Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Sep;6(3):279-284. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.3.279.
Quantitative Analysis of Tissue Injury after Minimally Invasive Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjcho@khmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ulsan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1794708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.3.279
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We intended to clarify the hypothesis that minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty (MI-THA) leads to less tissue damage and inflammatory response than does conventional total hip arthroplasty (C-THA).
METHODS
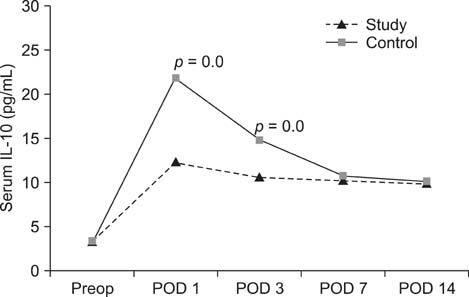
We performed 30 cases of THA between September 2005 and May 2006 and evaluated these cases prospectively. We chose 15 MI-THA cases for the study group and another 15 C-THA cases for the control group. We checked skeletal muscle marker enzymes, such as serum creatinine kinase and aldolase, the pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-6 and 8, and the anti-inflammatory cytokines, IL-10 and IL-1 receptor antagonist (ra) the day before surgery and at postoperative days 1, 7, and 14.
RESULTS
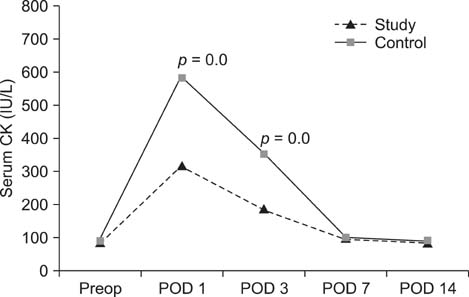
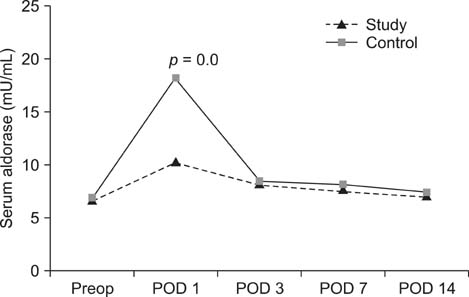
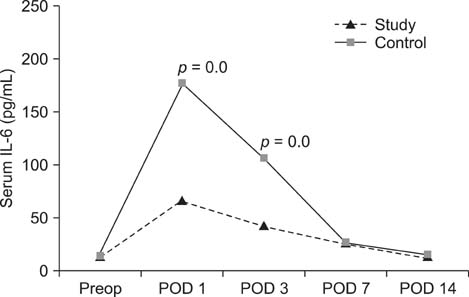
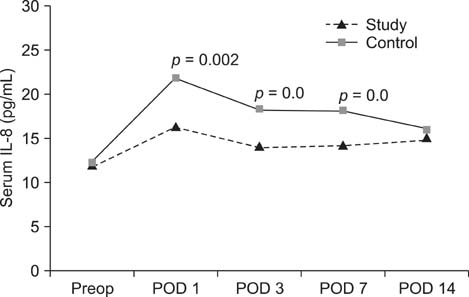
On postoperative days 1 and 3, the study group showed significantly lower serum creatinine kinase, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-1ra values than those in the control group. Additionally, IL-8 was significantly lower on day 7 after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
These data show that MI-THA decreased the release of muscle marker enzymes due to tissue damage immediately after surgery and minimized the inflammatory response related to the surgery during the early postoperative period.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Arthroplasty, Replacement, Hip/*adverse effects
Biological Markers/blood
Creatine Kinase/blood
Female
Fructose-Bisphosphate Aldolase/blood
Humans
Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist Protein/blood
Interleukin-10/blood
Interleukin-6/blood
Interleukin-8/blood
Male
Middle Aged
Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures/adverse effects
Soft Tissue Injuries/*blood/etiology
Biological Markers
Creatine Kinase
Fructose-Bisphosphate Aldolase
Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist Protein
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berger RA. Mini-incisions: two for the price of one! Orthopedics. 2002; 25(5):472. 498.2. Hartzband MA. Posterolateral minimal incision for total hip replacement: technique and early results. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(2):119–129.3. Sculco TP, Jordan LC, Walter WL. Minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: the Hospital for Special Surgery experience. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(2):137–142.4. Soni RK. An anterolateral approach to the hip joint. Acta Orthop Scand. 1997; 68(5):490–494.5. Wenz JF, Gurkan I, Jibodh SR. Mini-incision total hip arthroplasty: a comparative assessment of perioperative outcomes. Orthopedics. 2002; 25(10):1031–1043.6. Wright JM, Crockett HC, Delgado S, Lyman S, Madsen M, Sculco TP. Mini-incision for total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, controlled investigation with 5-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19(5):538–545.7. Marcy GH, Fletcher RS. Modification of the posterolateral approach to the hip for insertion of femoral-head prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1954; 36(1):142–143.8. Cameron HU. Mini-incisions: visualization is key. Orthopedics. 2002; 25(5):473.9. Ogonda L, Wilson R, Archbold P, et al. A minimal-incision technique in total hip arthroplasty does not improve early postoperative outcomes: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(4):701–710.10. Dufour DR, Lott JA, Henry JB. Clinical enzymology. In : Henry JB, editor. Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders;2001. p. 281–303.11. Parsons PE. Interleukin-10: the ambiguity in sepsis continues. Crit Care Med. 1998; 26(5):818–819.12. Biffl WL, Moore EE, Moore FA, Peterson VM. Interleukin-6 in the injured patient. Marker of injury or mediator of inflammation? Ann Surg. 1996; 224(5):647–664.13. Rossi GA. COPD patients or "healthy smokers": is IL-8 synthesis and release the borderline? Respiration. 2003; 70(5):457–459.14. Sakamoto K, Arakawa H, Mita S, et al. Elevation of circulating interleukin 6 after surgery: factors influencing the serum level. Cytokine. 1994; 6(2):181–186.15. Kim KT, Lee SH, Suk KS, Bae SC. The quantitative analysis of tissue injury markers after mini-open lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(6):712–716.16. Bone RC. Sir Isaac Newton, sepsis, SIRS, and CARS. Crit Care Med. 1996; 24(7):1125–1128.17. Igonin AA, Armstrong VW, Shipkova M, Lazareva NB, Kukes VG, Oellerich M. Circulating cytokines as markers of systemic inflammatory response in severe community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Biochem. 2004; 37(3):204–209.18. Lin E, Calvano SE, Lowry SF. Inflammatory cytokines and cell response in surgery. Surgery. 2000; 127(2):117–126.19. Takahashi J, Ebara S, Kamimura M, et al. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine increases after spinal instrumentation surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002; 15(4):294–300.20. Barnes PJ. IL-10: a key regulator of allergic disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31(5):667–669.