Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Dec;6(4):410-419. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.410.
Salient Features of the Maasai Foot: Analysis of 1,096 Maasai Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Mount Meru Regional Hospital, Arusha, Tanzania. osddr8151@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA.
- KMID: 1794729
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.410
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The Maasai are the most widely known African ethnic group located in Kenya and northern Tanzania. Most spend their days either barefoot or in their traditional shoes made of car tires. Although they walk long distances of up to sixty kilometers a day, they do not suffer from any foot ailments. Little is known about their foot structure and gait. The goal of this investigation was to characterize various aspects of Maasai foot in standing and walking.
METHODS
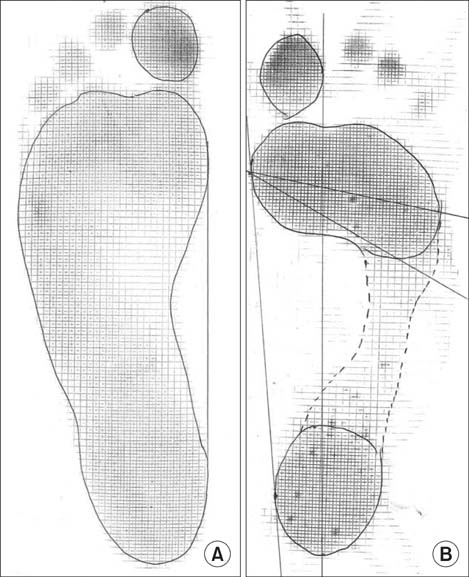
Foot length, calf circumference, hindfoot alignment, step length, cadence, and walking velocity were obtained from 1,096 adult Maasai people (545 males and 551 females; mean age, 40.28 +/- 14.69 years; age range, 16 to 65 years). All included subjects were from rural areas, where the primary terrain was sandy soil, who spend most of their lifetime barefoot, walking. They all denied any medical history or previous symptoms related to foot problems. A trained clinician scanned all feet for deformities. Static (standing) and dynamic (walking) Harris mat footprints were taken to determine the distribution of forefoot pressure patterns during walking.
RESULTS
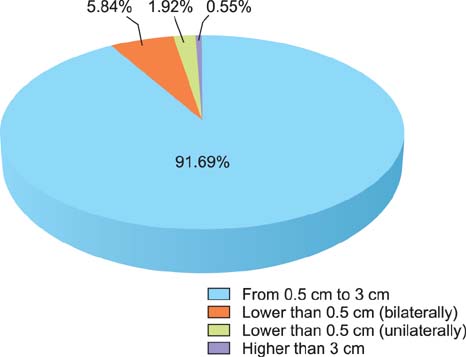
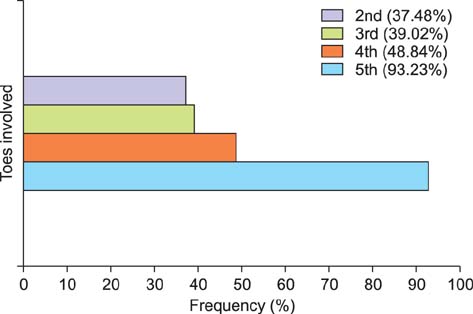
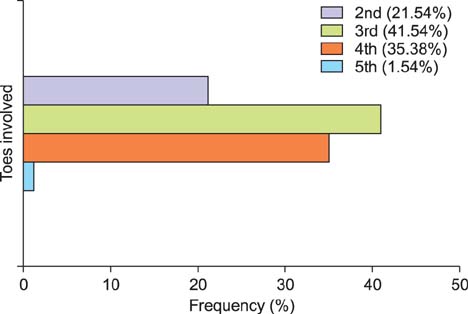
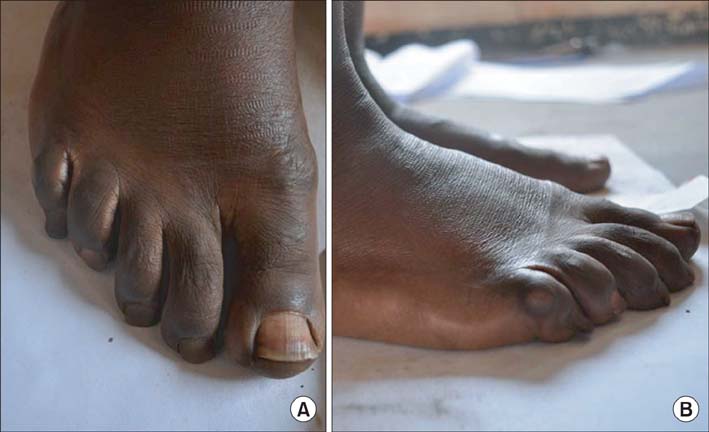
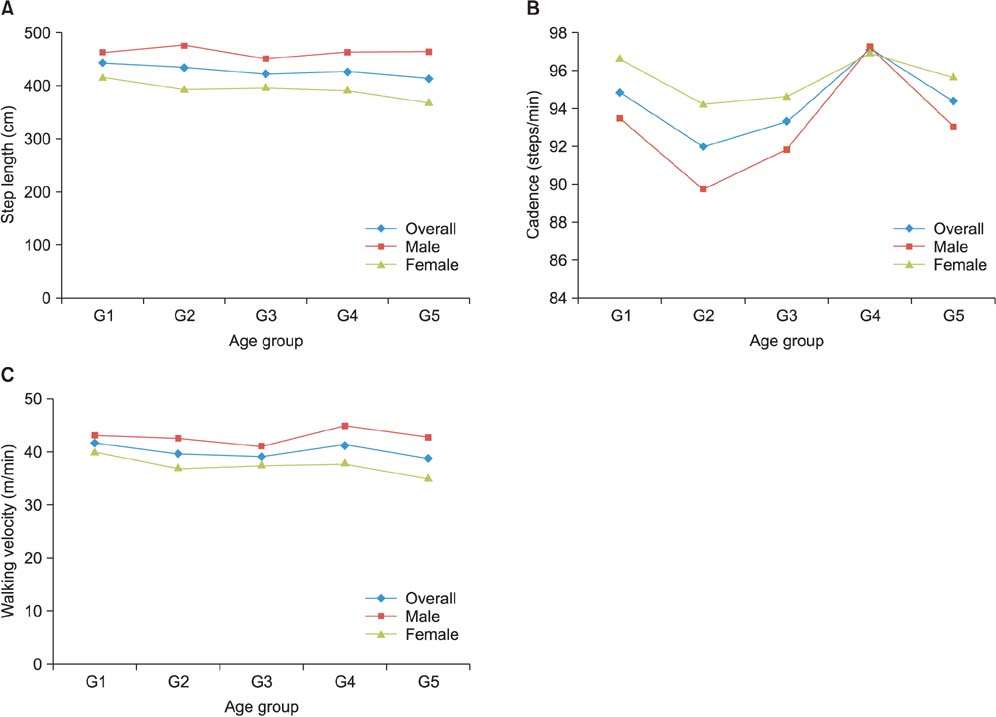
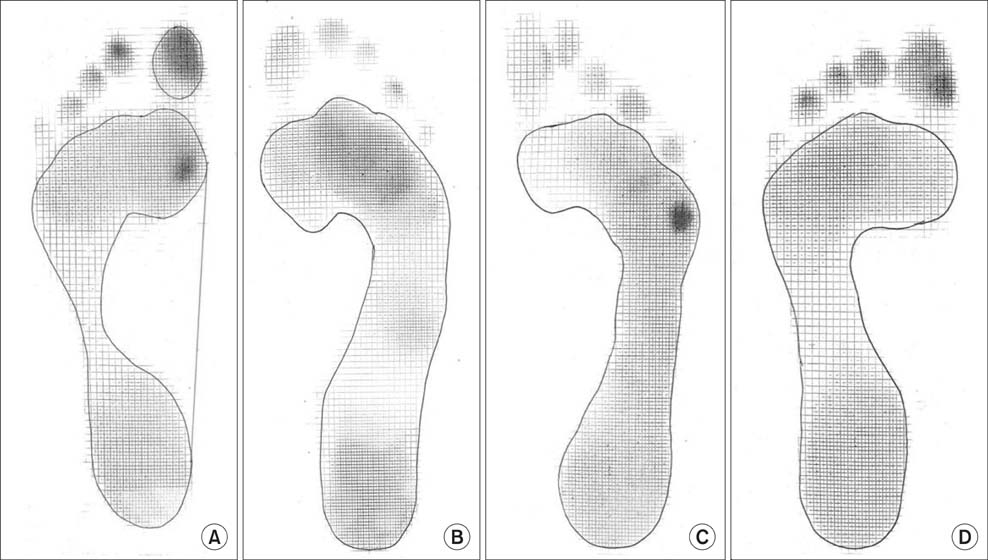
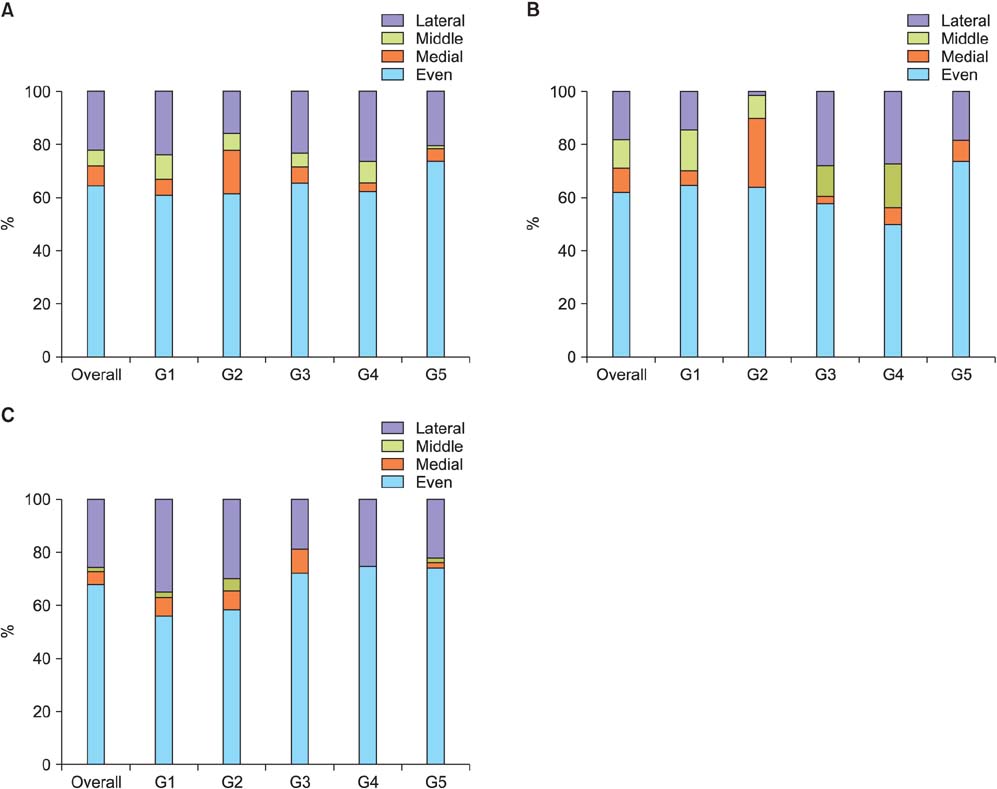
The average foot length was 250.14 +/- 18.12 mm (range, 210 to 295 mm) and calf circumference was 32.50 +/- 3.22 cm (range, 25 to 41 cm). The mean hindfoot alignment was 6.21degrees +/- 1.55degrees of valgus. Sixty-four subjects (5.84%) had bilateral flat-shaped feet with a low medial longitudinal arch that exactly matched the broad pattern of their static footprints. Step length, cadence, and walking velocity were 426.45 +/- 88.73 cm (range, 200 to 690 cm), 94.35 steps/min (range, 72 to 111 steps/min), and 40.16 +/- 8.36 m/min (range, 18.20 to 63.36 m/min), respectively. A total of 83.39% subjects showed unilateral or bilateral deformities of multiple toes regardless of age. The most frequent deformity was clawing (98.79%) of which the highest incidence occurred with the fifth toe (93.23%). Dynamic footprints showed even pressure patterns throughout the forefoot (64.87%), followed by lateral forefoot pressure concentration patterns (21.81%).
