Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Dec;6(4):468-475. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.468.
Comparison of Clinical and Physiological Efficacies of Different Intermittent Sequential Pneumatic Compression Devices in Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Prospective Randomized Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. turejsreal@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Radiology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1794737
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.468
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
There are few comparative studies about the optimal method of pneumatic compression to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The aim of this prospective randomized study was to compare venous hemodynamic changes and their clinical influences between two graded sequential compression groups (an alternate sequential compression device [ASCD] vs. a simultaneous sequential compression device [SSCD]).
METHODS
In total, 34 patients (68 limbs) undergoing knee and spine operations were prospectively randomized into two device groups (ASCD vs. SSCD groups). Duplex ultrasonography examinations were performed on the 4th and 7th postoperative days for the detection of DVT and the evaluation of venous hemodynamics. Continuous data for the two groups were analyzed using a two-tailed, unpaired t-test. Relative frequencies of unpaired samples were compared using Fisher exact test. Mixed effects models that might be viewed as ANCOVA models were also considered.
RESULTS
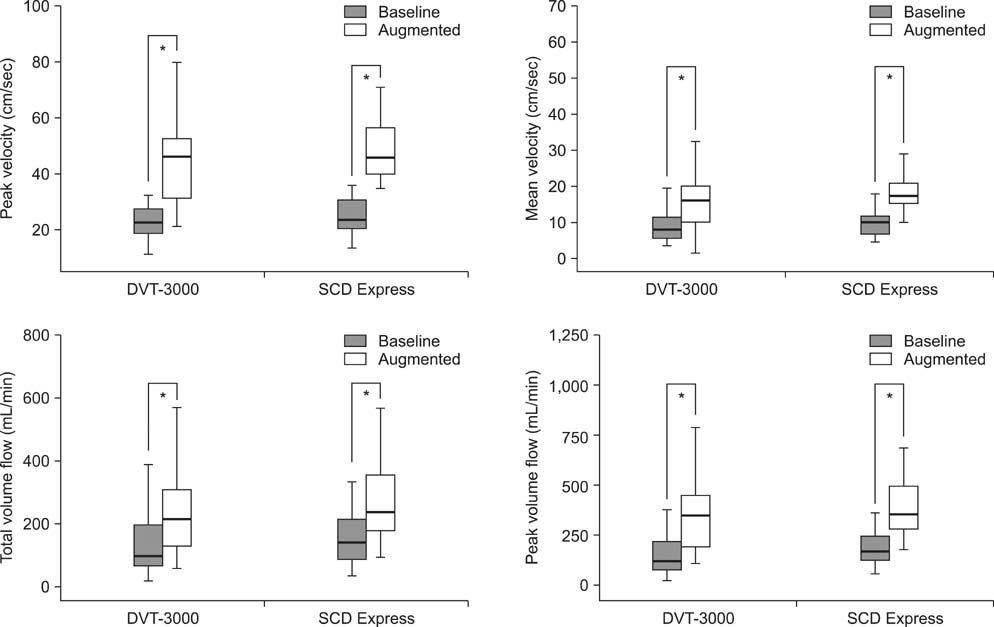
DVT developed in 7 patients (20.6%), all of whom were asymptomatic for isolated calf DVTs. Two of these patients were from the ASCD group (11.8%) and the other five were from the SSCD group (29.4%), but there was no significant difference (p = 0.331). Baseline peak velocity, mean velocity, peak volume flow, and total volume flow were enhanced significantly in both device groups (p < 0.001). However, the degrees of flow and velocity enhancement did not differ significantly between the groups. The accumulated expelled volumes for an hour were in favor of the ASCD group.
