J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Dec;40(6):285-290. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.285.
Comparison of resorbable plates and titanium plates for fixation stability of combined mandibular symphysis and angle fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. jumincw@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1799562
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.285
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We compared resorbable plates with titanium plates for treatment of combined mandibular angle and symphyseal fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
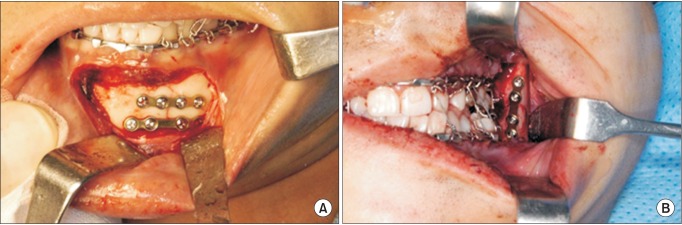
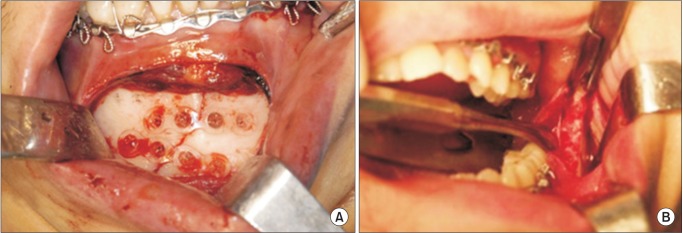
Patients with mandibular angle and symphysis fractures were divided into two groups. The control (T) group received titanium plates while the experimental (R) group received resorbable plates. All procedures were carried out under general anesthesia using standard surgical techniques. We compared the frequency of wound dehiscence, development of infection, malocclusion, malunion, screw breakage, and any other technical difficulties between the two groups.
RESULTS
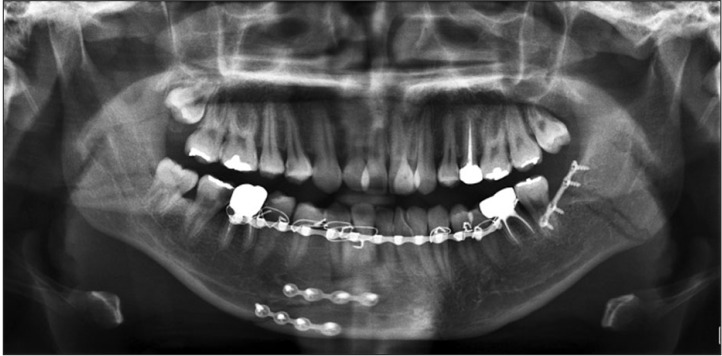
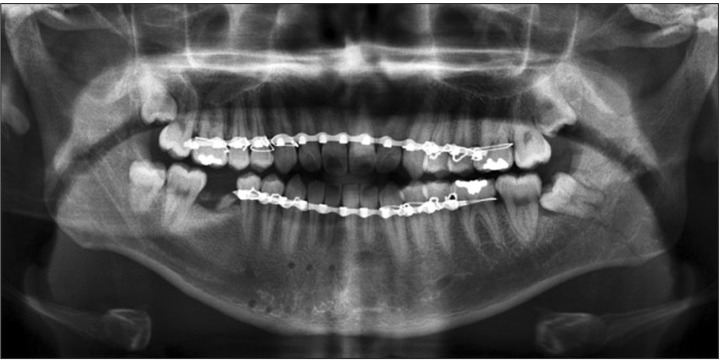
Thirteen patients were included in the R group, where 39 resorbable plates were applied. The T group consisted of 16 patients who received 48 titanium plates. The mean age in the R and T groups was 28.29 and 24.23 years, respectively. Primary healing of the fractured mandible was obtained in all patients in both groups. Postoperative complications were minor and transient. Moreover, there were no significant differences in the rates of various complications between the two groups. Breakage of 3 screws during the perioperative period was seen in the R group, while no screws or plates were broken in the T group.
CONCLUSION
Resorbable plates can be used to stabilize combined mandibular angle and symphysis fractures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ellis E 3rd, Moos KF, el-Attar A. Ten years of mandibular fractures: an analysis of 2,137 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985; 59:120–129. PMID: 3856795.
Article2. Haug RH, Prather J, Indresano AT. An epidemiologic survey of facial fractures and concomitant injuries. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 48:926–932. PMID: 2395044.
Article3. Tuovinen V, Nørholt SE, Sindet-Pedersen S, Jensen J. A retrospective analysis of 279 patients with isolated mandibular fractures treated with titanium miniplates. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994; 52:931–935. PMID: 8064456.
Article4. Kim YK, Yeo HH, Lim SC. Tissue response to titanium plates: a transmitted electron microscopic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:322–326. PMID: 9120693.
Article5. Suuronen R, Kallela I, Lindqvist C. Bioabsorbable plates and screws: current state of the art in facial fracture repair. J Craniomaxillofac Trauma. 2000; 6:19–27. PMID: 11373737.6. Leonhardt H, Demmrich A, Mueller A, Mai R, Loukota R, Eckelt U. INION compared with titanium osteosynthesis: a prospective investigation of the treatment of mandibular fractures. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 46:631–634. PMID: 18597909.
Article7. Choi EJ, Nam W, Jung YS, Kim KH, Kim HJ. Clinical and radiological comparison between titanium and biodegradable miniplate monocortical osteosynthesis in mandibular angle fractures. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 32:222–225.8. Jeong JC, Choi SH, Song MS, Jun CH, Kim HM. Clinical study of resorbable plate and screw for treatment of maxillofacial fractures. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 29:438–443.9. Kim YK, Kim SG. Treatment of mandible fractures using bioabsorbable plates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 110:25–31. PMID: 12087226.
Article10. Champy M, Loddé JP, Schmitt R, Jaeger JH, Muster D. Mandibular osteosynthesis by miniature screwed plates via a buccal approach. J Maxillofac Surg. 1978; 6:14–21. PMID: 274501.
Article11. Bos RR, Rozema FR, Boering G, Nijenhuis AJ, Pennings AJ, Verwey AB. Bio-absorbable plates and screws for internal fixation of mandibular fractures. A study of six dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989; 18:365–369. PMID: 2516105.12. Kim YK, Shim CH, Bae JH, Yun PY. Application of bioabsorbable plates in orthognathic surgery. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 32:60–64.13. Bessho K, Iizuka T, Murakami K. A bioabsorbable poly-L-lactide miniplate and screw system for osteosynthesis in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:941–945. PMID: 9294503.
Article14. Kallela I, Tulamo RM, Hietanen J, Pohjonen T, Suuronen R, Lindqvist C. Fixation of mandibular body osteotomies using biodegradable amorphous self-reinforced (70L:30DL) polylactide or metal lag screws: an experimental study in sheep. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1999; 27:124–133. PMID: 10342151.
Article15. Wittwer G, Adeyemo WL, Yerit K, Voracek M, Turhani D, Watzinger F, et al. Complications after zygoma fracture fixation: is there a difference between biodegradable materials and how do they compare with titanium osteosynthesis? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:419–425. PMID: 16545702.
Article16. Bayram B, Araz K, Uckan S, Balcik C. Comparison of fixation stability of resorbable versus titanium plate and screws in mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:1644–1648. PMID: 19615576.
Article17. Esen A, Ataoğlu H, Gemi L. Comparison of stability of titanium and absorbable plate and screw fixation for mandibular angle fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 106:806–811. PMID: 18718777.
Article18. Ellis E 3rd. Open reduction and internal fixation of combined angle and body/symphysis fractures of the mandible: how much fixation is enough? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 71:726–733. PMID: 23245520.
Article19. Fonseca RJ, Walker RV, Betts NJ, et al. Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma. Vol 2. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB saunders;1997.20. Ahmed W, Ali Bukhari SG, Janjua OS, Luqman U, Shah I. Bioresorbable versus titanium plates for mandibular fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013; 23:480–483. PMID: 23823951.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Selective Use of Bioabsorbable Plates and Screws According to Fracture Site and Aspect of Mandible
- Clinical study of resorbable plate and screw for treatment of maxillofacial fractures
- The prognosis of fixation of mandibular fractures with biodegradable plates and screws
- Stability of maxillary position after lefort i osteotomy using biodegradable plates and screws
- Resorbable plates for the fixation of mandibular fractures: case reports and review of the literature