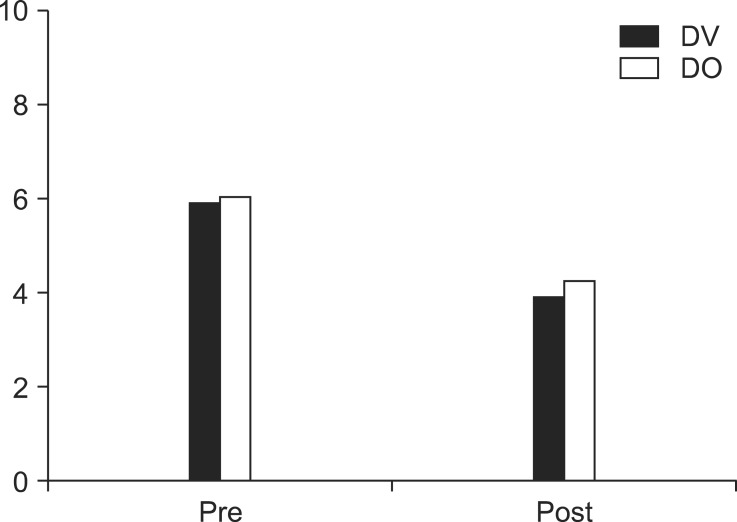
Fifty consecutive patients with lumbar radicular pain were enrolled. The participants were allocated into one of two groups: dexamethasone with volume (Group DV) and dexamethasone alone (Group DO). The volume was delivered by a forceful injection of 5ml of normal saline. The primary end-point for this study was a VAS pain score and modified MacNab score indicating the rate of effectiveness at the four-week follow-up.
RESULTS
There were no significant post-procedural VAS differences between two groups (P = .252). The effectiveness rate among the patients was 47.8% in DV group, 34.8% in DO group, measured by modified MacNab score. The difference was not statistically significant (P = .117).
CONCLUSIONS
A forceful saline injection did not have a significant effect during the treatment of radicular pain. Further studies with greater volumes and with additional techniques would offer a more conclusive perspective.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Which Methods of Epidural Steroid Injections Is More Effective in Reducing the Radicular Pain; Transforaminal or Interlaminar?
Mohamed Amin Ghobadifar, Armin Akbarzadeh, Zahra Mosallanejad
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(1):64-65. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.1.64.What is the Role of Epidural Injections in the Treatment of Lumbar Discogenic Pain: A Systematic Review of Comparative Analysis with Fusion
Laxmaiah Manchikanti, Peter S. Staats, Devi E. Nampiaparampil, Joshua A. Hirsch
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(2):75-87. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.2.75.
Reference
-
1. Cohen SP, Bicket MC, Jamison D, Wilkinson I, Rathmell JP. Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013; 38:175–200. PMID: 23598728.2. Manchikanti L, Abdi S, Atluri S, Benyamin RM, Boswell MV, Buenaventura RM, et al. An update of comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for interventional techniques in chronic spinal pain. Part II: guidance and recommendations. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:S49–S283. PMID: 23615883.3. Koc Z, Ozcakir S, Sivrioglu K, Gurbet A, Kucukoglu S. Effectiveness of physical therapy and epidural steroid injections in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:985–989. PMID: 19404172.
Article4. Luijsterburg PA, Verhagen AP, Ostelo RW, van Os TA, Peul WC, Koes BW. Effectiveness of conservative treatments for the lumbosacral radicular syndrome: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:881–899. PMID: 17415595.
Article5. Rabinovitch DL, Peliowski A, Furlan AD. Influence of lumbar epidural injection volume on pain relief for radicular leg pain and/or low back pain. Spine J. 2009; 9:509–517. PMID: 19398387.
Article6. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Fellows B. Fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections with or without steroids in managing pain of lumbar spinal stenosis: one-year results of randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25:226–234. PMID: 22652990.
Article7. Racz GB, Day MR, Heavner JE, Scott J. Lysis of epidural adhesions: the Racztechnique. In : Waldman SD, editor. Pain management. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders;2011. p. 1258–1272.8. Chun-jing H, Hao-xiong N, jia-xiang N. The application of percutaneous lysis of epidural adhesions in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Acta Cir Bras. 2012; 27:357–362. PMID: 22534813.
Article9. Lee JH, Moon J, Lee SH. Comparison of effectiveness according to different approaches of epidural steroid injection in lumbosacral herniated disk and spinal stenosis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2009; 22:83–89. PMID: 20023335.
Article10. Benzon HT, Chew TL, McCarthy RJ, Benzon HA, Walega DR. Comparison of the particle sizes of different steroids and the effect of dilution: a review of the relative neurotoxicities of the steroids. Anesthesiology. 2007; 106:331–338. PMID: 17264728.
Article11. Derby R, Lee SH, Date ES, Lee JH, Lee CH. Size and aggregation of corticosteroids used for epidural injections. Pain Med. 2008; 9:227–234. PMID: 18298706.
Article12. Furman MB, Mehta AR, Kim RE, Simon JI, Patel R, Lee TS, et al. Injectate volumes needed to reach specific landmarks in lumbar transforaminal epidural injections. PM R. 2010; 2:625–635. PMID: 20659718.
Article13. Park CH, Lee SH. Effectiveness of percutaneous transforaminal adhesiolysis in patients with lumbar neuroforaminal spinal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E37–E43. PMID: 23340543.14. Lee JH, Lee SH. Clinical effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis using Navicath for the management of chronic pain due to lumbosacral disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:213–221. PMID: 22622905.15. Jo DH, Yang HJ. The survey of the patient received the epiduroscopic laser neural decompression. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:27–31. PMID: 23342204.
Article16. Kim SH, Koh WU, Park SJ, Choi WJ, Suh JH, Leem JG, et al. Clinical experiences of transforaminal balloon decompression for patients with spinal stenosis. Korean J Pain. 2012; 25:55–59. PMID: 22259719.
Article17. Heavner JE, Racz GB, Raj P. Percutaneous epidural neuroplasty: prospective evaluation of 0.9% NaCl versus 10% NaCl with or without hyaluronidase. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1999; 24:202–207. PMID: 10338168.
Article18. Koh WU, Choi SS, Park SY, Joo EY, Kim SH, Lee JD, et al. Transforaminal hypertonic saline for the treatment of lumbar lateral canal stenosis: a double-blinded, randomized, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:197–211. PMID: 23703407.19. El-Yahchouchi C, Geske JR, Carter RE, Diehn FE, Wald JT, Murthy NS, et al. The noninferiority of the nonparticulate steroid dexamethasone vs the particulate steroids beta-methasone and triamcinolone in lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections. Pain Med. 2013; 14:1650–1657. PMID: 23899304.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Selective Epidural Steroid Injection in a Patient with Refractory Radicular Leg Pain: A case report
- Comparison of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection and Lumbar/Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Effects of Translaminar Approach and Transforaminal Approach in Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- Effect of Transforaminal Epidural Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain