J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Jun;29(6):825-830. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.825.
Prevalence of Chronic Sputum and Associated Factors in Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. kyionly@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1796946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.825
Abstract
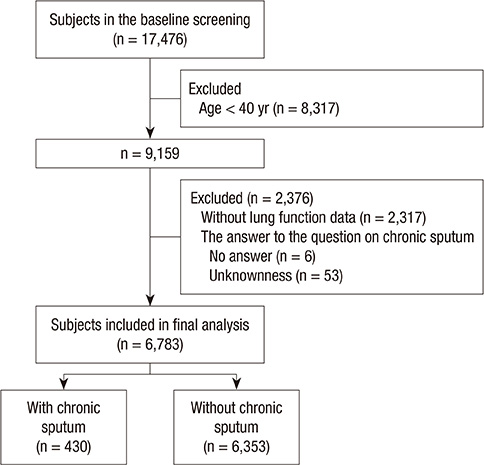
- Chronic sputum is a troublesome symptom in many respiratory diseases. The prevalence of chronic sputum varies from 1.2% to 13% according to the country. The purpose of this study was to estimate the prevalence of chronic sputum and to find its associated factors in a general Korean population. We analyzed the data of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010 and 2011. A total number of 6,783 subjects aged 40 yr or more were enrolled in this study with 3,002 men and 3,781 women. As a result, the prevalence of chronic sputum was 6.3% (n=430). Significant risk factors for chronic sputum by multivariate analysis were: age (> or =70 yr) (odds ratio [OR], 1.954; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.308-2.917), current smoking (OR, 4.496; 95% CI, 3.001-6.734), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (OR, 1.483; 95% CI, 1.090-2.018), and tuberculosis (OR, 1.959; 95% CI, 1.307-2.938). In conclusion, the prevalence of chronic sputum in Korea was in the intermediate range compared with other countries. Smoking is a preventable risk factor identified in this study, and major respiratory diseases, such as COPD and tuberculosis, should be considered in subjects with chronic sputum.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vestbo J, Prescott E, Lange P. Association of chronic mucus hypersecretion with FEV1 decline and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease morbidity: Copenhagen City Heart Study Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 153:1530–1535.2. Enright PL, Kronmal RA, Higgins MW, Schenker MB, Haponik EF. Prevalence and correlates of respiratory symptoms and disease in the elderly: Cardiovascular Health Study. Chest. 1994; 106:827–834.3. Anthonisen NR. The British hypothesis revisited. Eur Respir J. 2004; 23:657–658.4. Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1256–1276.5. Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187:347–365.6. Tanaka T, Asai M, Yanagita Y, Nishinakagawa T, Miyamoto N, Kotaki K, Yano Y, Kozu R, Honda S, Senjyu H. Longitudinal study of respiratory function and symptoms in a non-smoking group of long-term officially-acknowledged victims of pollution-related illness. BMC Public Health. 2013; 13:766.7. De Oca MM, Halbert RJ, Lopez MV, Perez-Padilla R, Tálamo C, Moreno D, Muiño A, Jardim JR, Valdivia G, Pertuzé J, et al. The chronic bronchitis phenotype in subjects with and without COPD: the PLATINO study. Eur Respir J. 2012; 40:28–36.8. Cerveri I, Accordini S, Corsico A, Zoia MC, Carrozzi L, Cazzoletti L, Beccaria M, Marinoni A, Viegi G, de Marco R. Chronic cough and phlegm in young adults. Eur Respir J. 2003; 22:413–417.9. De Marco R, Accordini S, Cerveri I, Corsico A, Antó JM, Künzli N, Janson C, Sunyer J, Jarvis D, Chinn S, et al. Incidence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a cohort of young adults according to the presence of chronic cough and phlegm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:32–39.10. Mahesh PA, Jayaraj BS, Prabhakar AK, Chaya SK, Vijayasimha R. Prevalence of chronic cough, chronic phlegm & associated factors in Mysore, Karnataka, India. Indian J Med Res. 2011; 134:91–100.11. Choi SW, Ryu SY, Han MA, Park J. The association between the socioeconomic status and thyroid cancer prevalence; based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2011. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1734–1740.12. Choi CJ, Seo M, Choi WS, Kim KS, Youn SA, Lindsey T, Choi YJ, Kim CM. Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and lung function among Korean adults in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008-2010. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:1703–1710.13. Choi KH, Park SM, Park JS, Park JH, Kim KH, Kim MJ. Prevalence of and factors associated with osteoporosis among Korean cancer survivors: a cross-sectional analysis of the Fourth and Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013; 14:4743–4750.14. Kim HW, Park H, Cho KH, Han K, Ko BJ. Parathyroid hormone, vitamin D levels and urine albumin excretion in older persons: the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 80:34–40.15. Joo H, Park J, Lee SD, Oh YM. Comorbidities of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Koreans: a population-based Study. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:901–906.16. Miravitlles M, Guerrero T, Mayordomo C, Sánchez-Agudo L, Nicolau F, Segú JL. Factors associated with increased risk of exacerbation and hospital admission in a cohort of ambulatory COPD patients: a multiple logistic regression analysis: the EOLO Study Group. Respiration. 2000; 67:495–501.17. Yoo KH, Kim YS, Sheen SS, Park JH, Hwang YI, Kim SH, Yoon HI, Lim SC, Park JY, Park SJ, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Korea: the fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008. Respirology. 2011; 16:659–665.18. Bae JM, Lee MS, Shin MH, Kim DH, Li ZM, Ahn YO. Cigarette smoking and risk of lung cancer in Korean men: the Seoul Male Cancer Cohort Study. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:508–512.19. Ahmadi-Motamayel F, Falsafi P, Hayati Z, Rezaei F, Poorolajal J. Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions in male smokers and nonsmokers. Chonnam Med J. 2013; 49:65–68.20. Hays JT, Dale LC, Hurt RD, Croghan IT. Trends in smoking-related diseases: why smoking cessation is still the best medicine. Postgrad Med. 1998; 104:56–62. 65–66. 7121. Lundgren JD, Baraniuk JN. Mucus secretion and inflammation. Pulm Pharmacol. 1992; 5:81–96.22. Saetta M, Finkelstein R, Cosio MG. Morphological and cellular basis for airflow limitation in smokers. Eur Respir J. 1994; 7:1505–1515.23. Ekberg-Aronsson M, Pehrsson K, Nilsson JA, Nilsson PM, Löfdahl CG. Mortality in GOLD stages of COPD and its dependence on symptoms of chronic bronchitis. Respir Res. 2005; 6:98.24. Pelkonen M, Notkola IL, Nissinen A, Tukiainen H, Koskela H. Thirty-year cumulative incidence of chronic bronchitis and COPD in relation to 30-year pulmonary function and 40-year mortality: a follow-up in middle-aged rural men. Chest. 2006; 130:1129–1137.25. Seemungal TA, Donaldson GC, Paul EA, Bestall JC, Jeffries DJ, Wedzicha JA. Effect of exacerbation on quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:1418–1422.26. Jordan TS, Spencer EM, Davies P. Tuberculosis, bronchiectasis and chronic airflow obstruction. Respirology. 2010; 15:623–628.27. Seddon J, Kasprowicz V, Walker NF, Yuen HM, Sunpath H, Tezera L, Meintjes G, Wilkinson RJ, Bishai WR, Friedland JS, et al. Procollagen III N-terminal propeptide and desmosine are released by matrix destruction in pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 2013; 208:1571–1579.28. Denning DW, Pleuvry A, Cole DC. Global burden of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis as a sequel to pulmonary tuberculosis. Bull World Health Organ. 2011; 89:864–872.29. Kim WD. Lung mucus: a clinician's view. Eur Respir J. 1997; 10:1914–1917.30. Kim C, Kim DG. Bronchiectasis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2012; 73:249–257.31. Kim HK, Choi EY, Lee JS, Bae YJ, Song JW, Kim TB, Cho YS, Moon HB, Lee SD, Oh YM. Relation between subjective symptoms and rhinolaryngoscopic findings or sputum eosinophilia in chronic cough patients. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2010; 69:368–374.32. DeLegge MH. Aspiration pneumonia: incidence, mortality, and at-risk populations. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002; 26:S19–S24.33. Van der Maarel-Wierink CD, Vanobbergen JN, Bronkhorst EM, Schols JM, de Baat C. Risk factors for aspiration pneumonia in frail older people: a systematic literature review. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011; 12:344–354.34. Po JY, FitzGerald JM, Carlsten C. Respiratory disease associated with solid biomass fuel exposure in rural women and children: systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax. 2011; 66:232–239.35. Park S, Lee MG, Lee KH, Park YB, Yoo KH, Park JW, Kim C, Lee YC, Park JS, Kwon YS, et al. A multicenter study of pertussis infection in adults with coughing in Korea: PCR-based study. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2012; 73:266–272.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Haemophilus influence isolated from sputum specimens: prevalence biotypes and antimicrobial susceptibility
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Korea: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Quality of Life
- Prevalence of Obesity, its Comorbidities, and Related Risk Factors among Young Korean Adults: Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
- The Relationship between Airway Inflammation and Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Relation between Subjective Symptoms and Rhinolaryngoscopic Findings or Sputum Eosinophilia in Chronic Cough Patients