Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Sep;6(3):258-266. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.3.258.
Korean Type Distal Radius Anatomical Volar Plate System: A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ghbaek@snu.ac.kr, hjleemd@gmail.com
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University College of Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1794705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.3.258
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
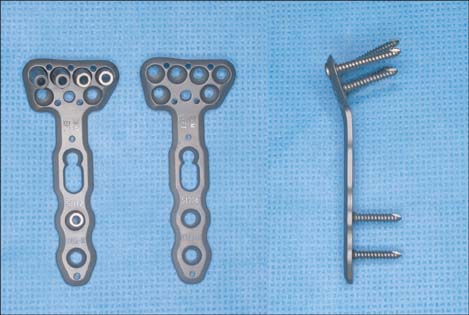
Distal radius fracture is the most common fracture of the upper extremity, and approximately 60,000 distal radius fractures occur annually in Korea. Internal fixation with an anatomical volar locking plate is widely used in the treatment of unstable distal radius fractures. However, most of the currently used distal radius anatomical plate systems were designed based on the anatomical characteristics of Western populations. Recently, the Korean-type distal radius anatomical volar plate (K-DRAVP) system was designed and developed based on the anatomical characteristics of the distal radius of Koreans. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the preliminary results of the new K-DRAVP system, and to compare its radiologic and functional results with those of the other systems.
METHODS
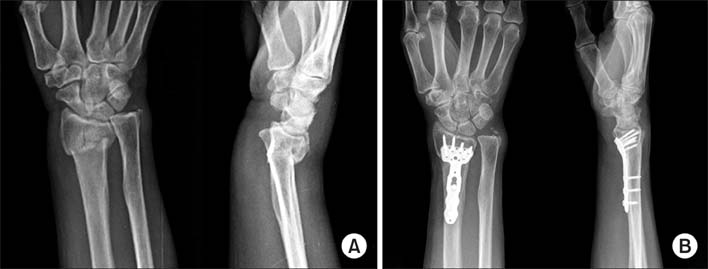
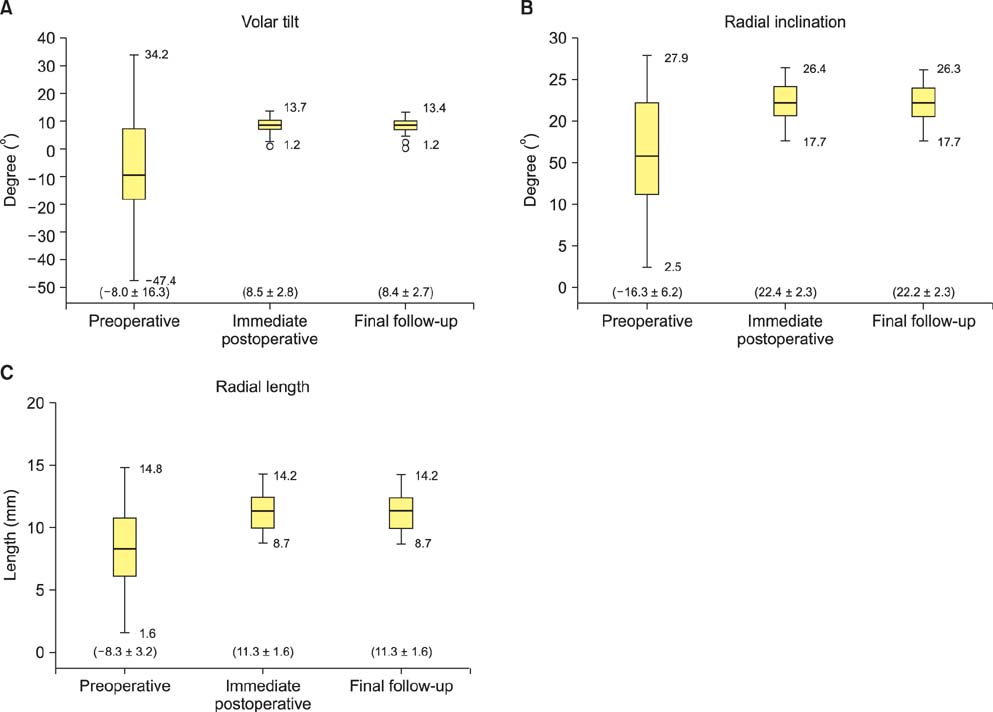
From March 2012 to October 2012, 46 patients with acute distal radius fractures who were treated with the K-DRAVP system at three hospitals were enrolled in this study. Standard posteroanterior and lateral radiographs were obtained to assess fracture healing, and three radiographic parameters (volar tilt, radial inclination, and radial length) were assessed to evaluate radiographic outcomes. The range of motion and grip strength, the Gartland and Werley scoring system, and the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) questionnaire were used to assess clinical and functional outcomes.
