Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):801-802. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.801.
Extensive Bullous Complication Associated with Intermittent Pneumatic Compression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. ykleemd@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1727902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.801
Abstract
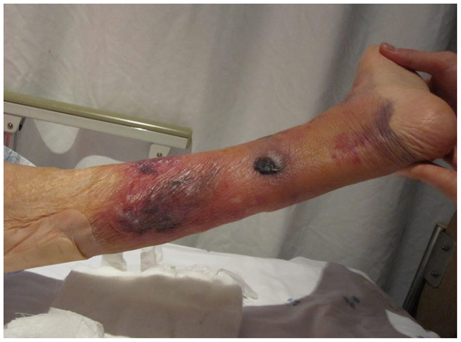
- Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) device is an effective method to prevent deep vein thrombosis. This method has been known to be safe with very low rate of complications compared to medical thromboprophylaxis. Therefore, this modality has been used widely in patients who underwent a hip fracture surgery. We report a patient who developed extensive bullae, a potentially serious skin complication, beneath the leg sleeves during the use of IPC device after hip fracture surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Letter to the Editor: Folliculitis Associated with Intermittant Pneumatic Compression
Alparslan Bayram Çarlı, Erkan Kaya, Hasan Turgut, Mehmet Burak Selek
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(2):545-546. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.2.545.Intermittent Pneumatic Compression for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip Arthroplasty
Hong Suk Kwak, Jai Ho Cho, Jung Taek Kim, Jeong Joon Yoo, Hee Joong Kim
Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):37-42. doi: 10.4055/cios.2017.9.1.37.
Reference
-
1. Fordyce MJ, Ling RS. A venous foot pump reduces thrombosis after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:45–49.2. Pitto RP, Hamer H, Heiss-Dunlop W, Kuehle J. Mechanical prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement a randomised clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:639–642.3. Warwick D. Intermittent pneumatic compression prophylaxis for proximal deep venous thrombosis after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:141–142.4. Warwick D, Harrison J, Glew D, Mitchelmore A, Peters TJ, Donovan J. Comparison of the use of a foot pump with the use of low-molecular-weight heparin for the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement. A prospective, randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:1158–1166.
Article5. Freedman KB, Brookenthal KR, Fitzgerald RH Jr, Williams S, Lonner JH. A meta-analysis of thromboembolic prophylaxis following elective total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. 82-A:929–938.
Article6. Handoll HH, Farrar MJ, McBirnie J, Tytherleigh-Strong G, Milne AA, Gillespie WJ. Heparin, low molecular weight heparin and physical methods for preventing deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism following surgery for hip fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. CD000305.
Article7. Werbel GB, Shybut GT. Acute compartment syndrome caused by a malfunctioning pneumatic-compression boot. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:1445–1446.
Article8. Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990. 113:941–948.
Article9. Lipowski ZJ. Delirium in the elderly patient. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320:578–582.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Common Peroneal Nerve Palsy by the Use of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Device after Hartmann's Operation
- Sequential Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Therapy in Lymphedema
- Prevention Effects of Graduated Compression Stockings and Intermittent Pneumatic Compression on Deep Vein Thrombosis in SICU Patients: Pilot Study
- Preventing Venous Thromboembolism with Use of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression after Total Hip Arthroplasty in Korean Patients
- Characteristics and Effects of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices Interventions to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Critical Care Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials