Clin Endosc.
2015 Mar;48(2):102-105. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.2.102.
Endoscopic Management of Mallory-Weiss Tearing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. dshskim@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1801199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.2.102
Abstract
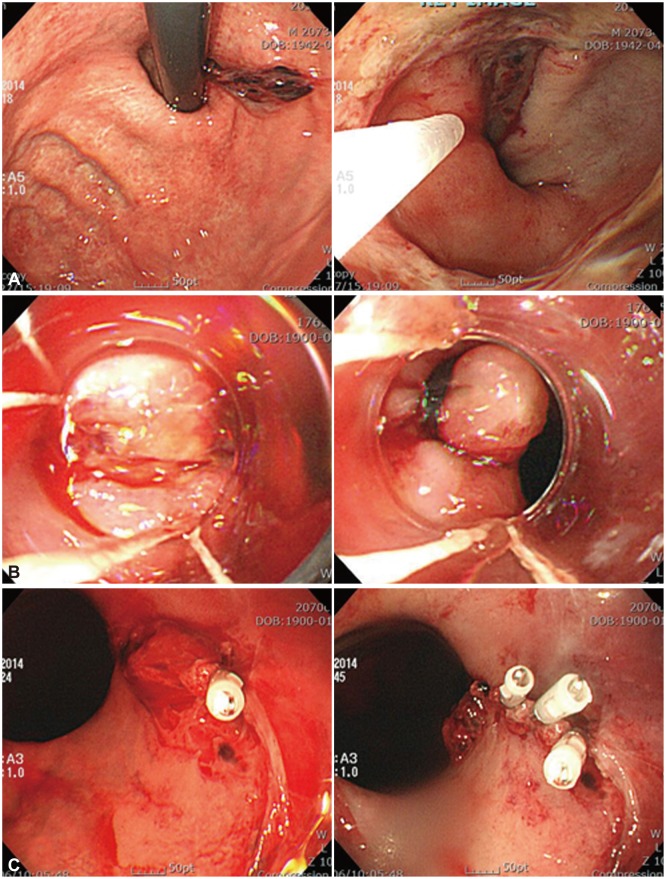
- Mallory-Weiss tearing (MWT) is a common cause of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Although the majority of patients with bleeding MWT require no intervention other than hemodynamic supports, spectrum of MWT is wide, and the condition sometimes results in a fatal outcome. Endoscopic management to stop the bleeding may be required during the index endoscopy, especially in those with active bleeding or stigmata of recurrent bleeding. Most commonly used endoscopic treatment for actively bleeding MWT is injection therapy, argon plasma coagulation, hemoclip placement, and band ligation. Selection of the optimal endoscopic hemostasis depends on the physician's ability and patient's clinical status.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Guidelines for Non-variceal Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Joon Sung Kim, Byung-Wook Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Chan Hyuk Park, Hyuk Lee, Moon Kyung Joo, Da Hyun Jung, Jun-Won Chung, Hyuk Soon Choi, Gwang Ho Baik, Jeong Hoon Lee, Kyo Young Song, Saebeom Hur
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;75(6):322-332. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.75.6.322.십이지장스텐트 삽입 중 발생한 위천공
Sung Woo Ko, Hoonsub So, Sung Jo Bang
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022;80(5):221-224. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.060.
Reference
-
1. Mallory GK, Weiss S. Hemorrhagic from laceration of the cardiac orifice of the sotmach due to vomiting. Am J Med Sci. 1929; 178:506–514.2. Katz PO, Salas L. Less frequent causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993; 22:875–889. PMID: 8307643.
Article3. Llach J, Elizalde JI, Guevara MC, et al. Endoscopic injection therapy in bleeding Mallory-Weiss syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:679–681. PMID: 11726841.
Article4. Park CH, Min SW, Sohn YH, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of endoscopic band ligation vs. epinephrine injection for actively bleeding Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:22–27. PMID: 15229420.
Article5. Peng YC, Tung CF, Chow WK, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic isotonic saline-epinephrine injection for the management of active Mallory-Weiss tears. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001; 32:119–122. PMID: 11205645.
Article6. Terada R, Ito S, Akama F, et al. Mallory-Weiss syndrome with severe bleeding: treatment by endoscopic ligation. Am J Emerg Med. 2000; 18:812–815. PMID: 11103735.
Article7. Laine L. Multipolar electrocoagulation in the treatment of active upper gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage. A prospective controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987; 316:1613–1617. PMID: 3295547.8. Ivekovic H, Rustemovic N, Brkic T, et al. The esophagus as a working channel: successful closure of a large Mallory-Weiss tear with clips and an endoloop. Endoscopy. 2011; 43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E170. PMID: 21563067.
Article9. Shimoda R, Iwakiri R, Sakata H, et al. Endoscopic hemostasis with metallic hemoclips for iatrogenic Mallory-Weiss tear caused by endoscopic examination. Dig Endosc. 2009; 21:20–23. PMID: 19691796.
Article10. Cho YS, Chae HS, Kim HK, et al. Endoscopic band ligation and endoscopic hemoclip placement for patients with Mallory-Weiss syndrome and active bleeding. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:2080–2084. PMID: 18395910.
Article11. Lecleire S, Antonietti M, Iwanicki-Caron I, et al. Endoscopic band ligation could decrease recurrent bleeding in Mallory-Weiss syndrome as compared to haemostasis by hemoclips plus epinephrine. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:399–405. PMID: 19485979.
Article12. Stevens PD, Lebwohl O. Hypertensive emergency and ventricular tachycardia after endoscopic epinephrine injection of a Mallory-Weiss tear. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994; 40:77–78. PMID: 8163143.
Article13. Bataller R, Llach J, Salmerón JM, et al. Endoscopic sclerotherapy in upper gastrointestinal bleeding due to the Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994; 89:2147–2150. PMID: 7977231.14. Kim JW, Kim HS, Byun JW, et al. Predictive factors of recurrent bleeding in Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:447–454. PMID: 16371719.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Endoscopic O-ring Band Ligation in the Management of Mallory - Weiss Syndrome
- The Usefulness of Endoscopic Hemoclipping in the Management of Mallory - Weiss syndrome
- A Case of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome Complicating Pregnancy in a Patient with Scleroderma
- Endoscopic local injection of hypertonic saline-epinephrine solution in bleeding peptic ulcer or Mallory-Weiss tear
- Weiss Syndrome by 0-ring Band Ligation