RESULTS
All radiologic parameters were restored to normal values, and maintained without any loosening or collapse until the time of final follow-up. Grip strength was restored to 84% of the value for the unaffected side. The mean range of motion of the wrist at final follow-up was restored to 77%-95% of the value for the unaffected side. According to the Gartland and Werley scoring system, there were 16 excellent, 26 good, and 4 fair results. The mean DASH score was 8.4 points. There were no complications after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
The newly developed K-DRAVP system could be used to restore and maintain good anatomical parameters, and provide good clinical outcomes with low complication rates. This system is a promising surgical option for the treatment of distal radius fractures in the Korean population.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thompson PW, Taylor J, Dawson A. The annual incidence and seasonal variation of fractures of the distal radius in men and women over 25 years in Dorset, UK. Injury. 2004; 35(5):462–466.2. Park C, Ha YC, Jang S, Jang S, Yoon HK, Lee YK. The incidence and residual lifetime risk of osteoporosis-related fractures in Korea. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011; 29(6):744–751.3. Orbay JL. The treatment of unstable distal radius fractures with volar fixation. Hand Surg. 2000; 5(2):103–112.4. Chung KC, Shauver MJ, Birkmeyer JD. Trends in the United States in the treatment of distal radial fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91(8):1868–1873.5. Lim ST, Yeom JS, Lee CH, Lee YH, Chang CB, Baek GH. Development of anatomical plating system for treatment of distal radius fractures. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2007; 12(3):95–104.6. Arora R, Lutz M, Hennerbichler A, Krappinger D, Espen D, Gabl M. Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21(5):316–322.7. Gartland JJ Jr, Werley CW. Evaluation of healed Colles' fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1951; 33(4):895–907.8. Sarmiento A, Pratt GW, Berry NC, Sinclair WF. Colles' fractures: functional bracing in supination. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57(3):311–317.9. Drobetz H, Kutscha-Lissberg E. Osteosynthesis of distal radial fractures with a volar locking screw plate system. Int Orthop. 2003; 27(1):1–6.10. Kamano M, Koshimune M, Toyama M, Kazuki K. Palmar plating system for Colles' fractures: a preliminary report. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30(4):750–755.11. Wong TC, Yeung CC, Chiu Y, Yeung SH, Ip FK. Palmar fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures using locking plates with Smartlock locking screws. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2009; 34(2):173–178.12. Figl M, Weninger P, Liska M, Hofbauer M, Leixnering M. Volar fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis of unstable distal radius fractures: 12 months results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129(5):661–669.13. Minegishi H, Dohi O, An S, Sato H. Treatment of unstable distal radius fractures with the volar locking plate. Ups J Med Sci. 2011; 116(4):280–284.14. Lattmann T, Meier C, Dietrich M, Forberger J, Platz A. Results of volar locking plate osteosynthesis for distal radial fractures. J Trauma. 2011; 70(6):1510–1518.15. Osada D, Kamei S, Masuzaki K, Takai M, Kameda M, Tamai K. Prospective study of distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate system. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33(5):691–700.16. Yasuda M, Ando Y. A new variable angled locking volar plate system for Colles' fracture: outcome study and time-course improvement of objective clinical variables. Hand Surg. 2009; 14(2-3):93–98.17. Matschke S, Marent-Huber M, Audige L, Wentzensen A. LCP Study Group. The surgical treatment of unstable distal radius fractures by angle stable implants: a multicenter prospective study. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25(5):312–317.18. Kim JY, Kang HJ, Yi Y. Multiple flexor tendon injuries after volar plate fixation for distal radius fracture: two cases report. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2012; 17(1):47–51.19. Lee SJ, Bae JY, Cho HJ, Suh KT. Short term results of AO type C fractures of the distal radius treated with volar locking plating system. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2011; 16(4):191–197.20. Lee SU, Park IJ, Kim HM, Lee JY, Yoo HH, Jeong C. K-wire fixation supplemented with external fixator versus volar locked plating for unstable fractures of the distal radius. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2010; 15(4):157–163.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon at the Proximal Screw of Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Failure of Distal Locking Screws in an Intraarticular Distal Radius Fracture Treated with Volar Locking Plate Fixation
- Multiple Flexor Tendon Injuries after Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: Two Cases Report
- Surgical Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures and Treatment of Common Accompanying Lesions
- Comparative Analysis of the Results of Fixed-angle versus Variable-angle Volar Locking Plate for Distal Radius Fracture Fixation