CONCLUSIONS
Our study shows the distinct parameters that provide more insight into the Maasai foot.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Roberts S, Birch I, Otter S. Comparison of ankle and subtalar joint complex range of motion during barefoot walking and walking in Masai Barefoot Technology sandals. J Foot Ankle Res. 2011; 4:1.2. Nigg B, Hintzen S, Ferber R. Effect of an unstable shoe construction on lower extremity gait characteristics. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006; 21(1):82–88.3. Vernon T, Wheat J, Naik R, Pettit G. Changes in gait characteristics of a normal healthy population due to an unstable shoe construction. Sheffield: Sheffield Hallam University Centre for Sports and Exercise Science;2004.4. Buchecker M, Lindinger S, Pfusterschmied J, Muller E. Effects of age on lower extremity joint kinematics and kinetics during level walking with Masai barefoot technology shoes. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2013; 49(5):675–686.5. Elveru RA, Rothstein JM, Lamb RL, Riddle DL. Methods for taking subtalar joint measurements: a clinical report. Phys Ther. 1988; 68(5):678–682.6. Michaud TC. Foot orthoses and other forms of conservative foot care. . New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1997.7. Phillips RD, Christeck R, Phillips RL. Clinical measurement of the axis of the subtalar joint. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1985; 75(3):119–131.8. Root ML, Orien WP, Weed JH. Clinical biomechanics. Vol. 2. Normal and abnormal function of the foot. Los Angeles: Clinical Biomechanics Co.;1977.9. Keenan AM, Bach TM. Clinicians' assessment of the hindfoot: a study of reliability. Foot Ankle Int. 2006; 27(6):451–460.10. Queen RM, Mall NA, Hardaker WM, Nunley JA 2nd. Describing the medial longitudinal arch using footprint indices and a clinical grading system. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28(4):456–462.11. Hawes MR, Nachbauer W, Sovak D, Nigg BM. Footprint parameters as a measure of arch height. Foot Ankle. 1992; 13(1):22–26.12. Welton EA. The Harris and Beath footprint: interpretation and clinical value. Foot Ankle. 1992; 13(8):462–468.13. Young CC, Niedfeldt MW, Morris GA, Eerkes KJ. Clinical examination of the foot and ankle. Prim Care. 2005; 32(1):105–132.14. Harris RI, Beath T. Hypermobile flat-foot with short tendo achillis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948; 30(1):116–140.15. Biga N. Clinical examination of the foot and the ankle: data collection and interpretation of the pathogenic causal sequence of disorders. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009; 95:4 Suppl 1. S41–S48.16. Murray MP, Drought AB, Kory RC. Walking patterns of normal men. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964; 46(2):335–360.17. Murray MP, Kory RC, Sepic SB. Walking patterns of normal women. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1970; 51(11):637–650.18. Silvino N, Evanski PM, Waugh TR. The Harris and Beath footprinting mat: diagnostic validity and clinical use. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; (151):265–269.19. Woodburn J, Helliwell PS. Relation between heel position and the distribution of forefoot plantar pressures and skin callosities in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996; 55(11):806–810.20. Cavanagh PR, Morag E, Boulton AJ, Young MJ, Deffner KT, Pammer SE. The relationship of static foot structure to dynamic foot function. J Biomech. 1997; 30(3):243–250.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Changes of the Foot Shape with the Weight Loading by One Foot
- Changes of Gait Patterns by the Ankle Foot Orthoses with a Variable Ankle Joint Stop
- Prevention and Education for Diabetic Foot
- Two Cases of Hand, Foot and Month Disease
- The Effects of Foot Reflexology on Pain and Depression of Middle-aged Women with Osteoarthritis