CONCLUSIONS
Both graded sequential compression devices showed similar results both in clinical and physiological efficacies. Further studies are required to investigate the optimal intermittent pneumatic compression method for enhanced hemodynamic efficacy and better thromboprophylaxis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
*Arthroplasty, Replacement, Knee/adverse effects
*Fracture Fixation/adverse effects
Hemodynamics
Humans
*Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices
Knee/surgery
Prospective Studies
Risk Factors
*Spinal Fusion/adverse effects
Spine/surgery
Treatment Outcome
Venous Thrombosis/etiology/physiopathology/*prevention & control/ultrasonography
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bang SM, Jang MJ, Oh D, et al. Korean guidelines for the prevention of venous thromboembolism. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25(11):1553–1559.2. Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008; 133:6 Suppl. 381S–453S.3. Nicolaides AN, Breddin HK, Fareed J, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism. International Consensus Statement. Guidelines compiled in accordance with the scientific evidence. Int Angiol. 2001; 20(1):1–37.4. Pidala MJ, Donovan DL, Kepley RF. A prospective study on intermittent pneumatic compression in the prevention of deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing total hip or total knee replacement. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992; 175(1):47–51.5. Woolson ST, Watt JM. Intermittent pneumatic compression to prevent proximal deep venous thrombosis during and after total hip replacement. A prospective, randomized study of compression alone, compression and aspirin, and compression and low-dose warfarin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73(4):507–512.6. Kaempffe FA, Lifeso RM, Meinking C. Intermittent pneumatic compression versus coumadin. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis in lower-extremity total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (269):89–97.7. Morris RJ, Giddings JC, Ralis HM, et al. The influence of inflation rate on the hematologic and hemodynamic effects of intermittent pneumatic calf compression for deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 44(5):1039–1045.8. Proctor MC, Greenfield LJ, Wakefield TW, Zajkowski PJ. A clinical comparison of pneumatic compression devices: the basis for selection. J Vasc Surg. 2001; 34(3):459–463.9. Kakkos SK, Szendro G, Griffin M, Sabetai MM, Nicolaides AN. Improved hemodynamic effectiveness and associated clinical correlations of a new intermittent pneumatic compression system in patients with chronic venous insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2001; 34(5):915–922.10. Malone MD, Cisek PL, Comerota AJ Jr, Holland B, Eid IG, Comerota AJ. High-pressure, rapid-inflation pneumatic compression improves venous hemodynamics in healthy volunteers and patients who are post-thrombotic. J Vasc Surg. 1999; 29(4):593–599.11. Kakkos SK, Szendro G, Griffin M, Daskalopoulou SS, Nicolaides AN. The efficacy of the new SCD response compression system in the prevention of venous stasis. J Vasc Surg. 2000; 32(5):932–940.12. Comerota AJ, Chouhan V, Harada RN, et al. The fibrinolytic effects of intermittent pneumatic compression: mechanism of enhanced fibrinolysis. Ann Surg. 1997; 226(3):306–313.13. Kakkos SK, Griffin M, Geroulakos G, Nicolaides AN. The efficacy of a new portable sequential compression device (SCD Express) in preventing venous stasis. J Vasc Surg. 2005; 42(2):296–303.14. Katz ML, Comerota AJ, Kerr RP, Caputo GC. Variability of venous-hemodynamics with daily activity. J Vasc Surg. 1994; 19(2):361–365.15. Blackshear WM Jr, Prescott C, LePain F, Benoit S, Dickstein R, Seifert KB. Influence of sequential pneumatic compression on postoperative venous function. J Vasc Surg. 1987; 5(3):432–436.16. Christopoulos DG, Nicolaides AN, Szendro G, Irvine AT, Bull ML, Eastcott HH. Air-plethysmography and the effect of elastic compression on venous hemodynamics of the leg. J Vasc Surg. 1987; 5(1):148–159.17. Bickel A, Shturman A, Grevtzev I, Roguin N, Eitan A. The physiological impact of intermittent sequential pneumatic compression (ISPC) leg sleeves on cardiac activity. Am J Surg. 2011; 202(1):16–22.18. Cordell-Smith JA, Williams SC, Harper WM, Gregg PJ. Lower limb arthroplasty complicated by deep venous thrombosis. Prevalence and subjective outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(1):99–101.19. Kim YH, Kim JS. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(4):566–570.20. Ko PS, Chan WF, Siu TH, Khoo J, Wu WC, Lam JJ. Deep venous thrombosis after total hip or knee arthroplasty in a "low-risk" Chinese population. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18(2):174–179.21. Haddad FS, Kerry RM, McEwen JA, et al. Unanticipated variations between expected and delivered pneumatic compression therapy after elective hip surgery: a possible source of variation in reported patient outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16(1):37–46.22. Delis KT, Azizi ZA, Stevens RJ, Wolfe JH, Nicolaides AN. Optimum intermittent pneumatic compression stimulus for lower-limb venous emptying. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000; 19(3):261–269.23. Tarnay TJ, Rohr PR, Davidson AG, Stevenson MM, Byars EF, Hopkins GR. Pneumatic calf compression, fibrinolysis, and the prevention of deep venous thrombosis. Surgery. 1980; 88(4):489–496.24. Giddings JC, Morris RJ, Ralis HM, Jennings GM, Davies DA, Woodcock JP. Systemic haemostasis after intermittent pneumatic compression. Clues for the investigation of DVT prophylaxis and travellers thrombosis. Clin Lab Haematol. 2004; 26(4):269–273.25. Comerota AJ, Katz ML, White JV. Why does prophylaxis with external pneumatic compression for deep vein thrombosis fail? Am J Surg. 1992; 164(3):265–268.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Common Peroneal Nerve Palsy by the Use of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Device after Hartmann's Operation
- Prevention Effects of Graduated Compression Stockings and Intermittent Pneumatic Compression on Deep Vein Thrombosis in SICU Patients: Pilot Study
- Extensive Bullous Complication Associated with Intermittent Pneumatic Compression
- Effects on Changes in Femoral Vein Blood Flow Velocity with the Use of Lower Extremity Compression for Critical Patients with Brain injury
- Preventing Venous Thromboembolism with Use of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression after Total Hip Arthroplasty in Korean Patients